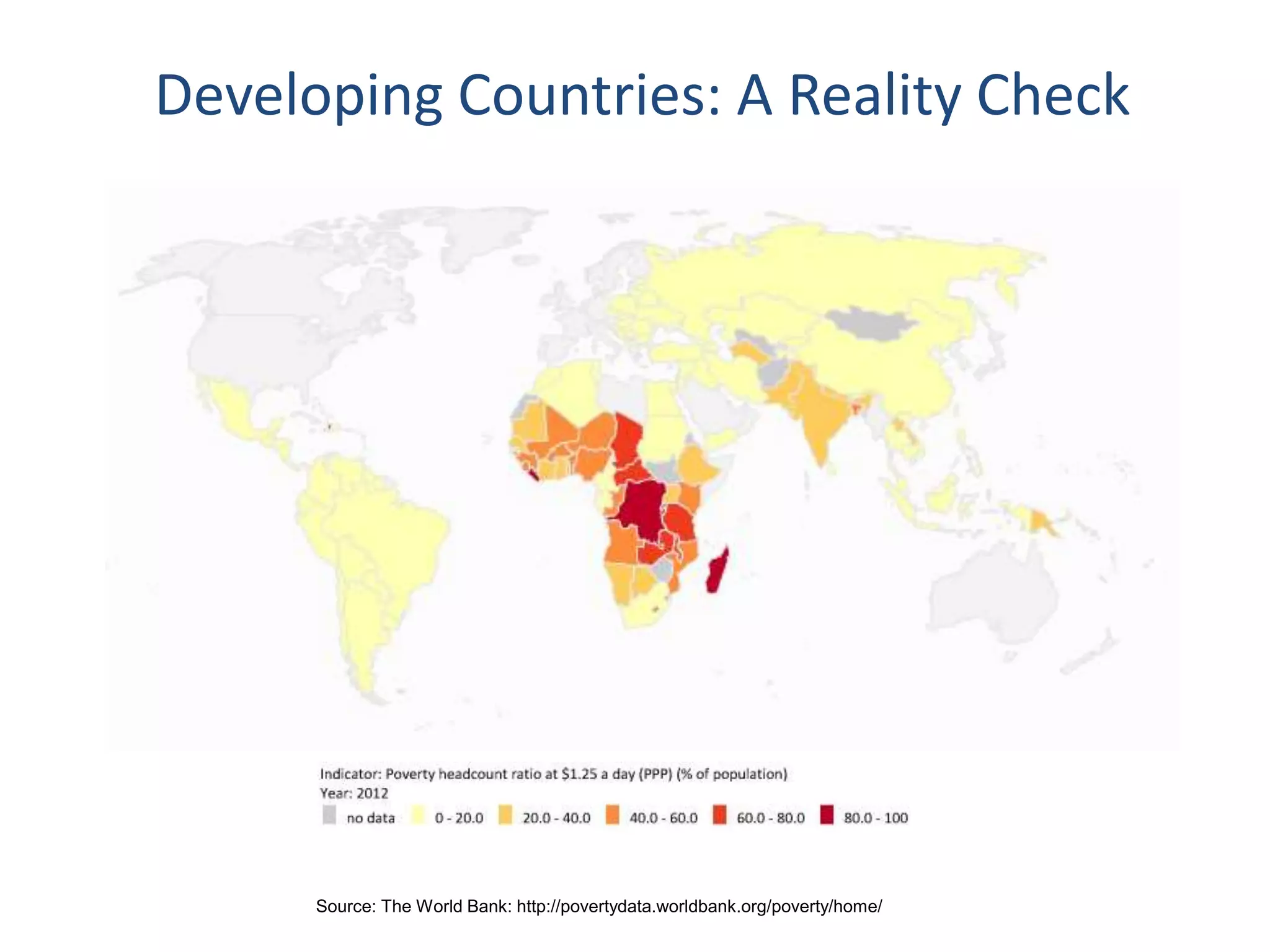
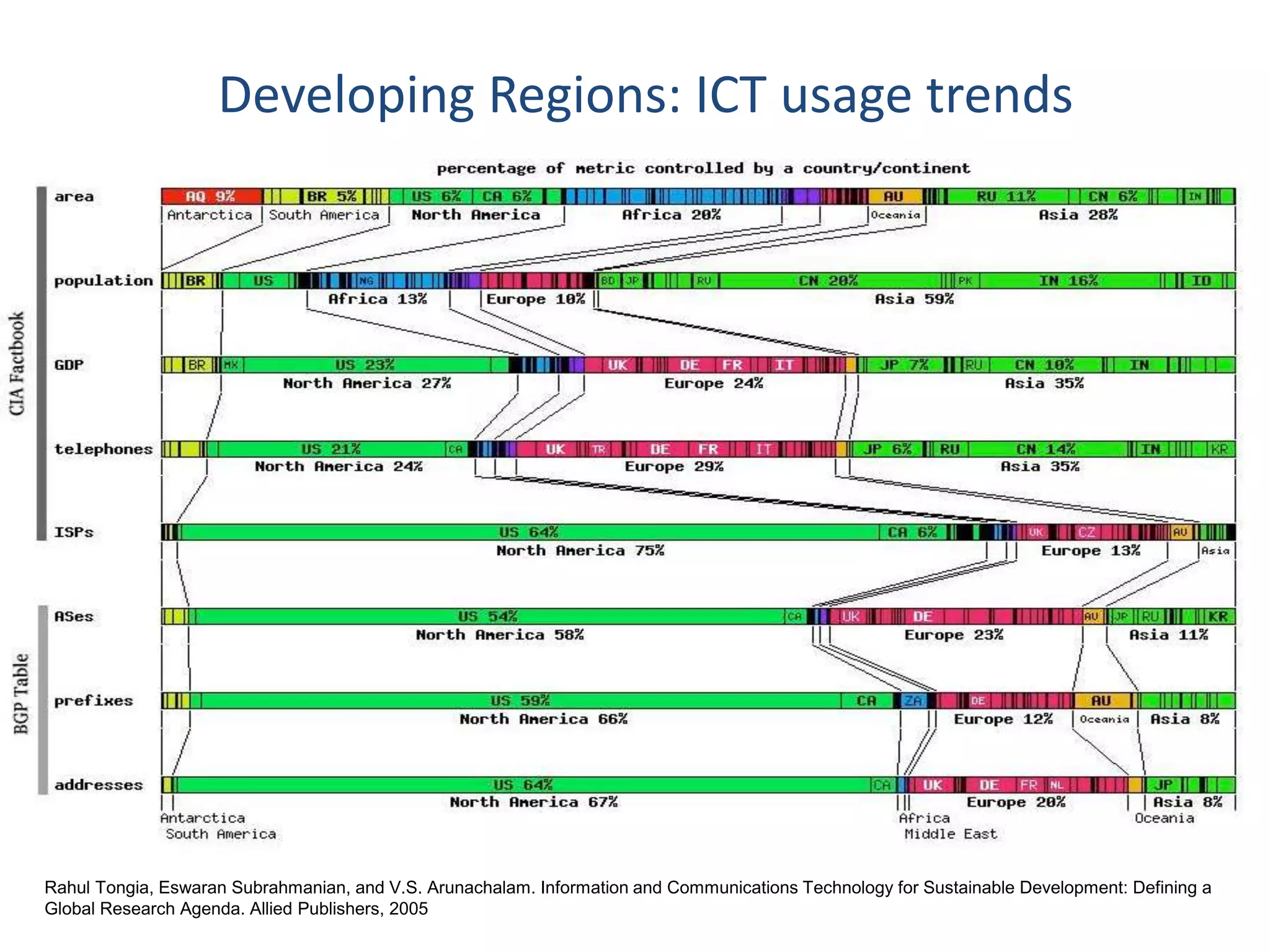
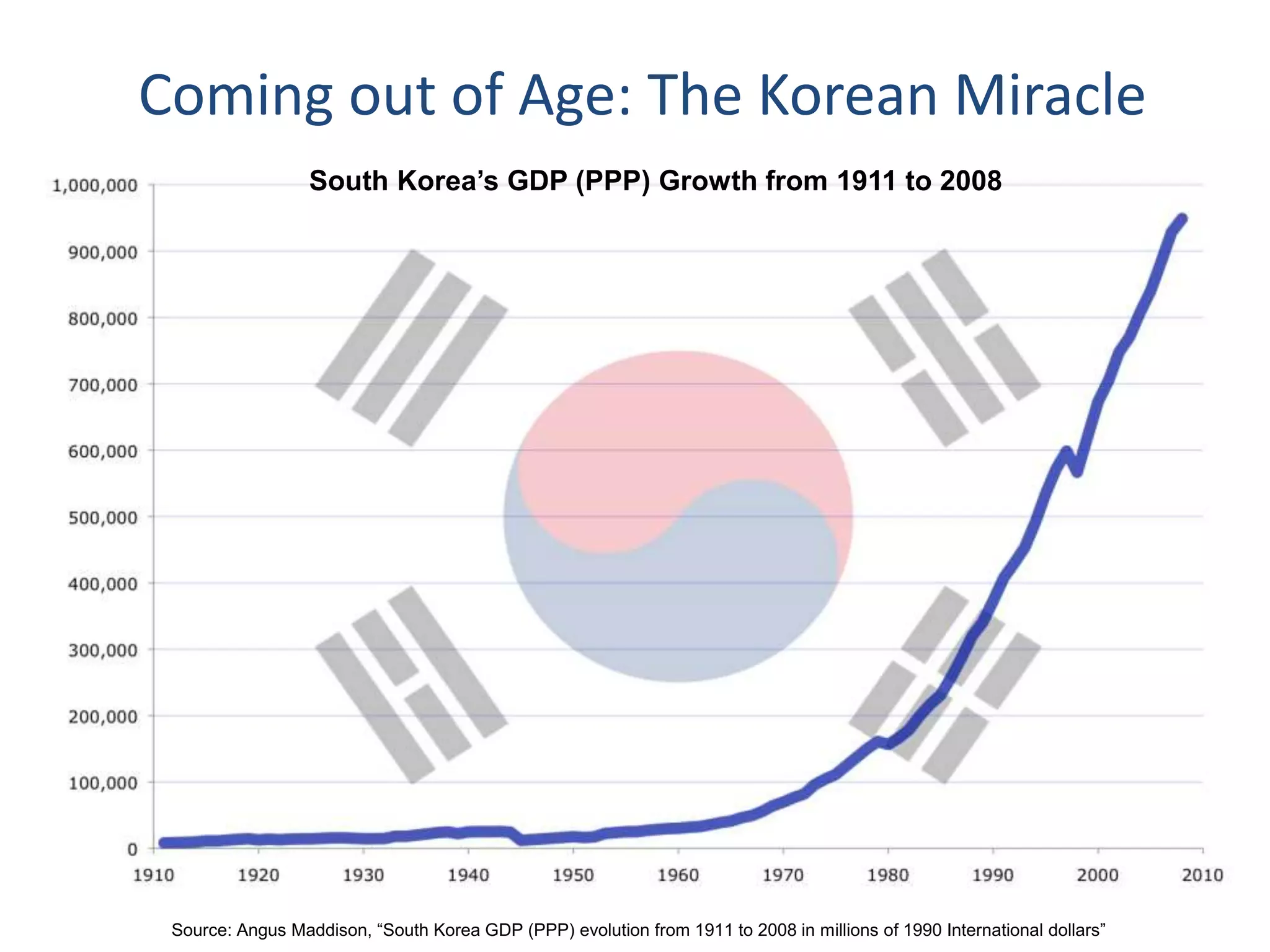
