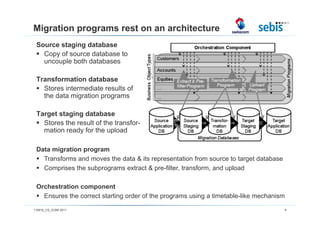
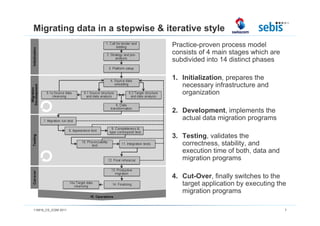
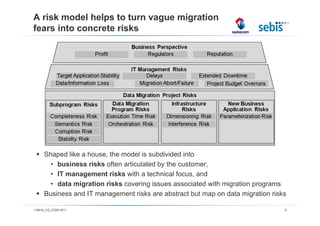
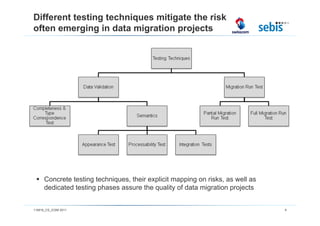
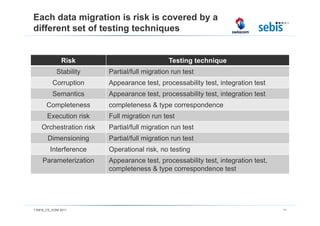
The document discusses challenges and methodologies in testing and quality assurance for data migration projects, highlighting that a significant percentage of such projects fail due to a lack of necessary skills and planning. It outlines a comprehensive process model consisting of four main stages, emphasizing the importance of risk management and various testing techniques to ensure successful data migration. Future directions include the evaluation of these processes in practice and enhancements for handling more complex database scenarios.


![Mastering data migration projects is a
challenging task
„83% of data migrations fail outright or exceed their allotted budgets
and implementation schedules.“
[Gartner Group, 2005]
”..current success rate for the data migration portion of projects (that is
those that were delivered on time and on budget) is just 16%.”
[Bloor research, 2007]
“Few companies have the necessary skills to manage, build and
implement a successful data migration.”
[Endava, 2007]
110816_CS_ICSM 2011 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingqualityassuranceindatamigrationprojects-icsm2011-111015134210-phpapp02/85/Industry-Testing-Quality-Assurance-in-Data-Migration-Projects-3-320.jpg)