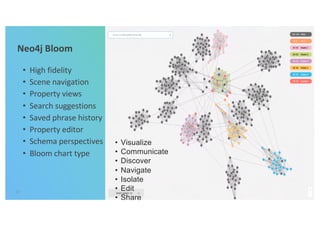
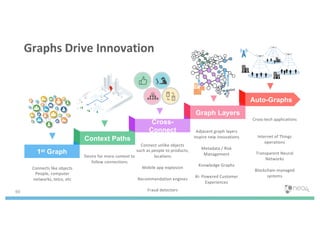
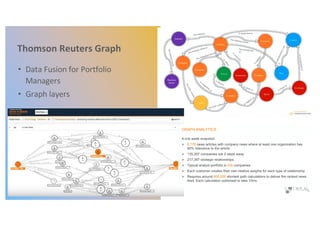
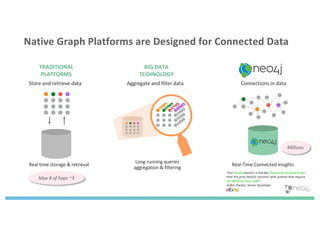
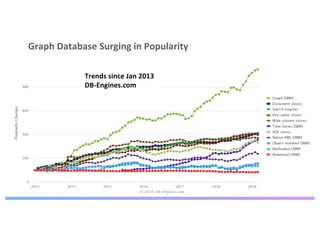
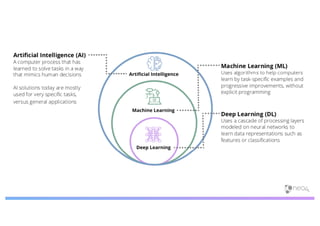
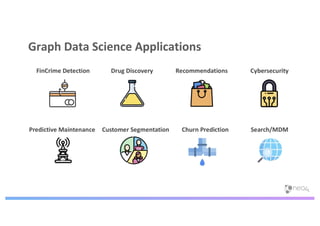
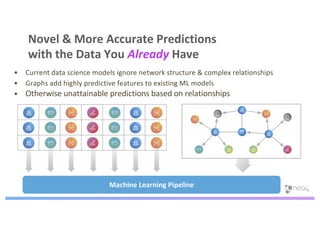
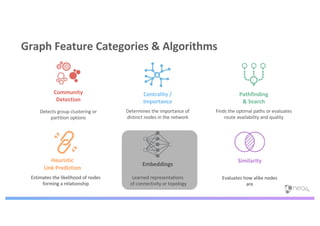
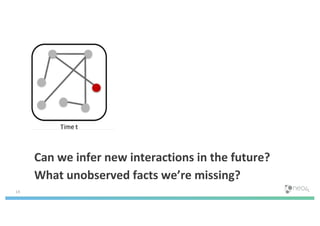
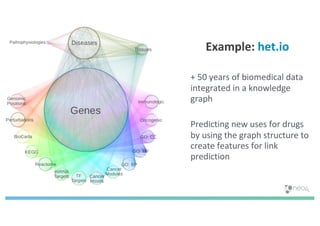
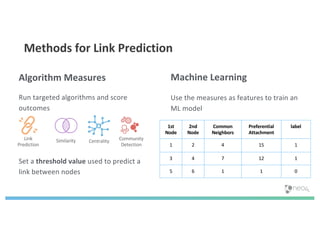
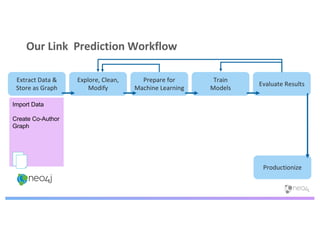
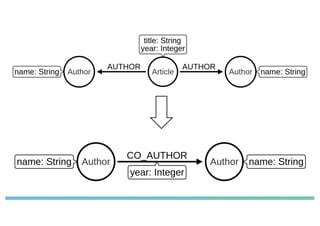
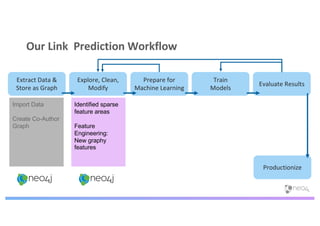
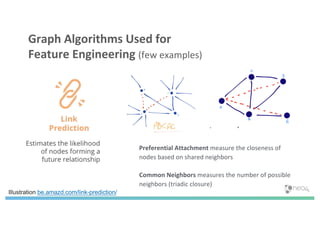
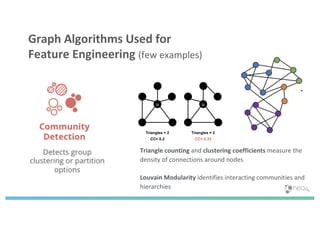
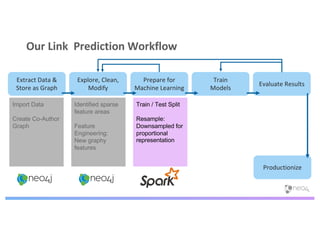
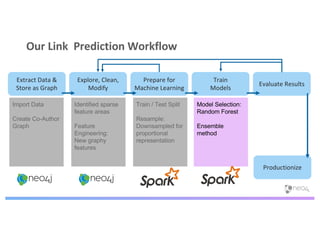
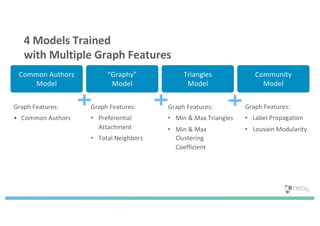
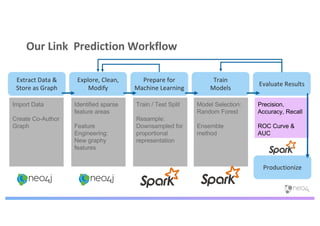
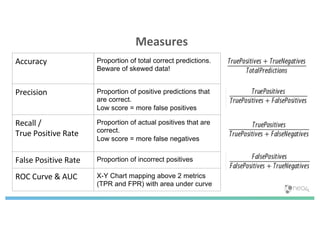
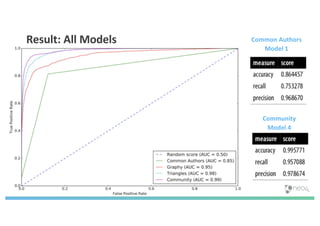
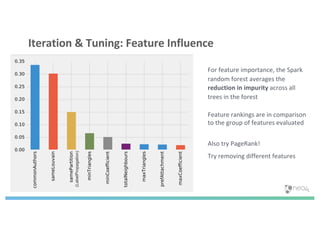
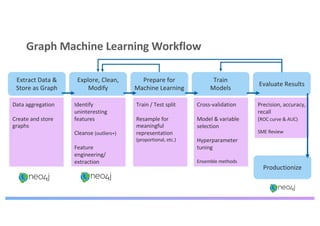
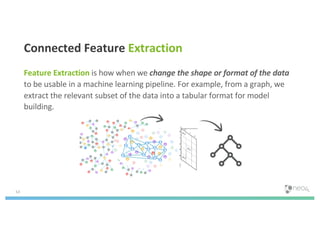
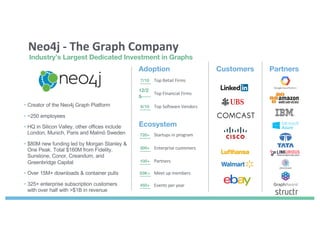
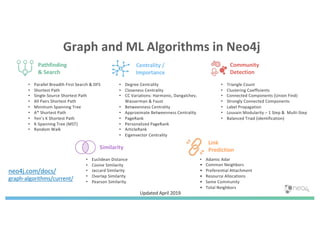
