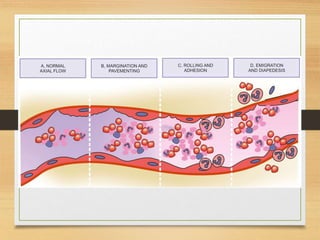
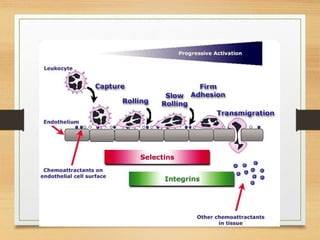
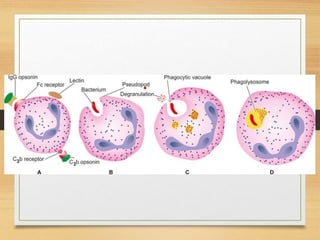
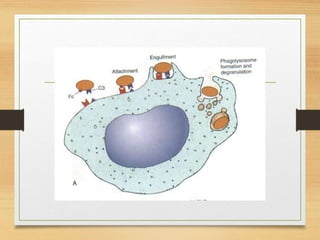
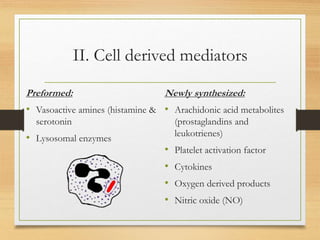
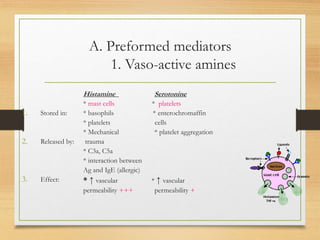
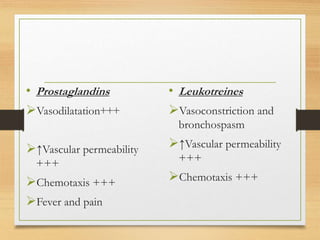
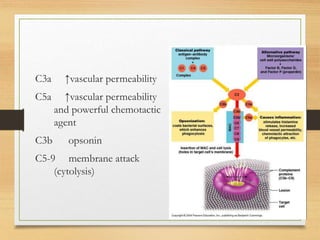
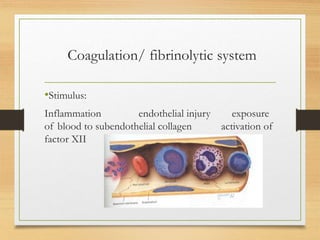
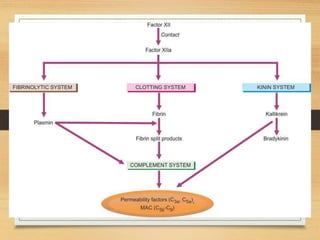
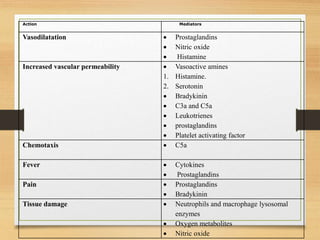
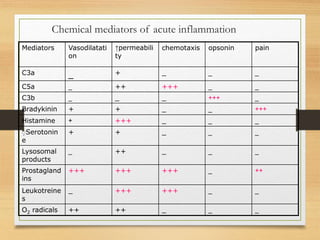
Inflammation is mediated by chemical signals that recruit leukocytes to sites of injury. Leukocytes are activated upon binding to endothelial cells or mediators and emigrate from blood vessels through a process of margination, rolling, adhesion, migration, and chemotaxis. At the injury site, leukocytes undergo phagocytosis and degranulation to engulf and kill pathogens. Mediators of inflammation include vasoactive amines, lysosomal enzymes, arachidonic acid metabolites, cytokines, oxygen radicals, nitric oxide, kinins, complement components, and coagulation/fibrinolytic factors that promote processes like vasodilation, increased permeability, chemotaxis, fever, pain, and tissue damage.