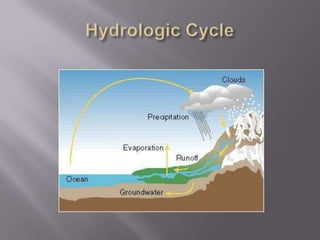
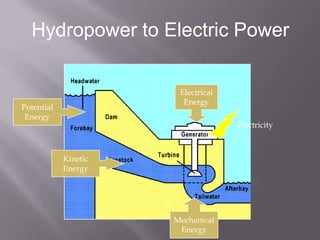
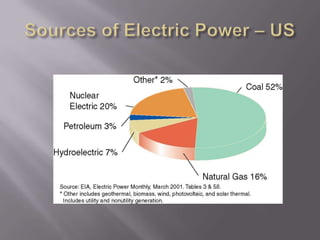
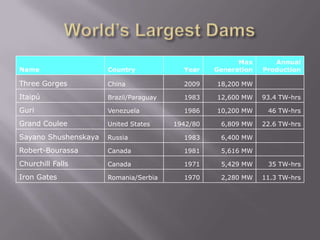
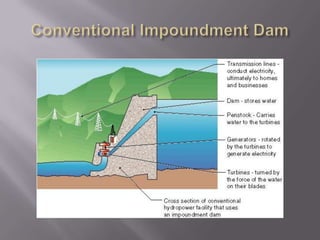
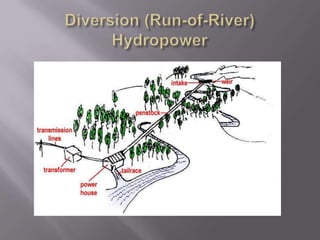
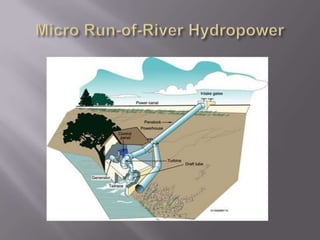
This document provides an overview of hydropower as a renewable energy source. It discusses different types of hydropower technologies including large hydroelectric dams, medium and small hydro, mini hydro, micro hydro, and pico hydro. It also discusses key design aspects of hydropower including head, dams, and the relationship between power output and head and flow. Examples of some of the largest hydroelectric power plants in the world are listed along with their location, year of operation, maximum generation capacity and annual production. The document emphasizes that hydropower is a modern technology that can be improved to make better use of available water resources.