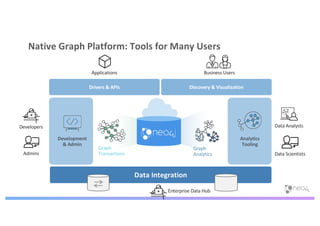
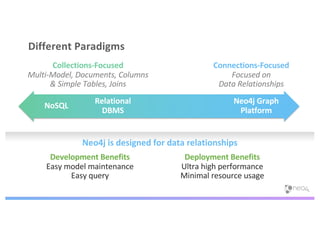
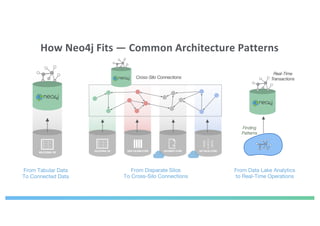
The document discusses enhancing machine learning (ML) predictions through graph algorithms, emphasizing the importance of relationships in predicting behavior. It highlights features extraction and engineering from graph databases like Neo4j, which provide novel insights and improve ML models by utilizing connected data structures. Various use cases, such as predicting collaboration in academic networks and applications in industries like healthcare and finance, illustrate the advantages of integrating graph algorithms into ML workflows.





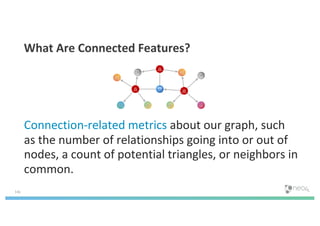
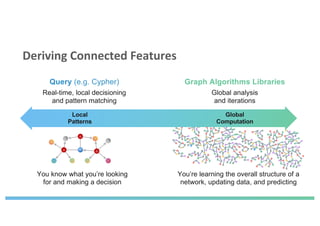
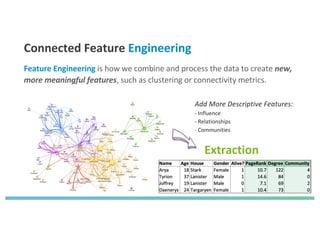














![Cypher: Powerful & Expressive Query Language
MATCH (:Person { name:“Dan”} ) -[:MARRIED_TO]-> (spouse)
MARRIED_TO
Dan Ann
NODE RELATIONSHIP TYPE
LABEL PROPERTY VARIABLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improvingmachinelearningpredictionswebinar-190509072141/85/Improving-Machine-Learning-using-Graph-Algorithms-64-320.jpg)