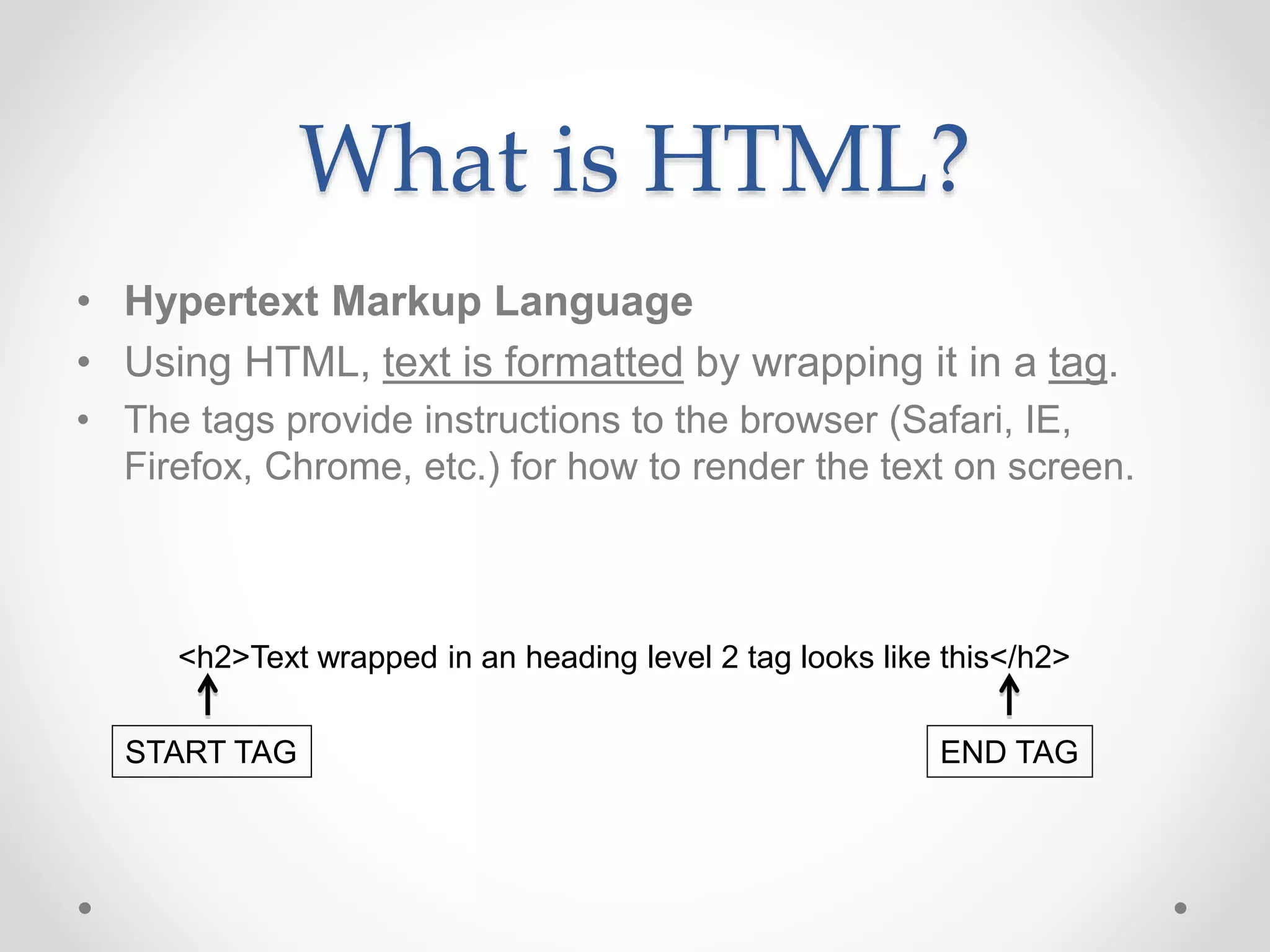