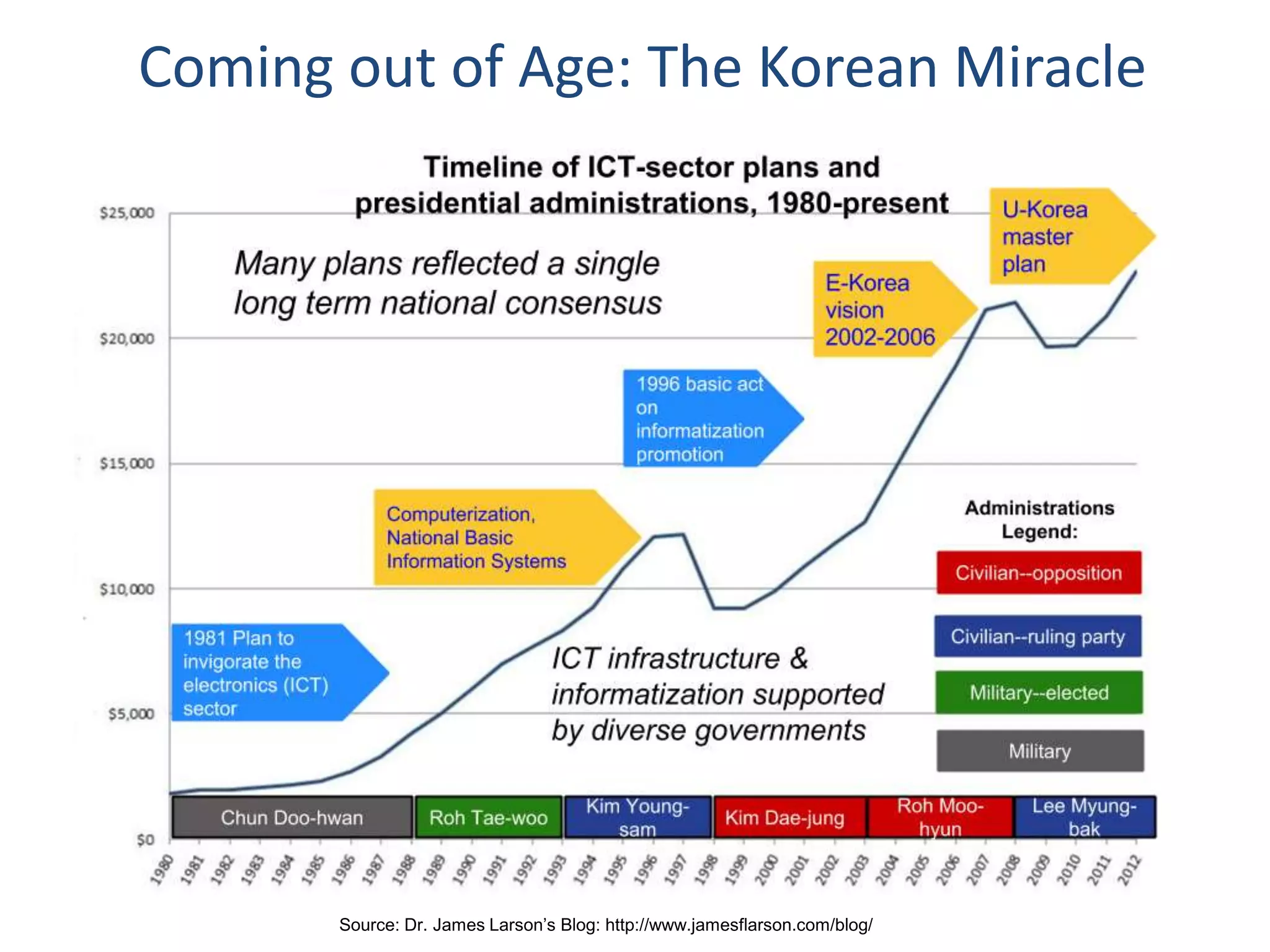
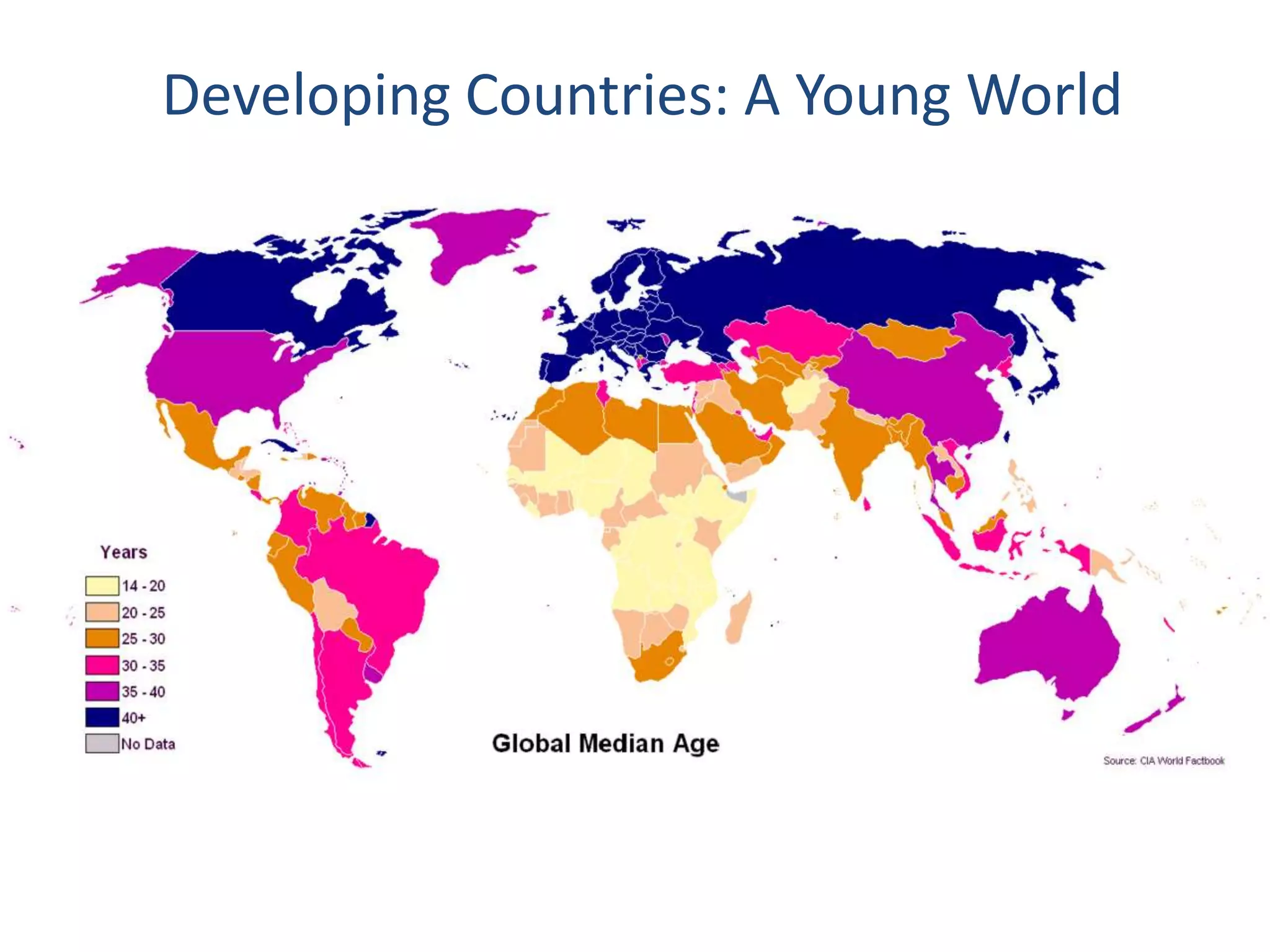
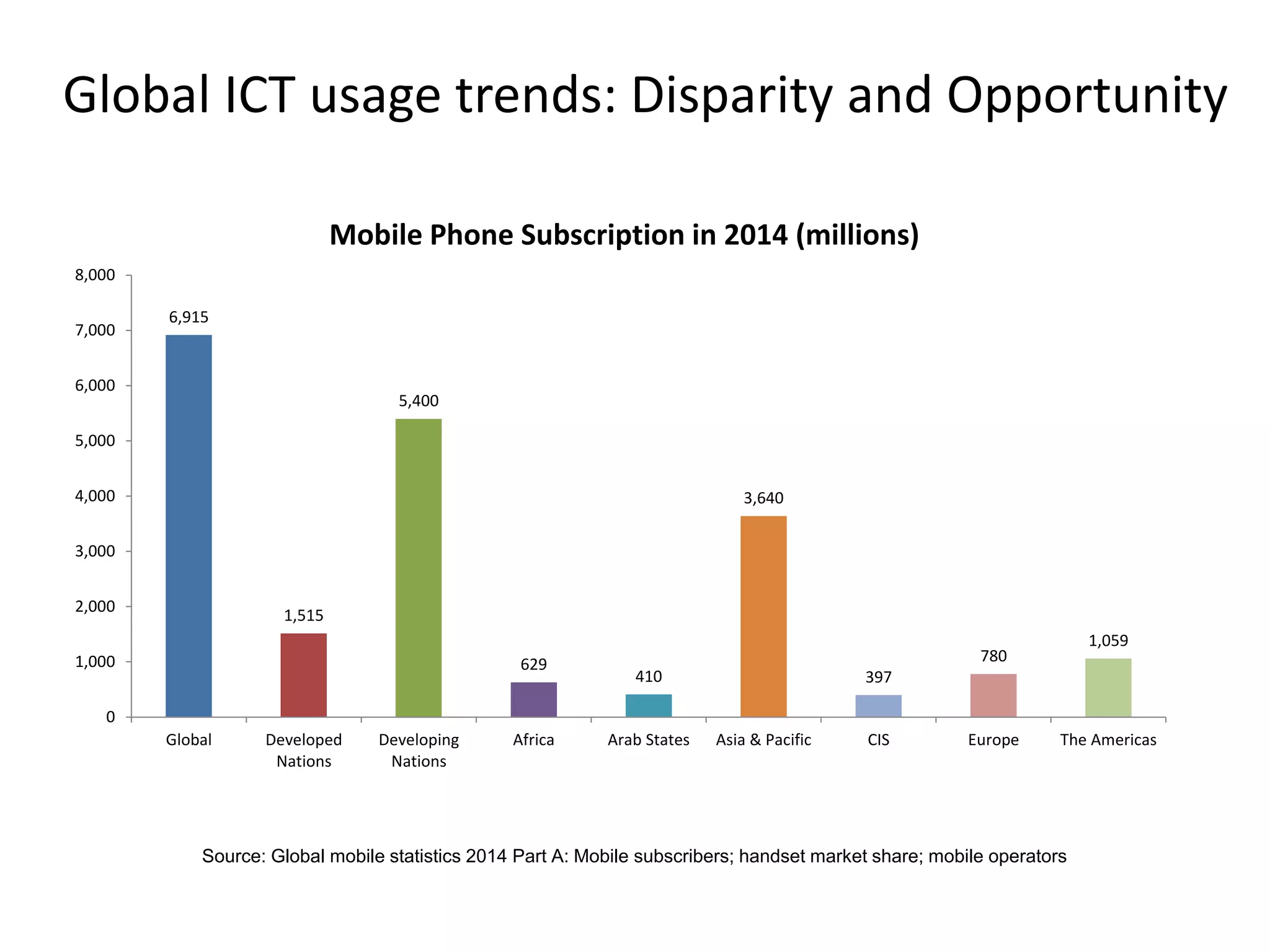
