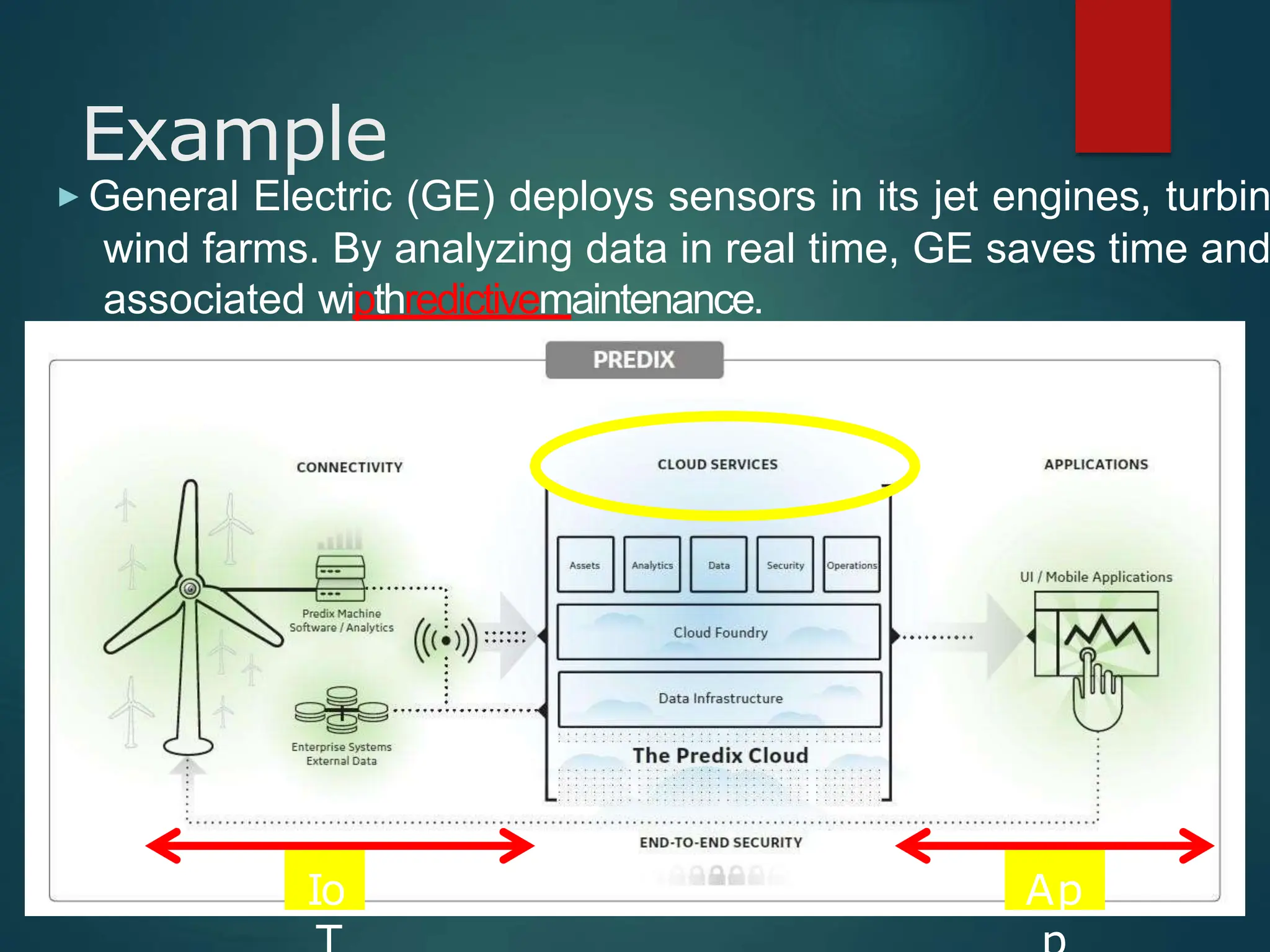
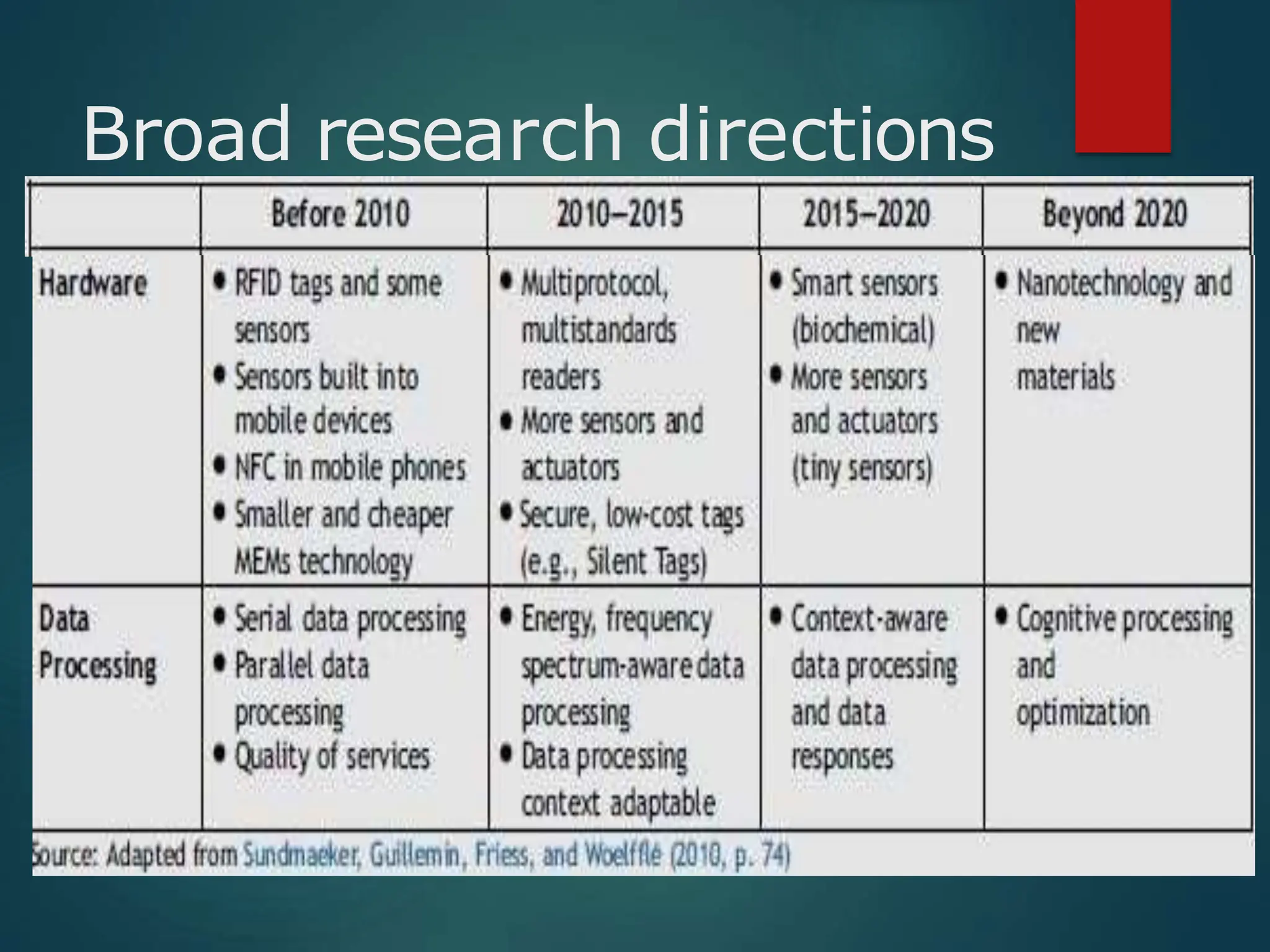
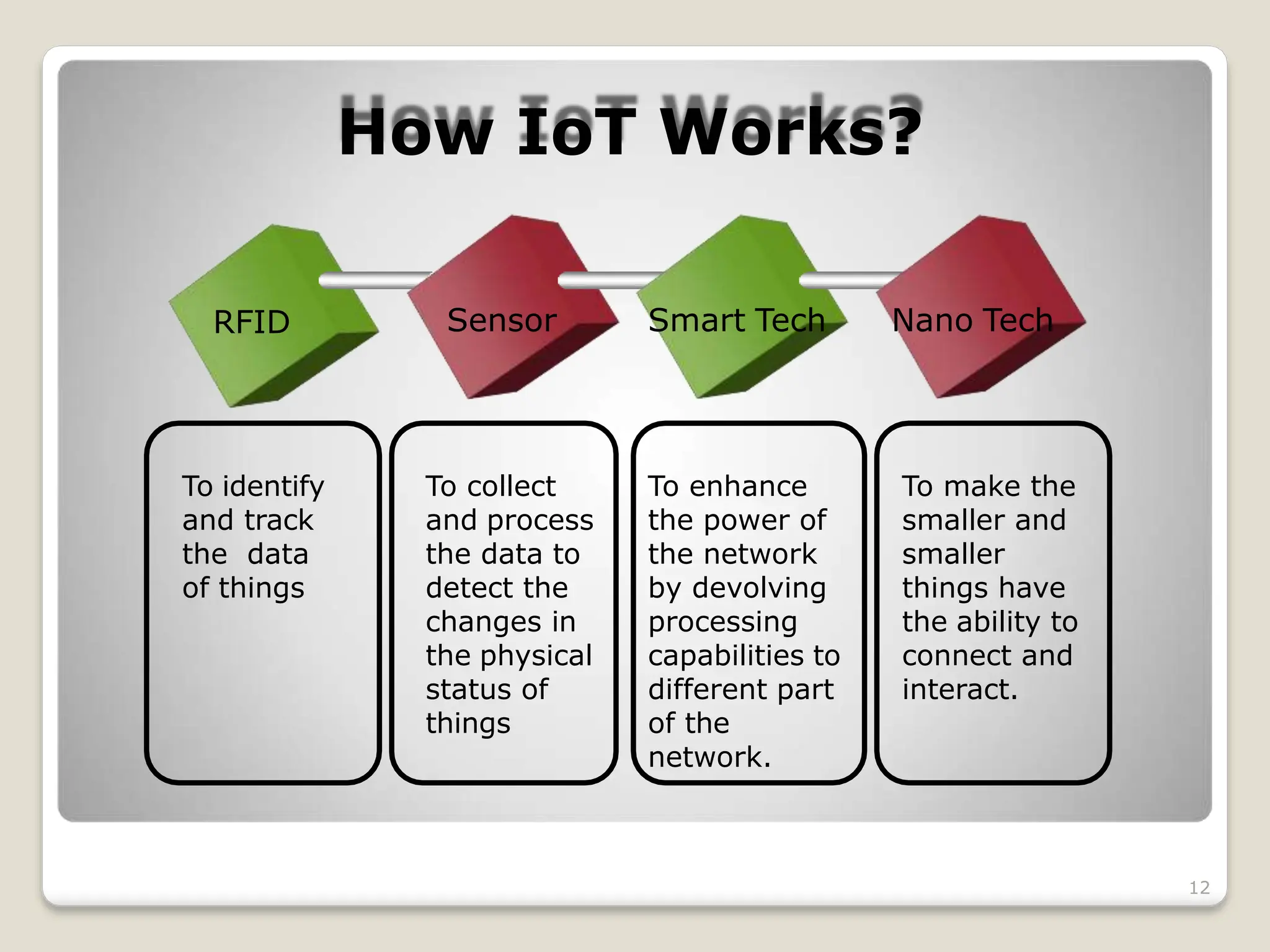
