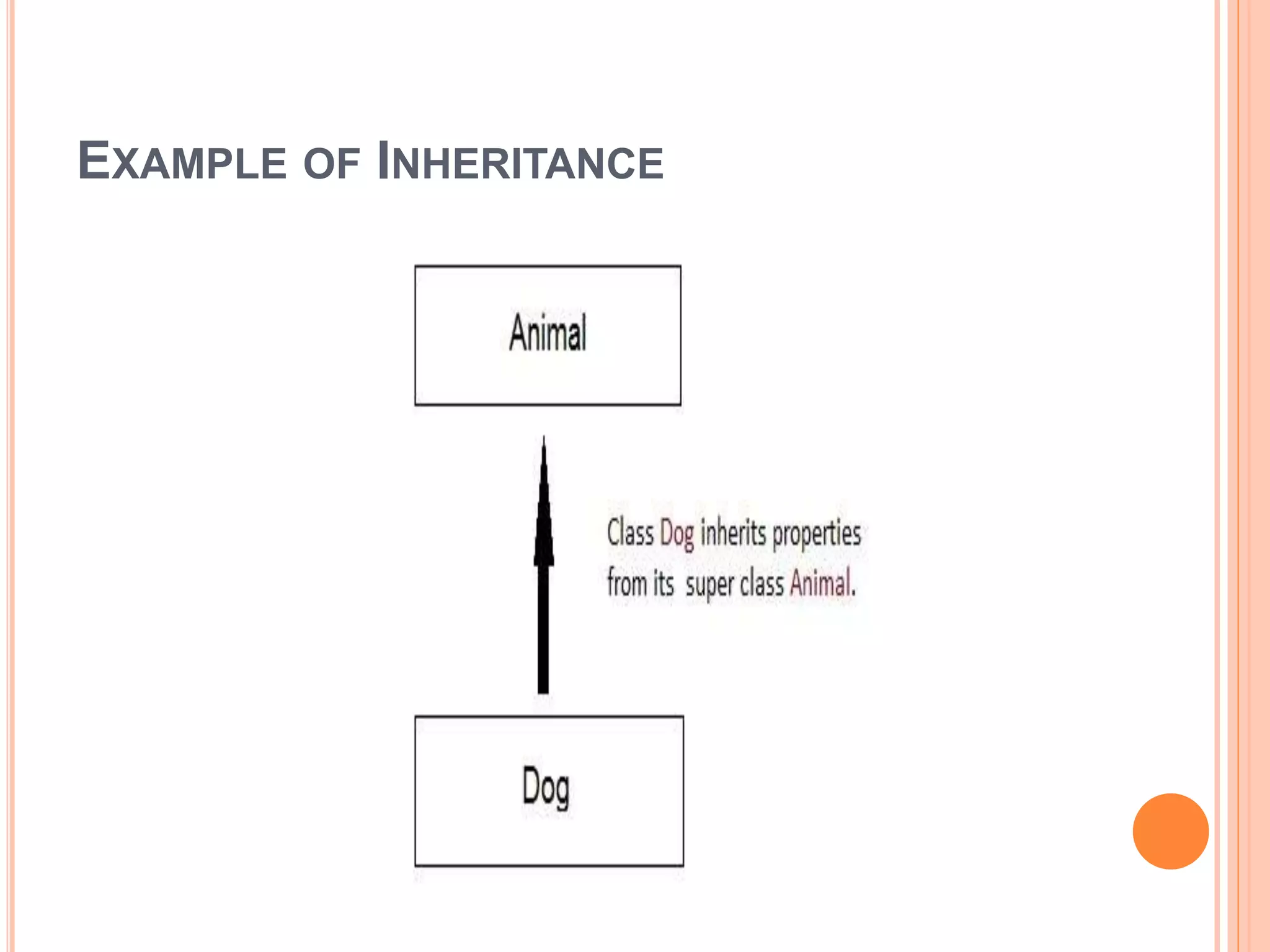
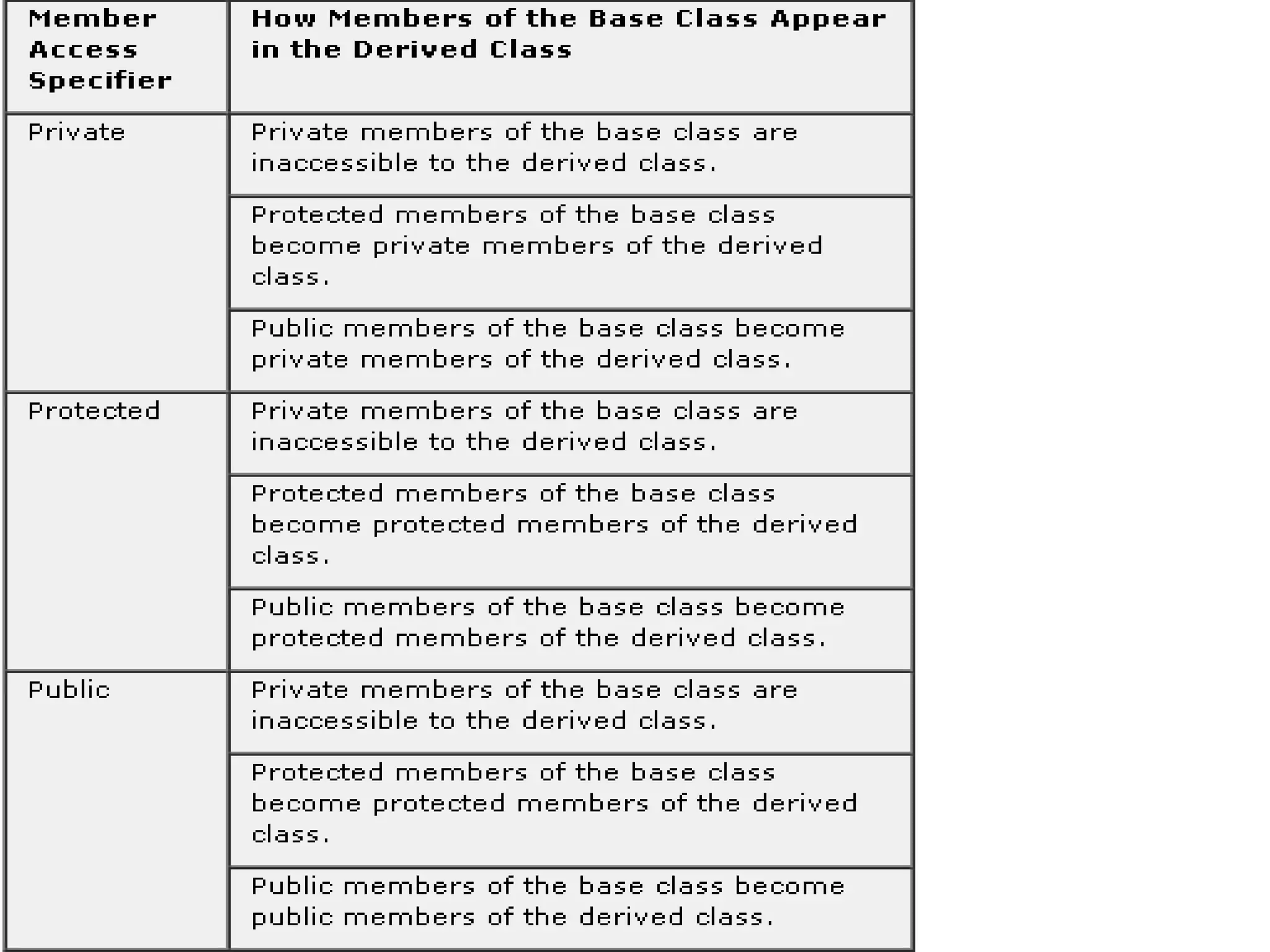
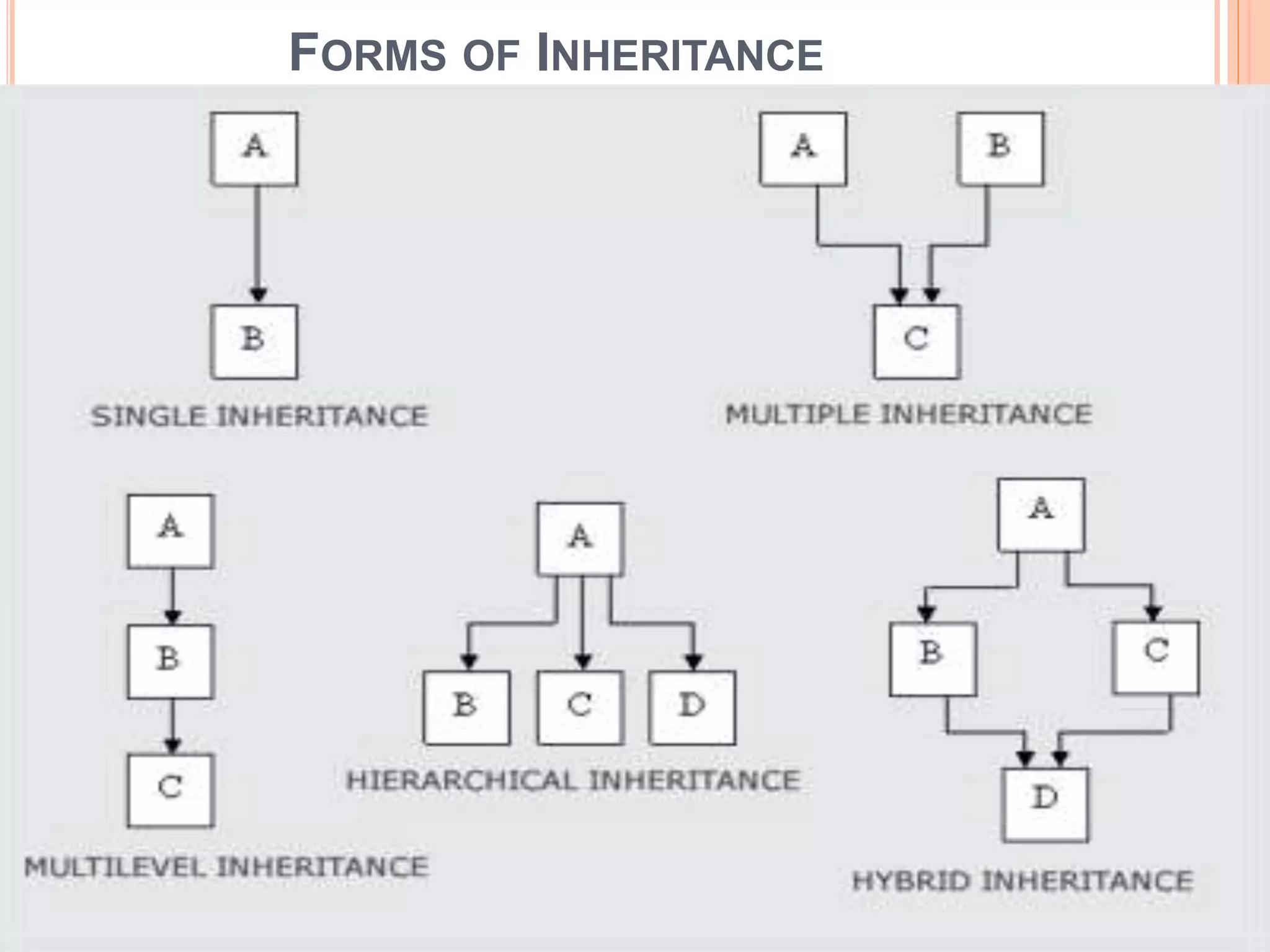
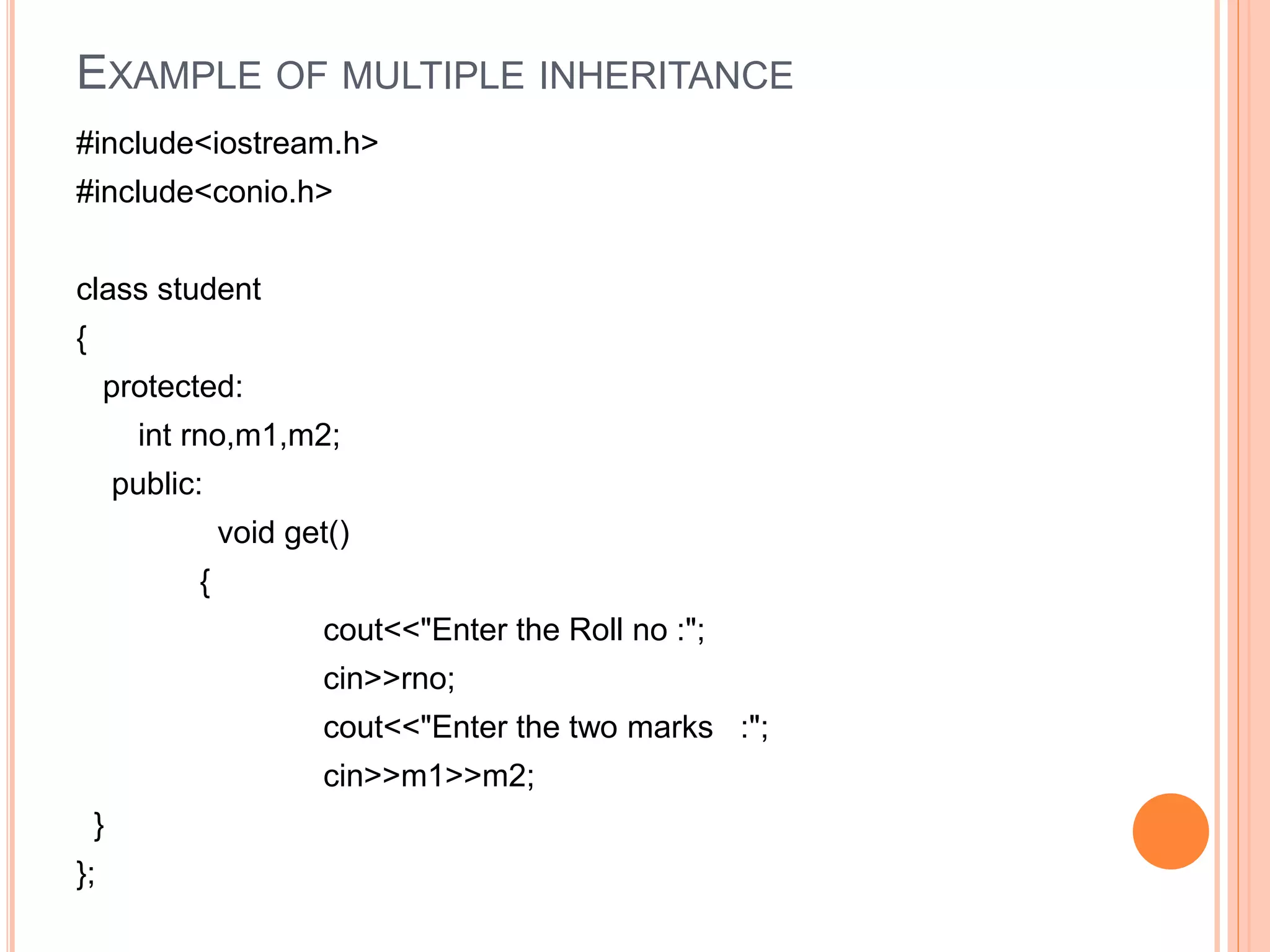
This document discusses inheritance in C++. It defines inheritance as a mechanism that allows classes to acquire properties from other classes. The class that inherits properties is called the derived or child class, while the class being inherited from is called the base or parent class. The key advantages of inheritance are that it saves memory, time, and development efforts by promoting code reuse. The document provides examples of single inheritance with one parent and one child class, and multiple inheritance with a class inheriting from multiple parent classes.