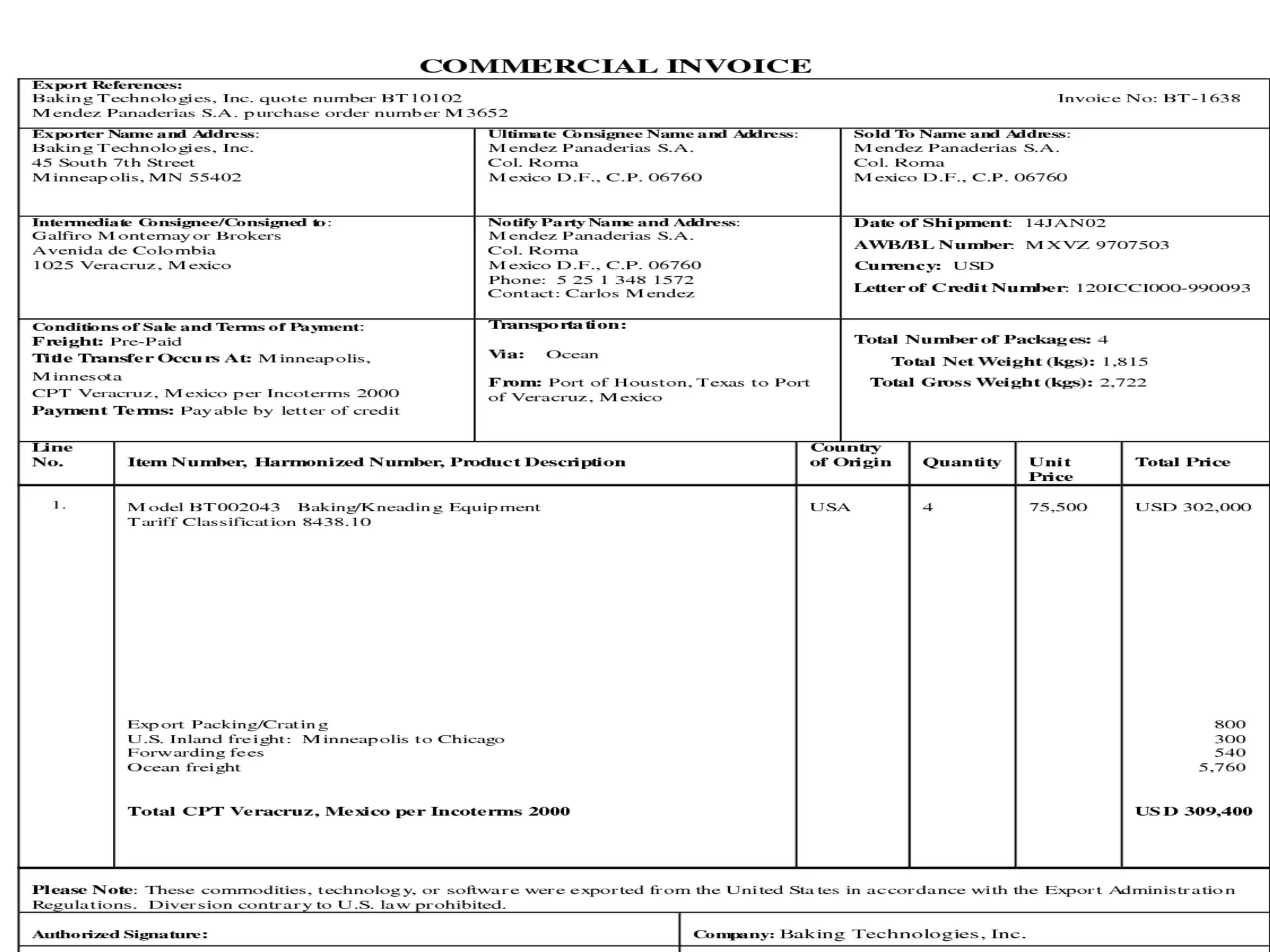
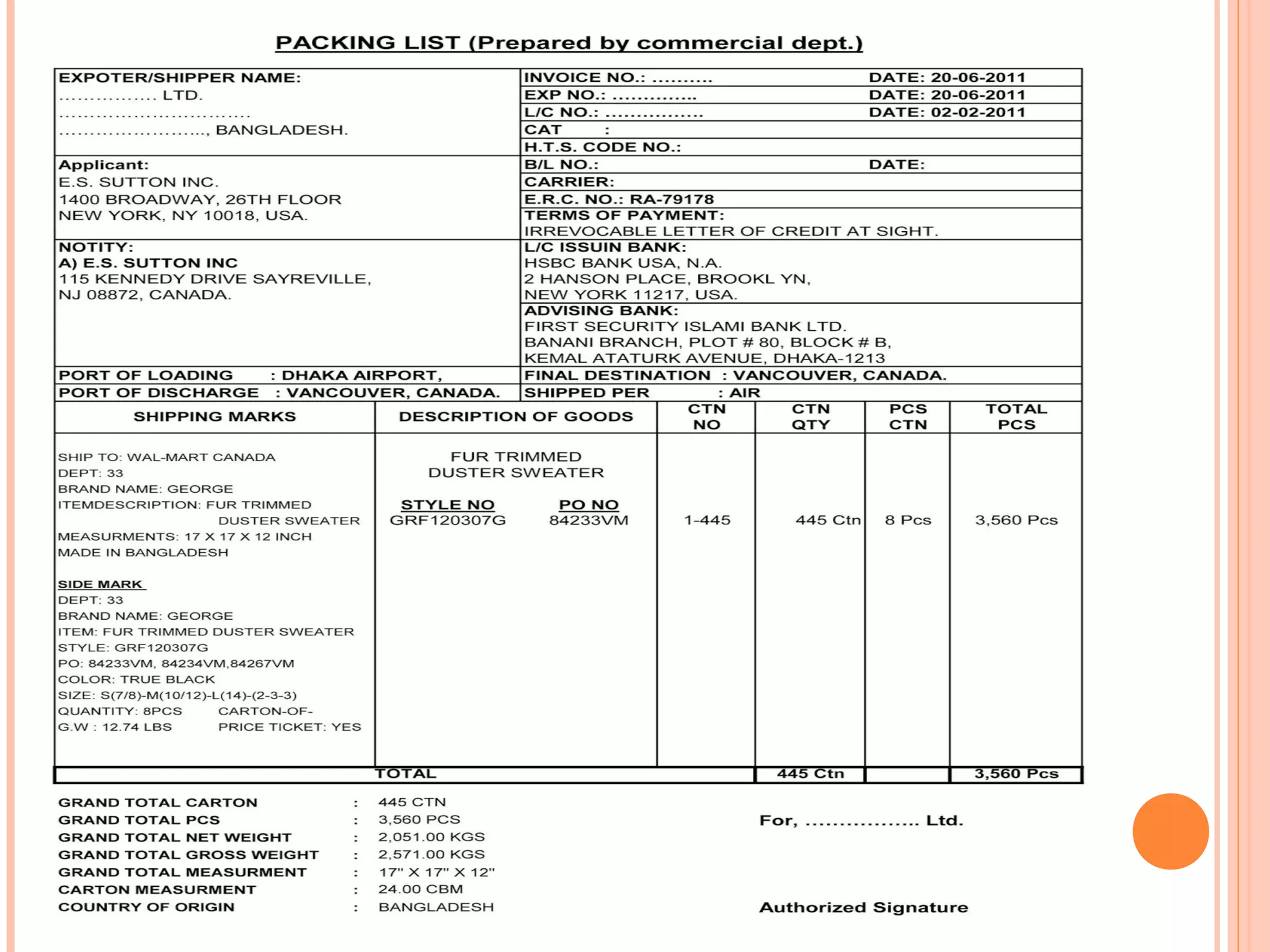
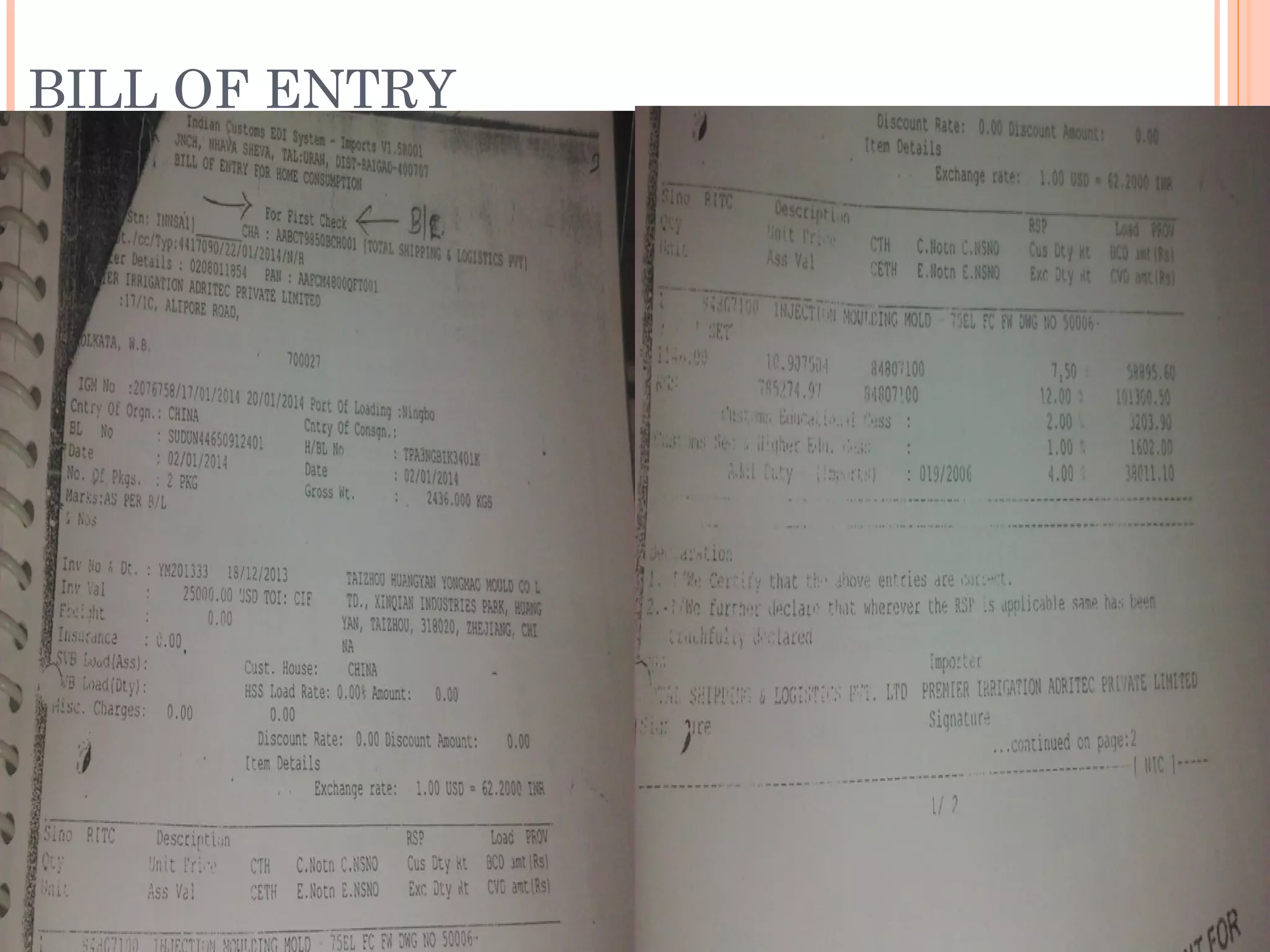
This document provides information on import and export procedures and documentation in India. It discusses the key steps in the import process, including trade enquiry, obtaining an import license, acquiring foreign exchange, opening a letter of credit, obtaining necessary documents, customs formalities, payment, and closing the transaction. Similarly, it outlines the export process and various pre-shipment documents, shipping documents, regulatory documents, and other auxiliary documents involved. The document aims to explain the standardized documentation requirements and procedures for imports and exports according to Indian laws and regulations.







![Established Importer
If the person imported goods of the class in which he is interested during
the basic period prescribed for such class, he is treated as an established
importer.
Actual user
If the person[importer]import goods for his own use in industrial
manufacturing process is called actual users.
Registered exporter
Registered exporter importing against exports made under a scheme of
export promotion and others have to obtain license from the chief controller
of exports and imports.
Open General Licence List[O.G.L]
The Government issues from time to time a list of commodities and
products which can be imported obtaining a general permission only. This
is called open General Licence List.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/importexportdocumentation-161023191357/75/Import-export-documentation-8-2048.jpg)