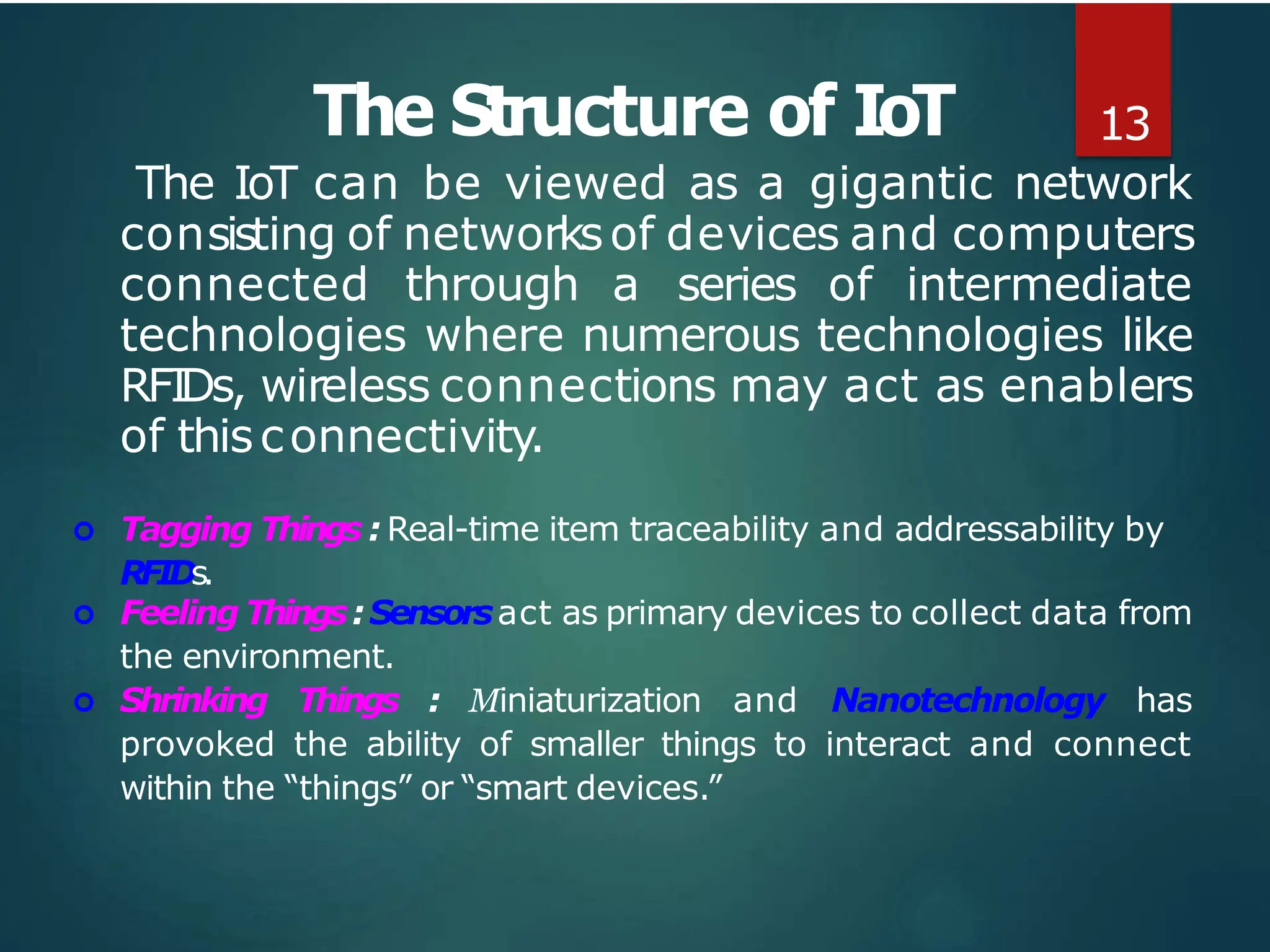
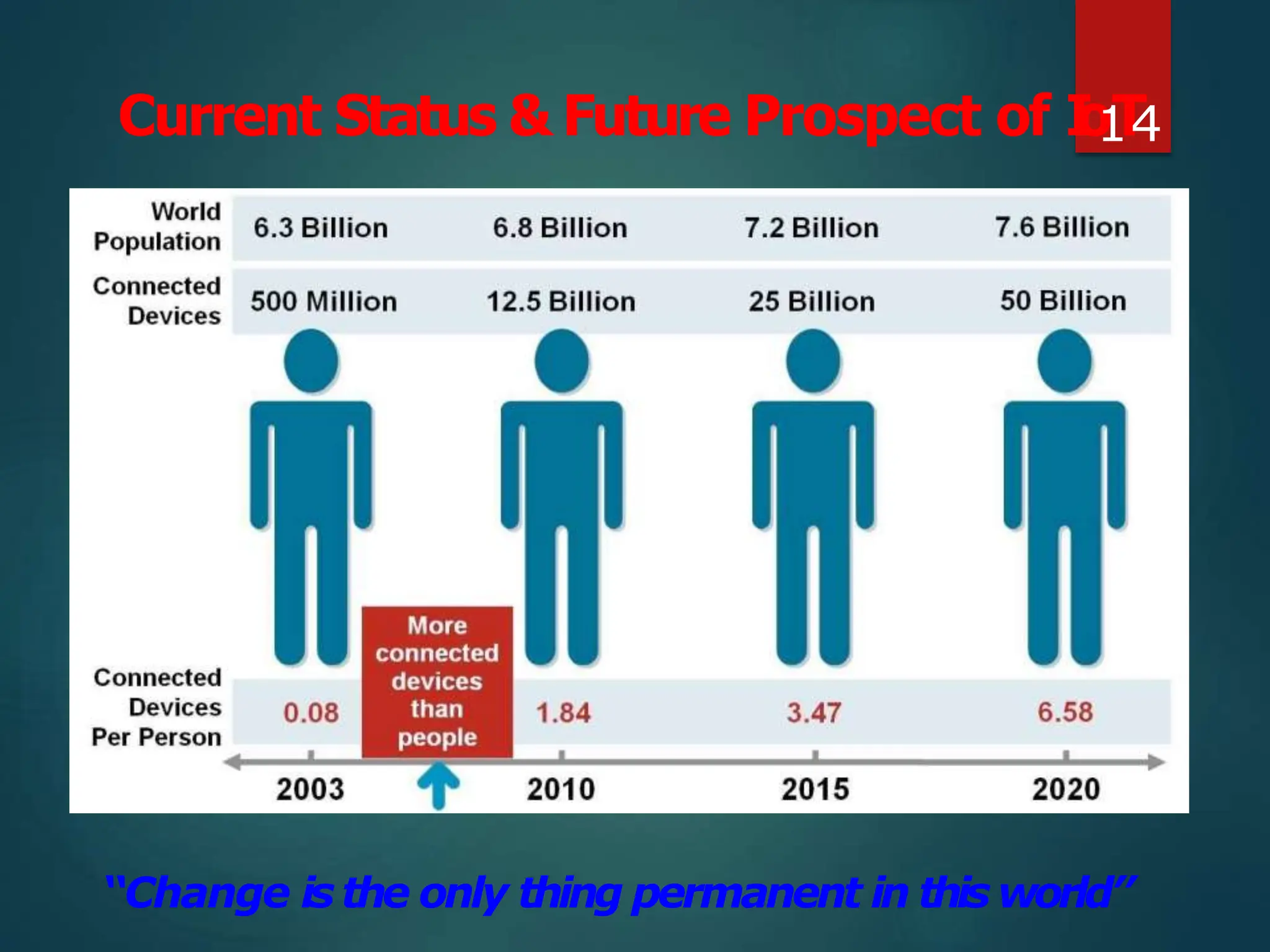
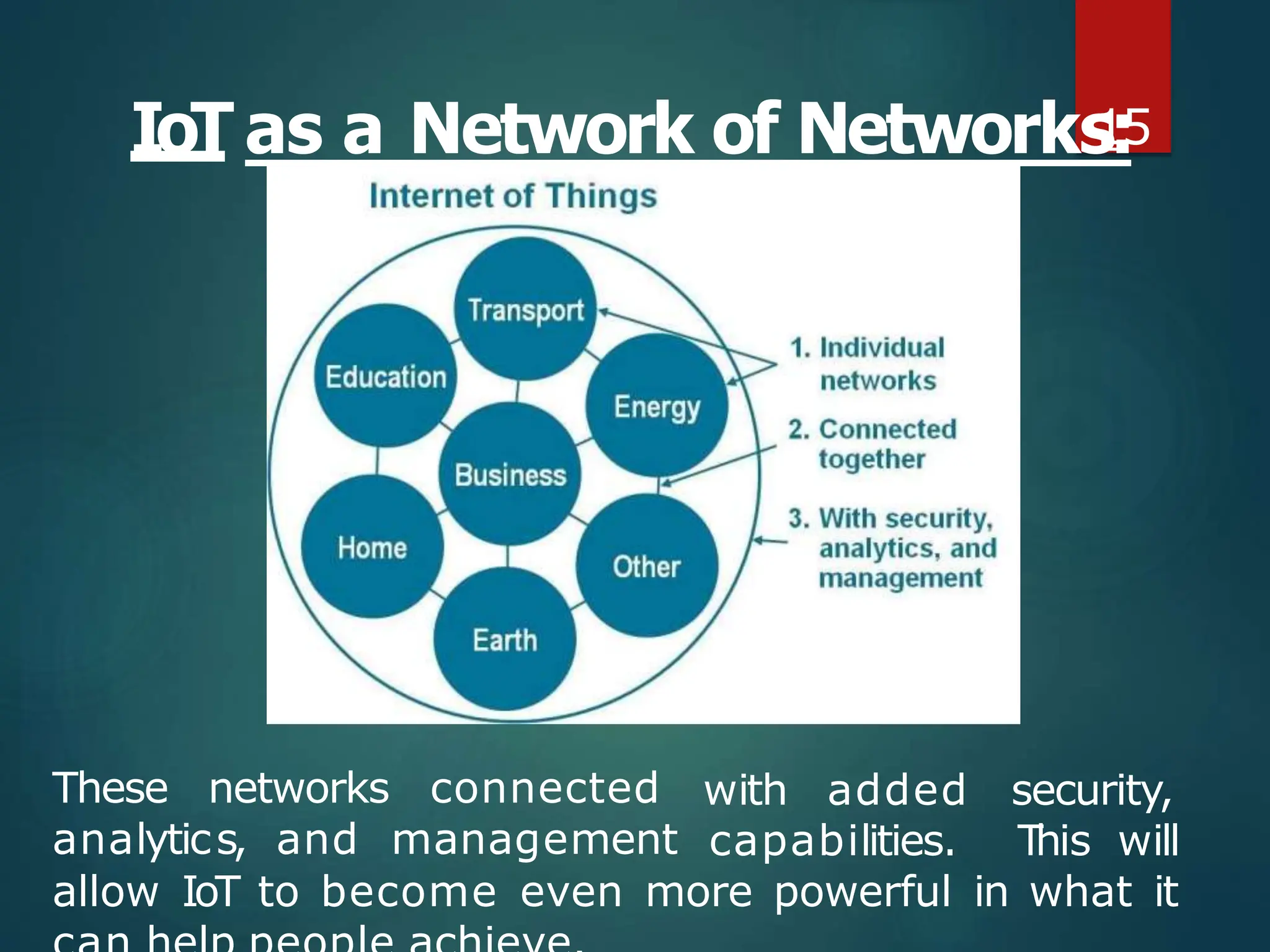
