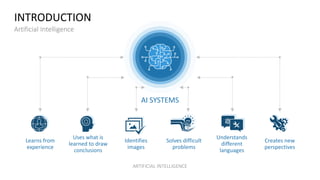
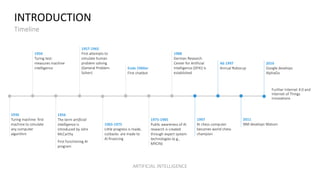
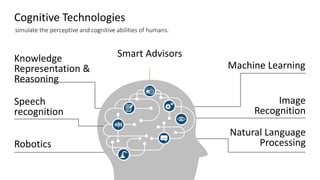
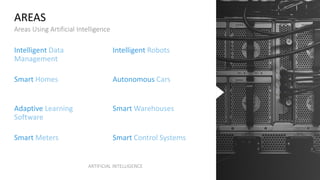
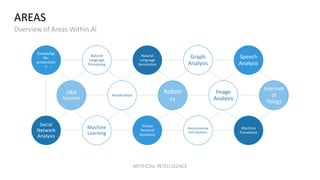
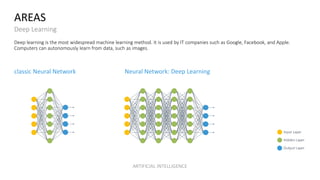
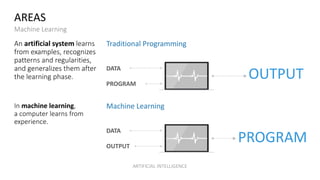
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI) and provides definitions, a timeline of important developments, opportunities and challenges of AI, and examples of areas where AI is used. It defines AI as simulating human intelligence through machine learning, using experience to draw conclusions, and working independently. The document outlines key areas of AI application like robotics, machine translation, and image analysis. It also discusses deep learning and machine learning, defining them as systems that can learn autonomously from data.