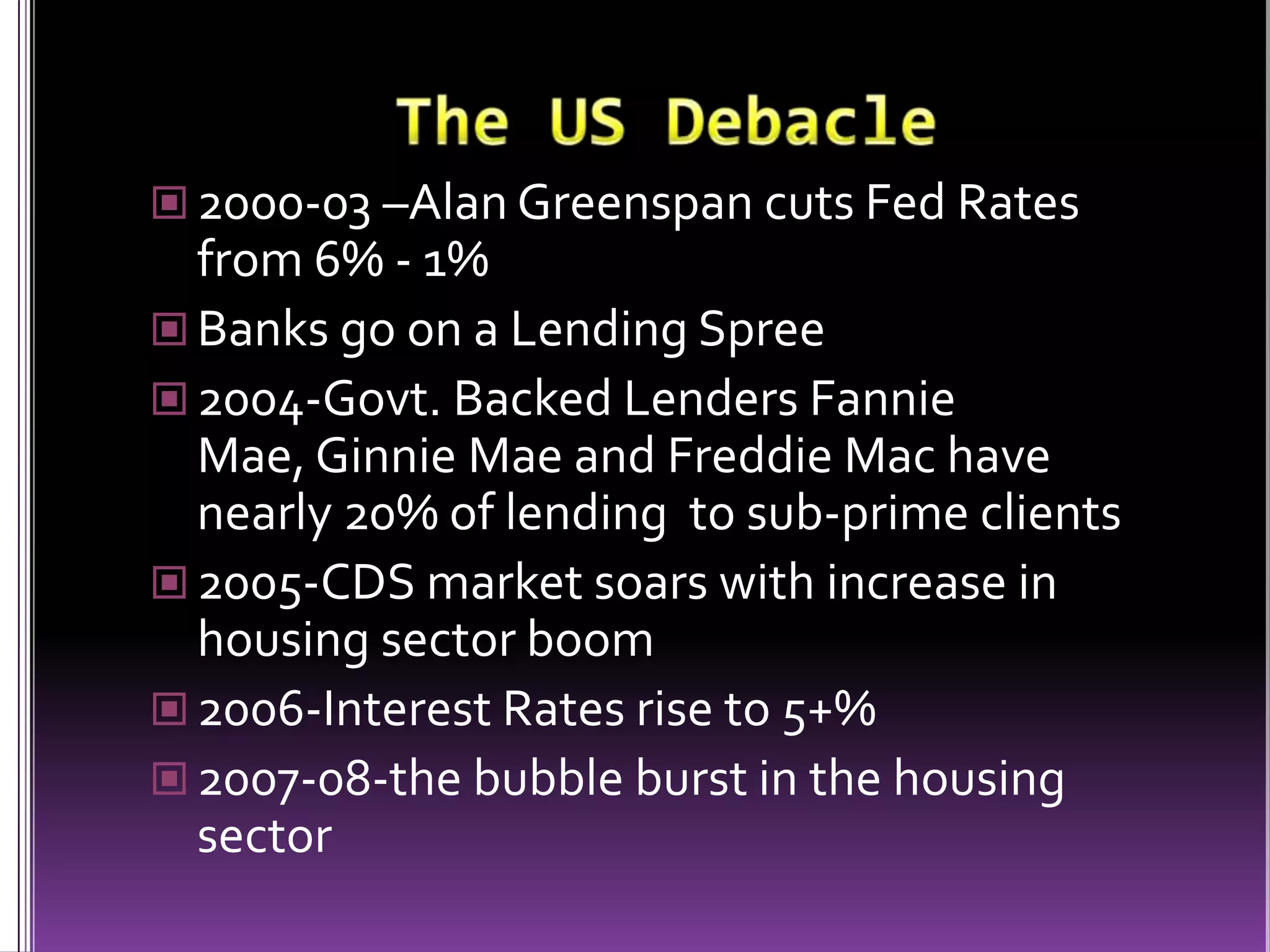
This document discusses innovative financial instruments introduced by various institutions like the Reserve Bank of India and corporations in India and the United States. It provides details on instruments introduced by RBI like liquidity adjustment facility (repo and reverse repo), collateralized borrowing and lending obligations, and market stabilization scheme. It also describes corporate instruments in India like bonus debentures, zero coupon bonds, foreign currency convertible bonds, and shares with differential voting rights. The document further discusses financial instruments in the US that led to the 2008 financial crisis, such as collateralized debt obligations, mortgage-backed securities, credit default swaps, and subprime mortgages. It analyzes both the benefits and dangers of financial innovation.