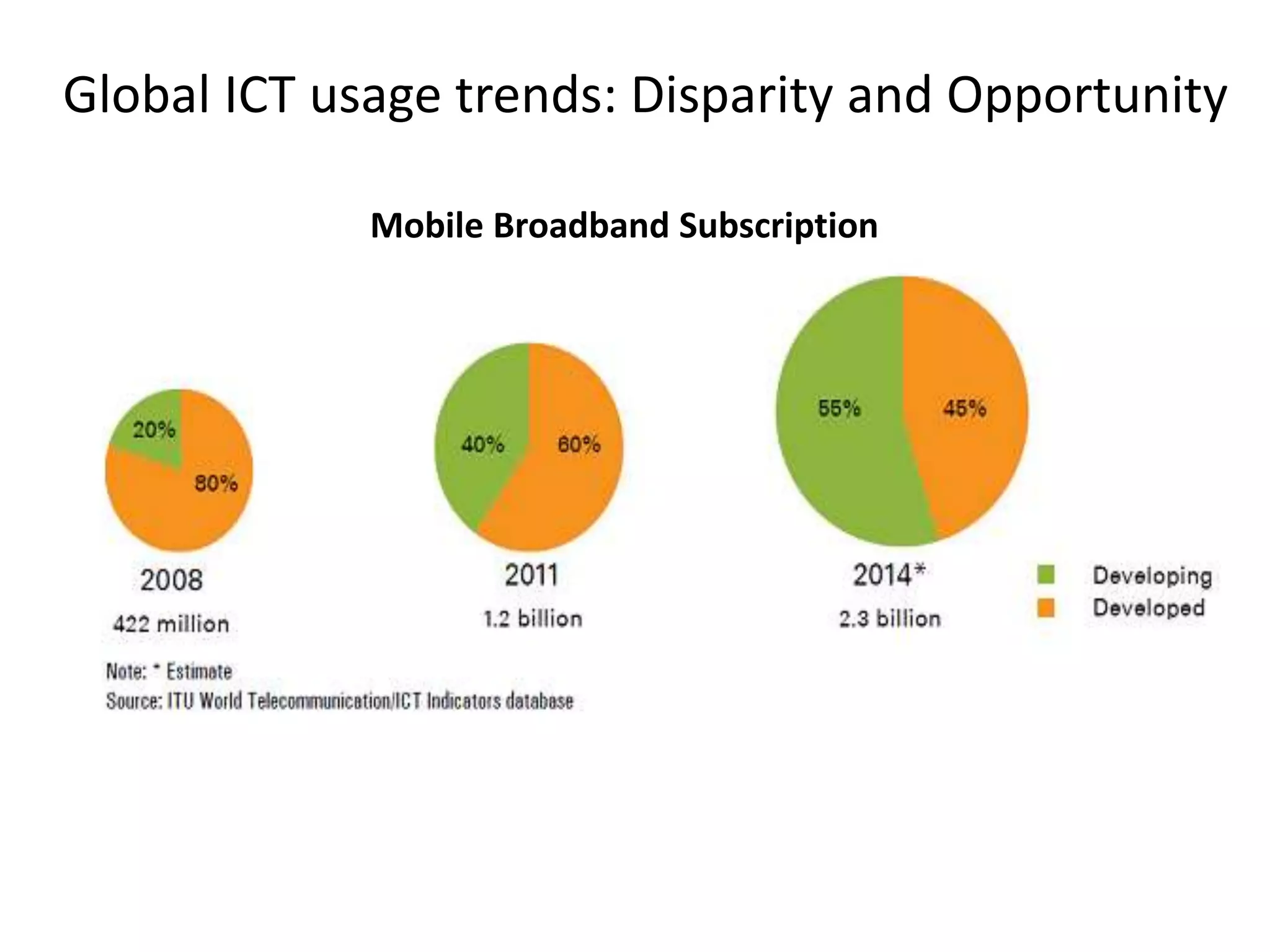
Dr. Faheem Hussain presented on ICT entrepreneurship in developing countries. He discussed how ICT entrepreneurs utilize digital tools to ensure participation, return on investment, and expand access. However, developing countries face many challenges, including outdated policies, lack of intellectual property protection, and inefficient financial systems. Opportunities exist through collaborative approaches between government, private sector, and entrepreneurs to develop infrastructure, inclusive services, and support mechanisms.