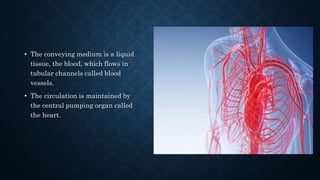
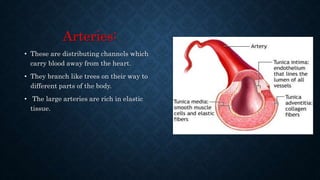
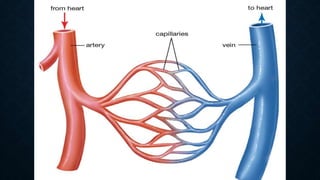
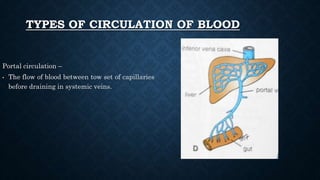
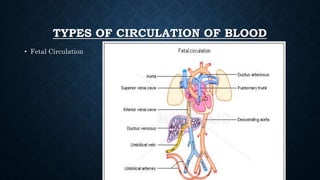
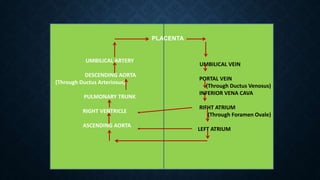
The cardiovascular system transports nutrients, removes waste, and facilitates gas exchange through the blood and heart. It consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart is a four-chambered muscular pump located in the chest that circulates blood through two circuits: systemic circulation between the heart and body and pulmonary circulation between the heart and lungs. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins return blood to the heart. Capillaries connect arterioles and venules to exchange materials. The cardiovascular system maintains circulation through these components and circuits.