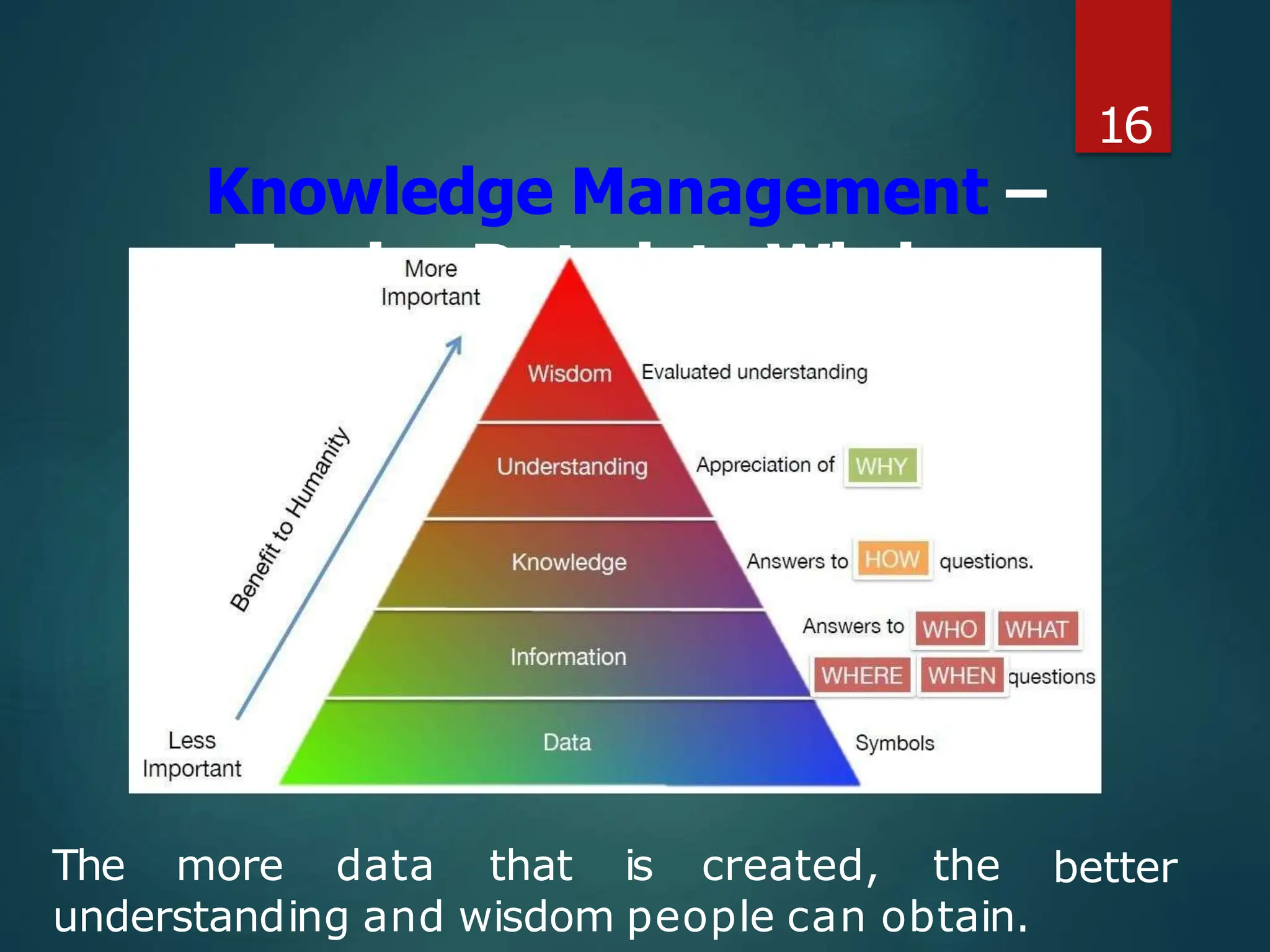
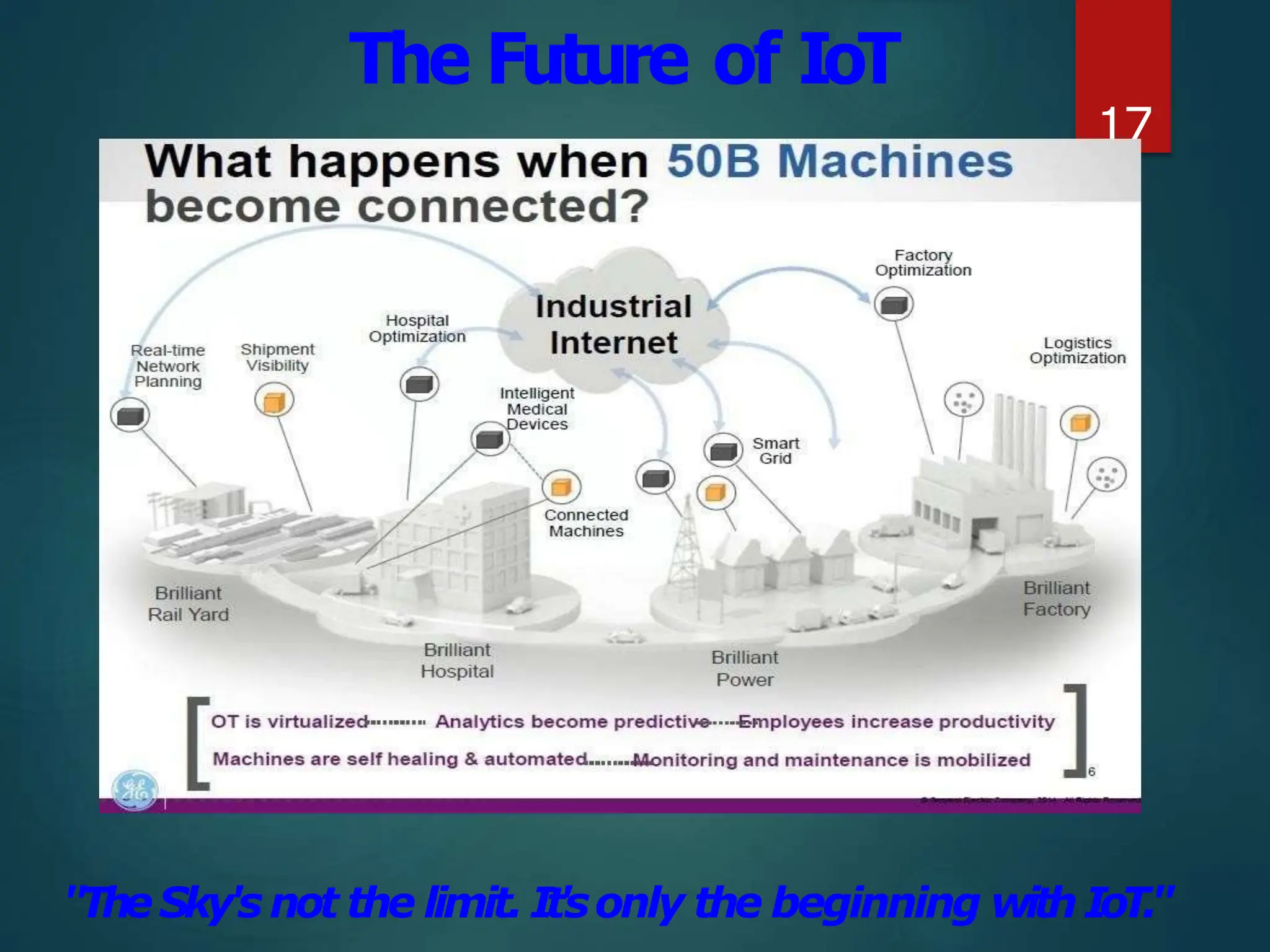
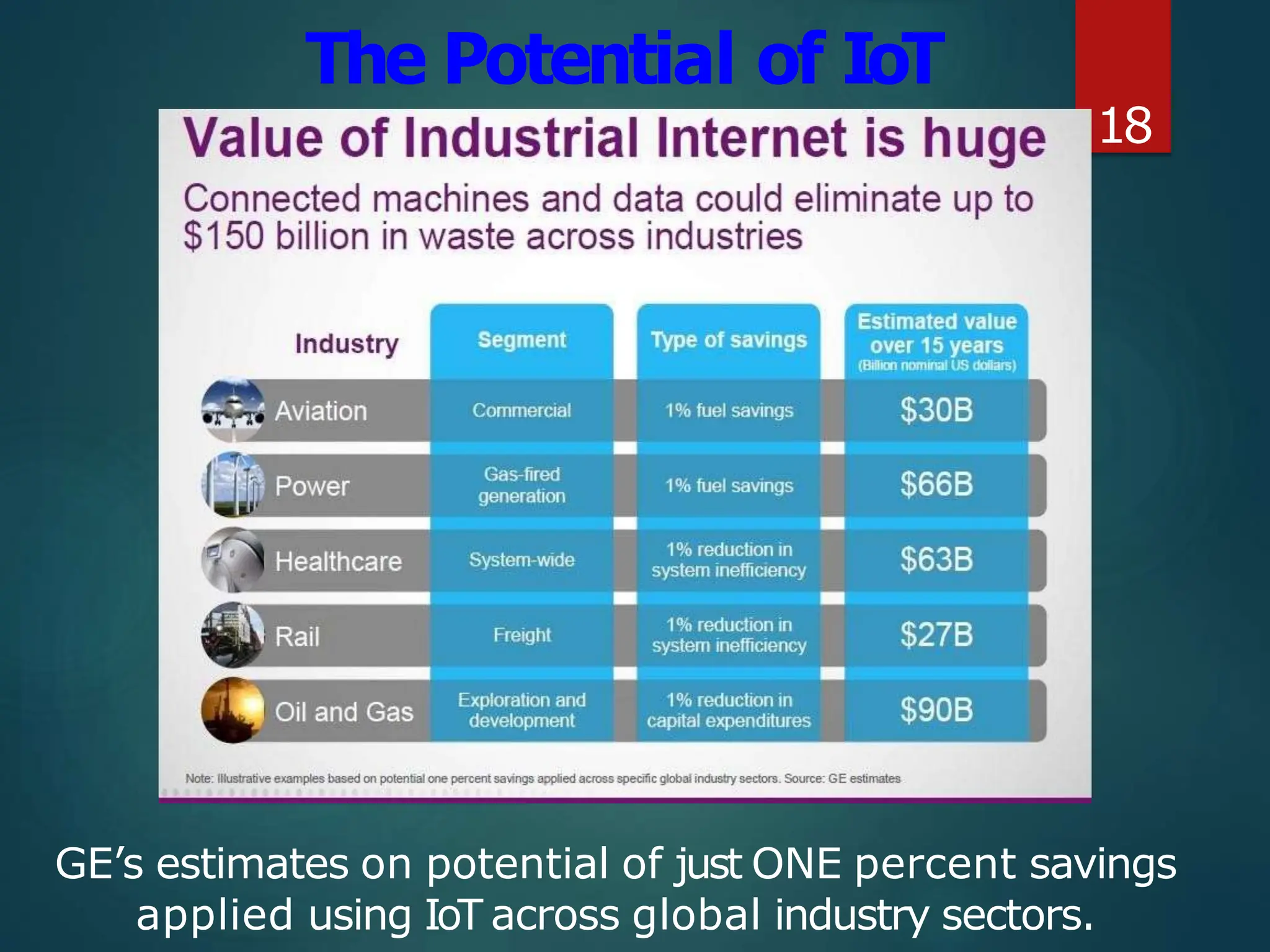
