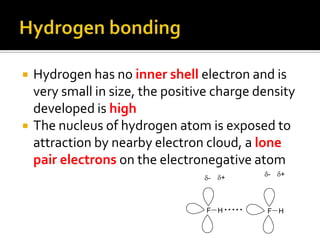
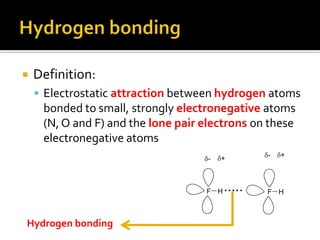
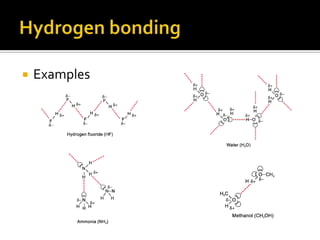
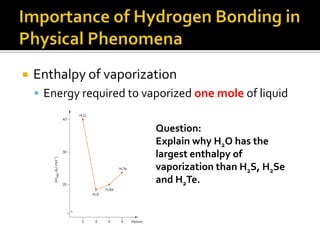
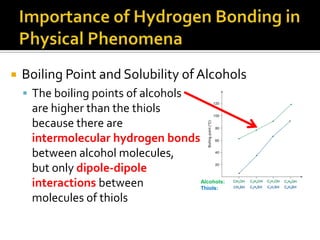
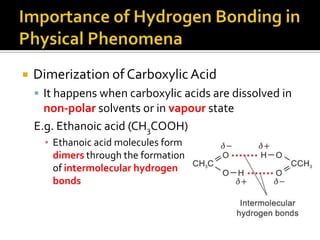
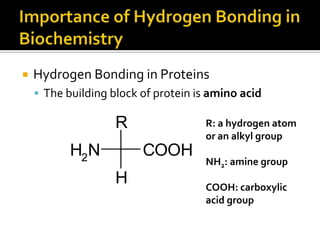
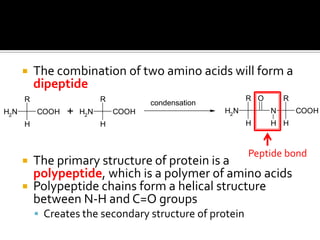
1. Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom like nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine interacts with another electronegative atom via electrostatic attraction between the hydrogen and the lone pair of electrons.
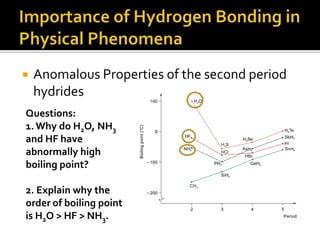
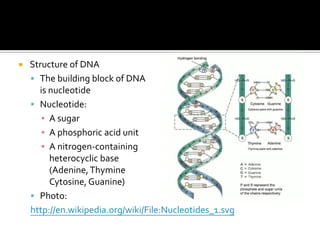
2. This leads to higher boiling points and enthalpies of vaporization for compounds that can form multiple hydrogen bonds like water. It also allows for the formation of structures like DNA base pairs and protein secondary structures.
3. Hydrogen bonding plays important roles in determining physical properties of compounds and enabling key biological molecules like DNA and proteins to form their functional three-dimensional structures.