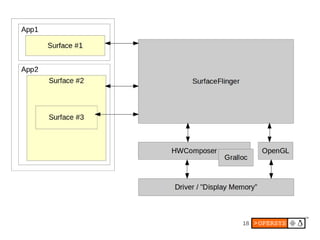
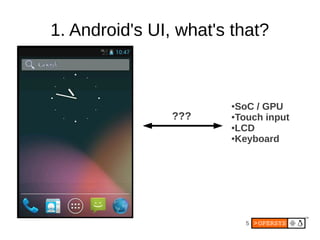
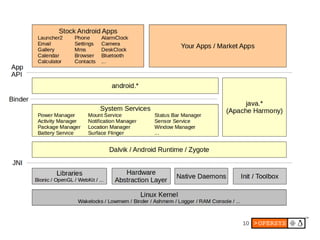
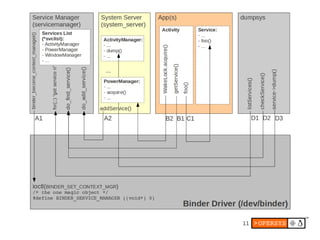
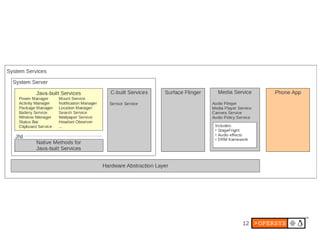
1) Android's UI consists of layers including the display hardware, kernel driver, HAL modules, SurfaceFlinger, Window Manager and key apps.
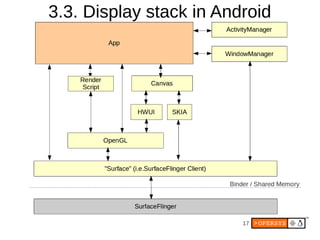
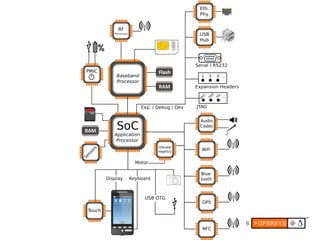
2) The display stack includes the kernel driver, HAL definition and module, SurfaceFlinger for compositing surfaces, and Window Manager for managing app windows.
3) OpenGL involves kernel drivers, EGL libraries, and native/Java interfaces to provide 3D graphics capabilities to apps through the GPU hardware.






![/frameworks/base/core/...
/frameworks/base/services/java/...
AOSP-provided
ASL
/frameworks/base/services/jni/
/hardware/libhardware/
/device/[MANUF.]/[DEVICE]
Manuf.-provided /sdk/emulator/
Manuf. license
Kernel or module
Manuf.-provided
GPL-license
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inside-androids-ui-121105-121112115231-phpapp01/85/Inside-Android-s-UI-13-320.jpg)