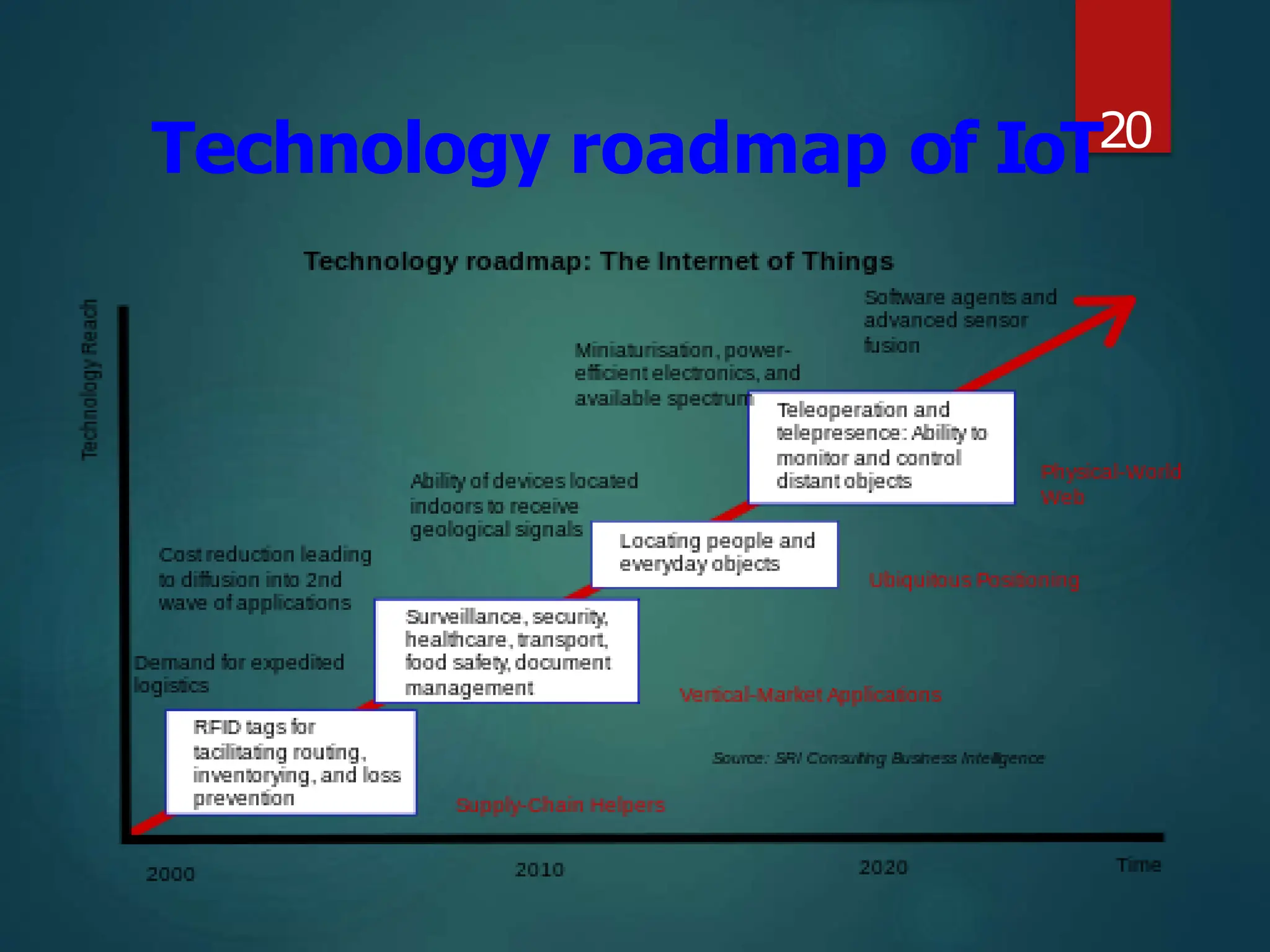
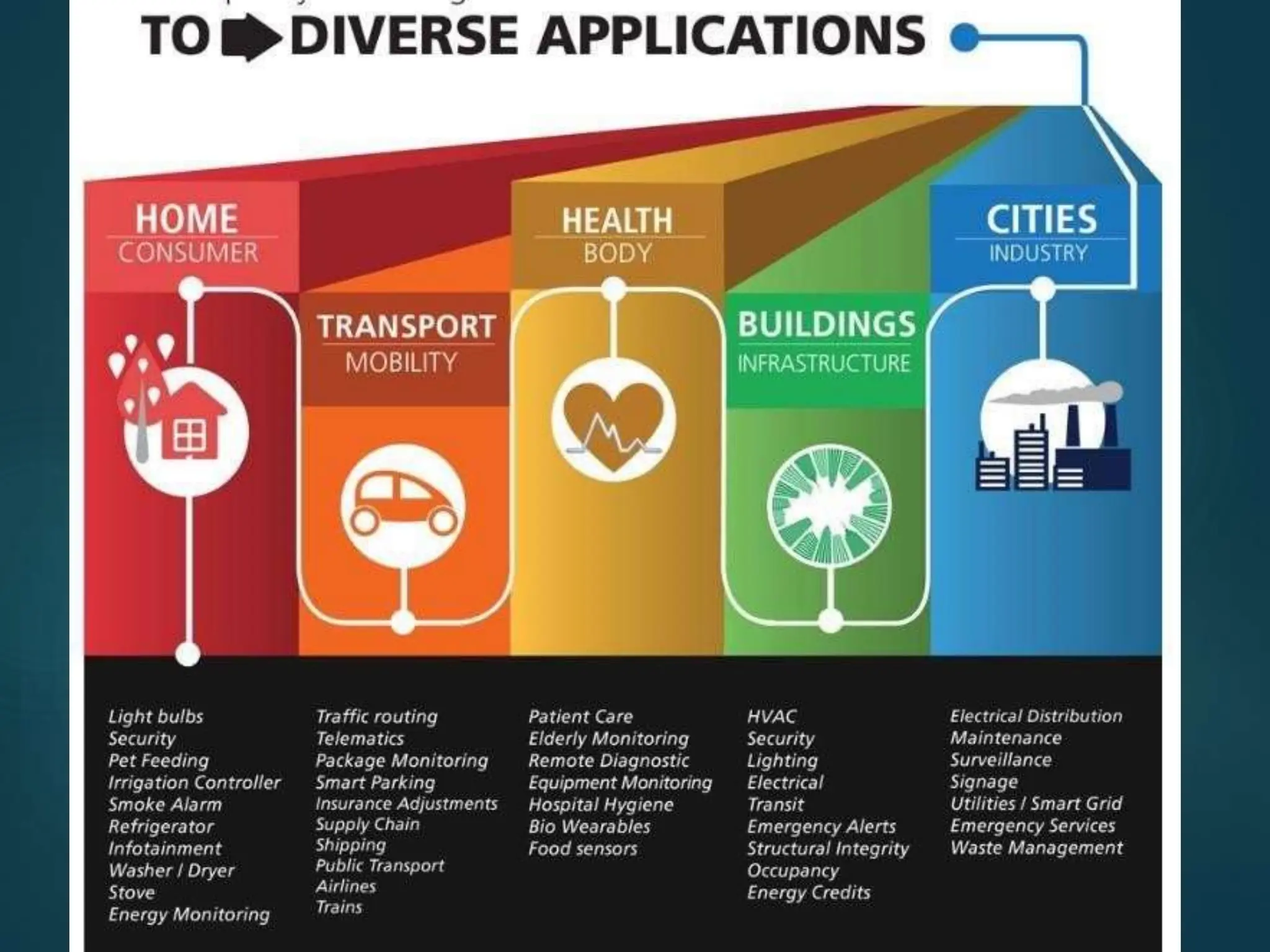
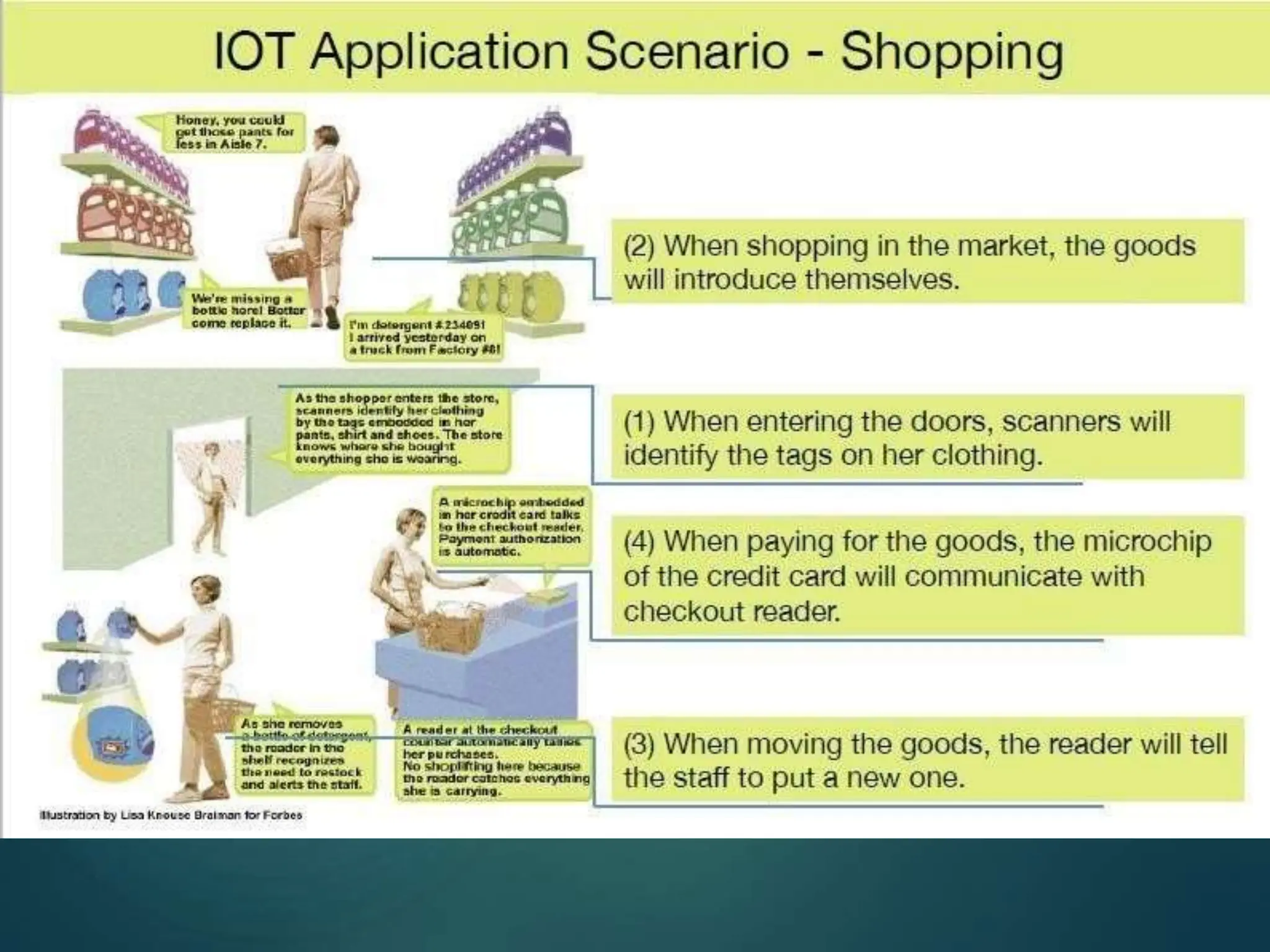
