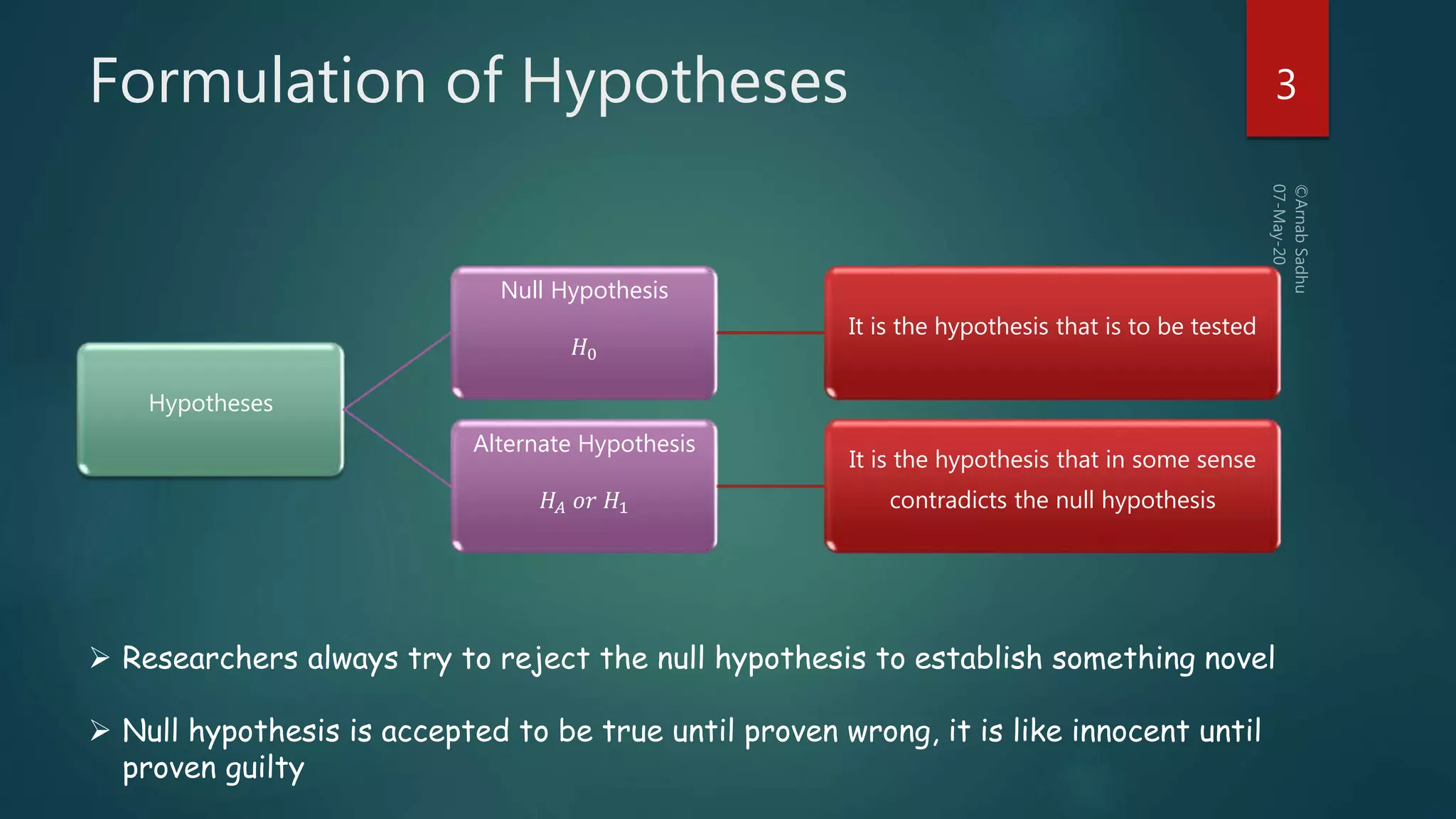
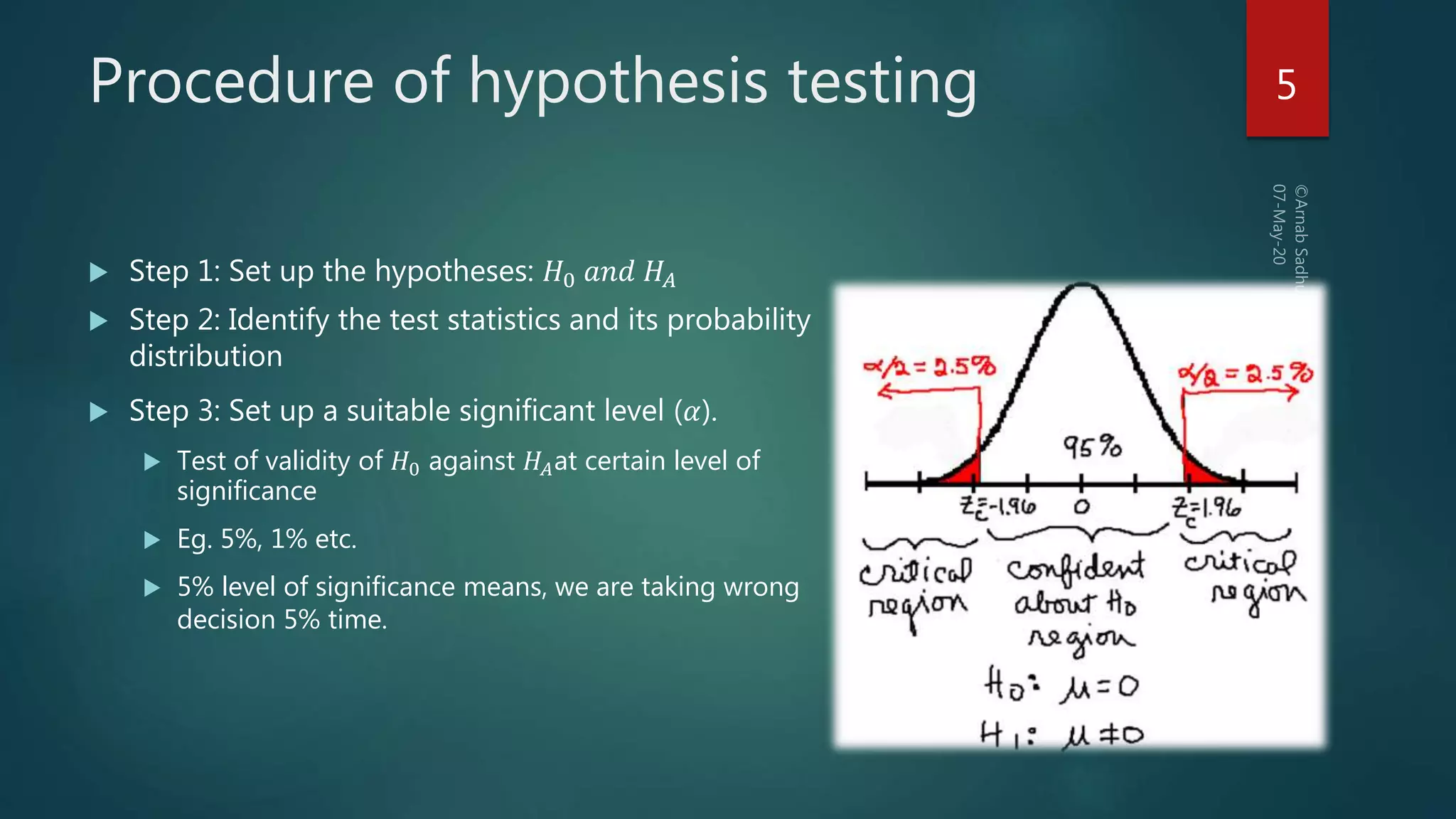
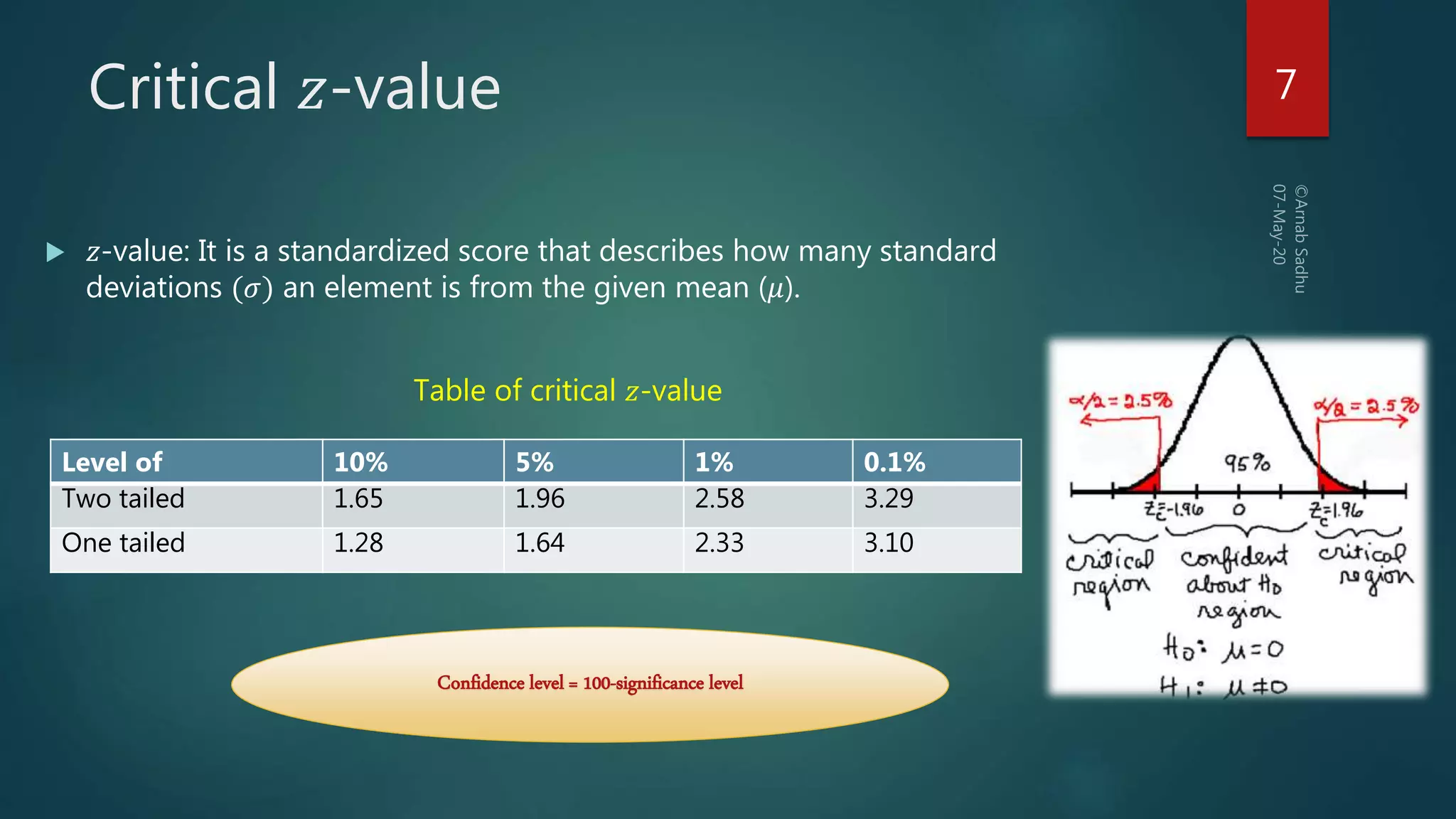
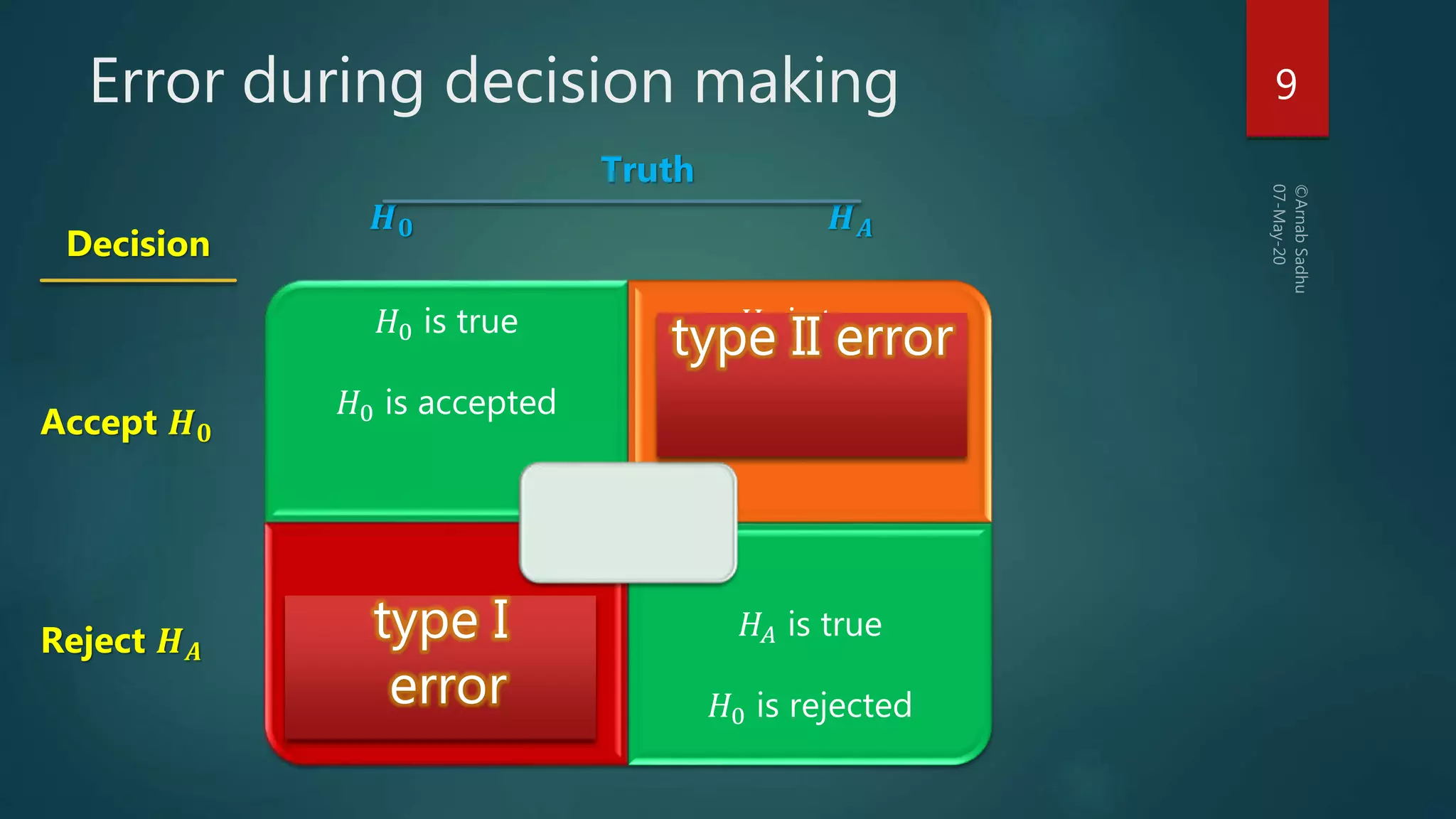
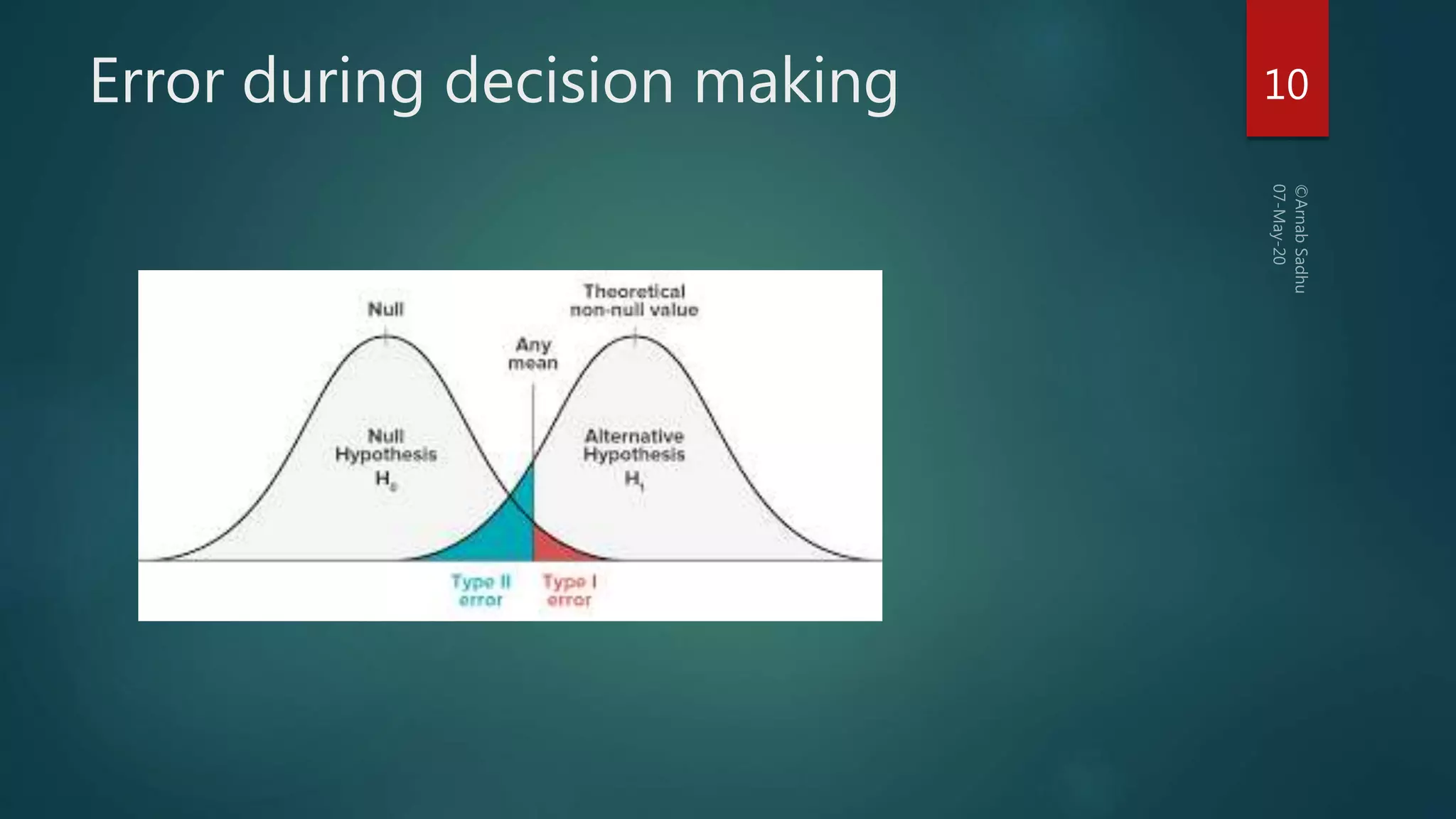
This document discusses hypotheses testing, which is a statistical technique used to test hypotheses about populations based on sample data. It defines key terms like the null hypothesis (H0), which is the hypothesis being tested, and the alternative hypothesis (HA or H1), which contradicts the null hypothesis. Researchers aim to reject the null hypothesis to establish something novel. The document outlines the steps of hypothesis testing, including formulating the hypotheses, identifying relevant test statistics, setting a significance level, doing computations, and making a decision to either accept or reject the null hypothesis. It discusses types of tests like z-tests and t-tests and the concept of critical values. The document also explains the two types of errors that can occur in decision making