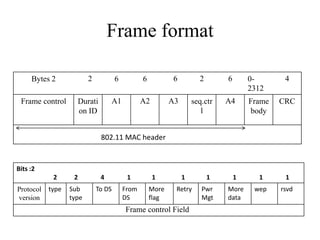
The document provides an overview of IEEE 802.11 standards for wireless local area networks. It discusses the creation of 802.11 by IEEE, the physical layer, frame formats, and various 802.11 protocols including 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac. It also describes the media access control including CSMA/CA and security features like authentication and WEP encryption.