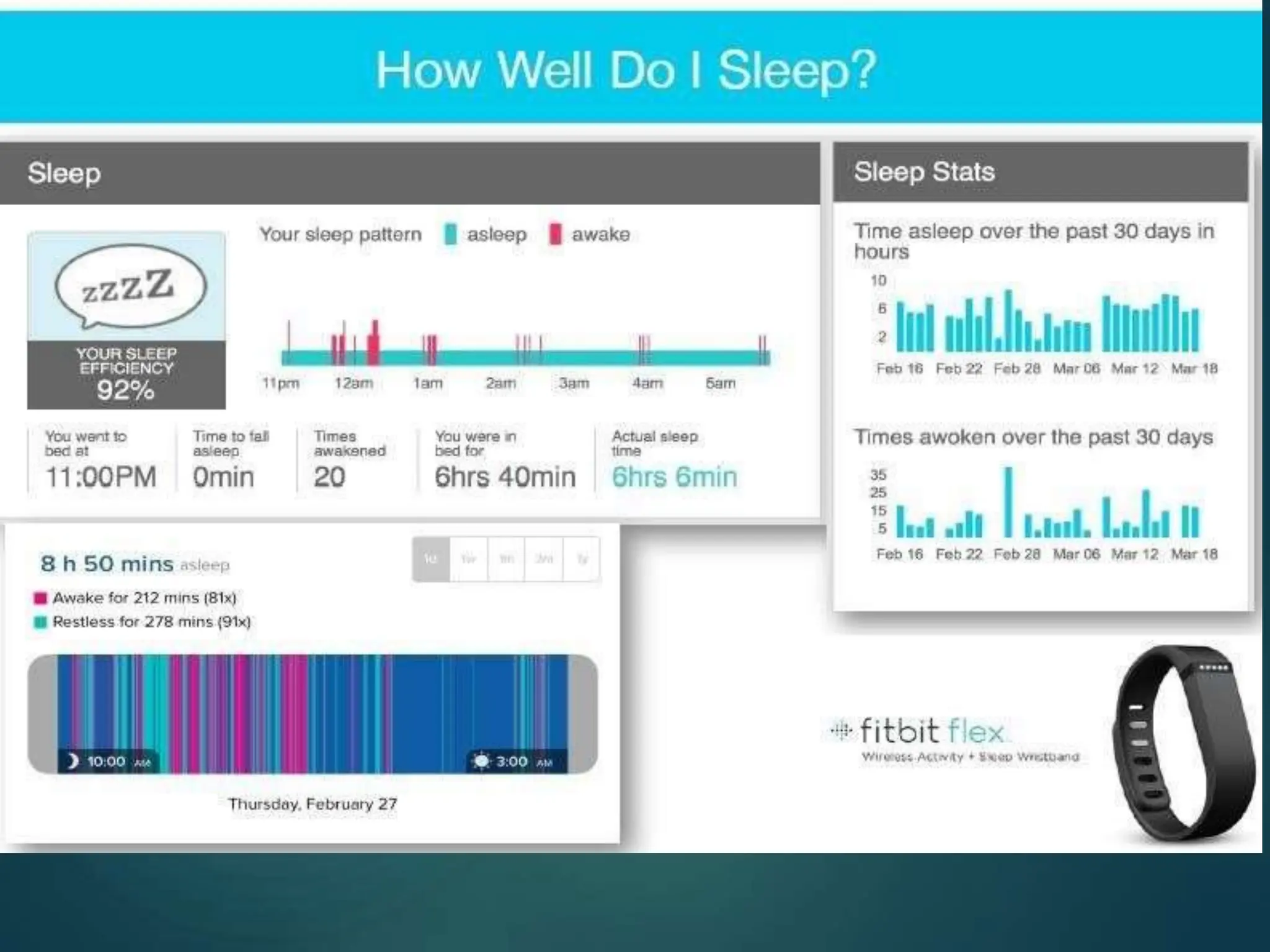
The document presents a seminar on the Internet of Things (IoT), explaining it as a network of physical objects equipped with technology to collect and exchange data. It discusses the components of the IoT ecosystem, its historical background, how it functions, and its various applications across industries. The seminar also highlights challenges and criticisms related to IoT, such as privacy and technological standardization.