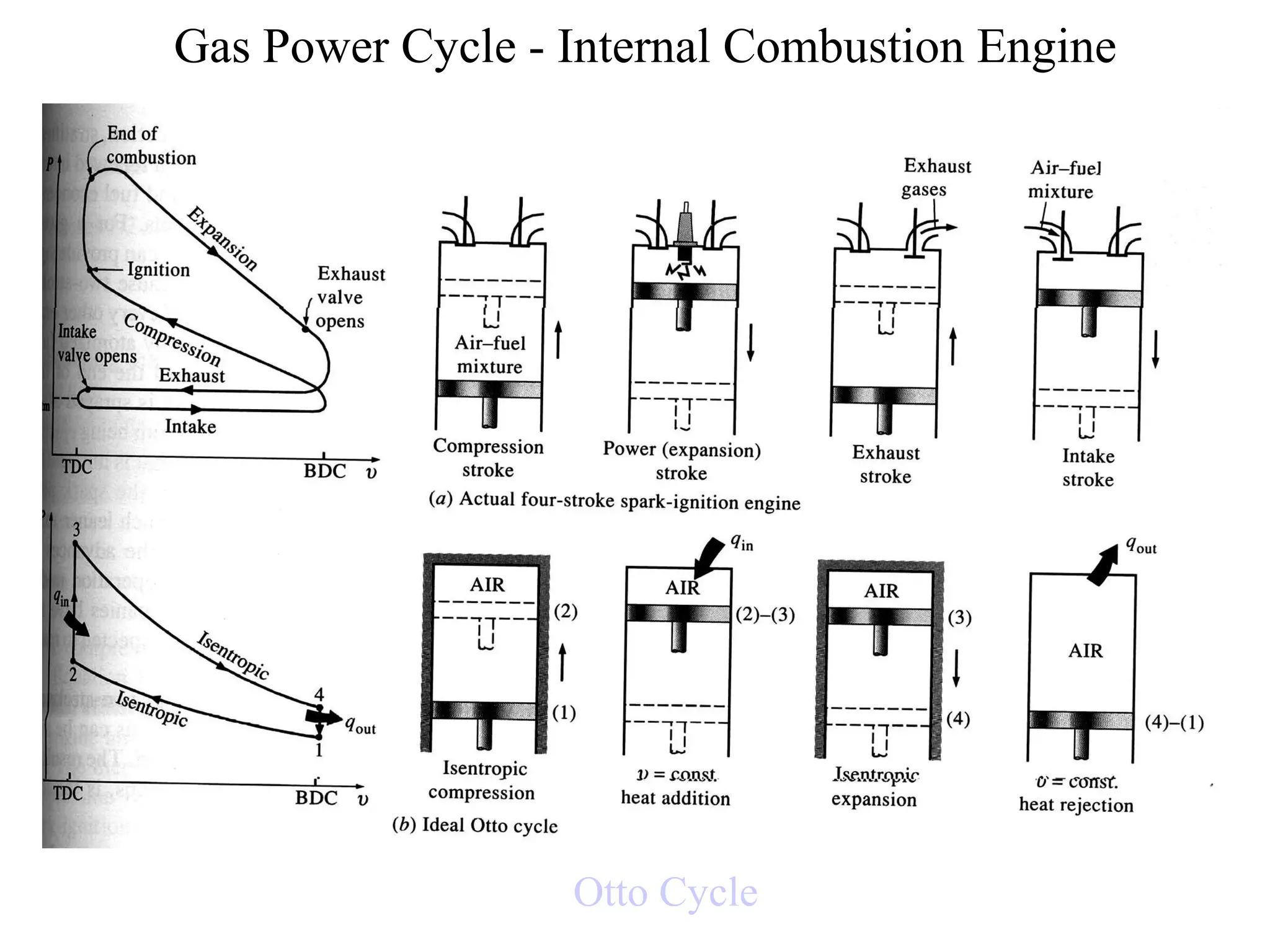
The document summarizes the Otto cycle and Diesel cycle, which are two common thermodynamic cycles used in internal combustion engines.
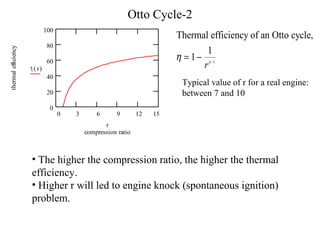
The Otto cycle consists of four processes: (1) isentropic compression, (2) constant volume heat addition, (3) isentropic expansion, (4) constant volume heat rejection. The thermal efficiency of an Otto cycle engine increases with compression ratio.
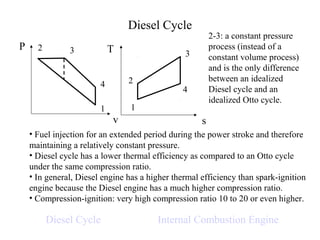
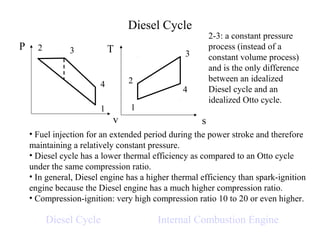
The Diesel cycle differs from the Otto cycle in that the combustion process (2-3) occurs at constant pressure rather than constant volume. As a result, Diesel cycle engines can operate at higher compression ratios than Otto cycle engines, giving them a higher overall thermal efficiency.
![Otto Cycle
P
v
1
2
3
4
T
s
1
2
3
4
( )cycle 3 4 1 234 12 4 1
in 23 3 2 3 2
4 14 1 1 4 1
v
3 2 3 2 2 3 2
4 1
Thermal efficiency of the system:
W [ ( )] ( )
= 1
Q ( ) ( )
( )( ) / 1
For an ideal gas, u=C , =1 1 1
( ) ( ) / 1
Since /
v
v
m u u u uW W u u
Q m u u u u
C T Tu u T T T
T
u u C T T T T T
T T
η
η
− + −+ −
= = = −
− −
−− −
− = − = −
− − −
3 2
1
2
1
1 2 1
1
2 1 2
/ (why?)
1 . From isentropic compression relation for an ideal gas
1
, where r= is the volume compression ratio
k
k
T T
T
T
T V V
T V r V
η
−
−
=
= −
= =
• 1-2 isentropic compression
• 2-3 constant volume heat
transfer
• 3-4 isentropic expansion
• 4-1 constant volume heat
rejection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internalcombustionengine-170628064223/85/Internal-combustion-engine-2-320.jpg)