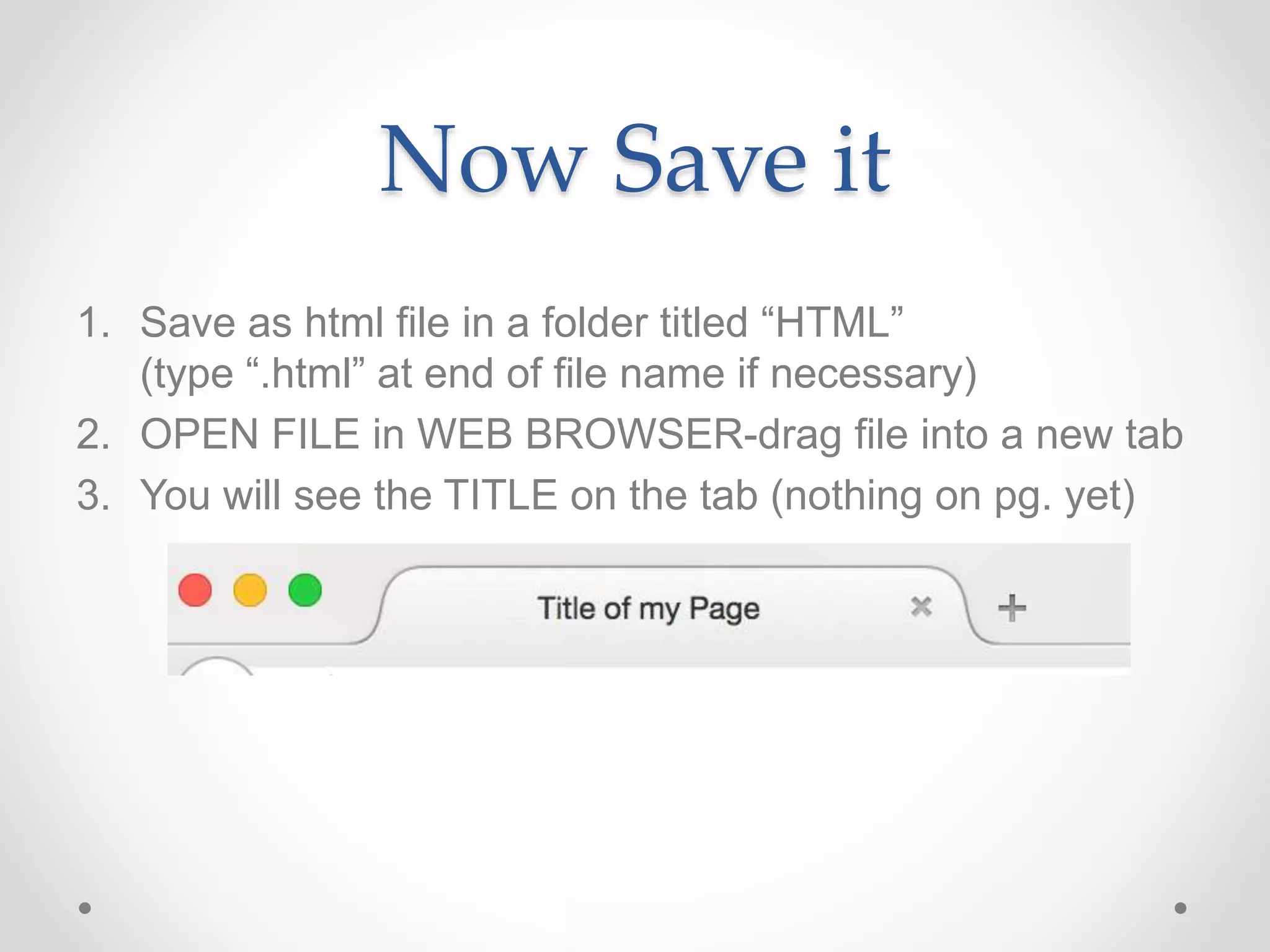
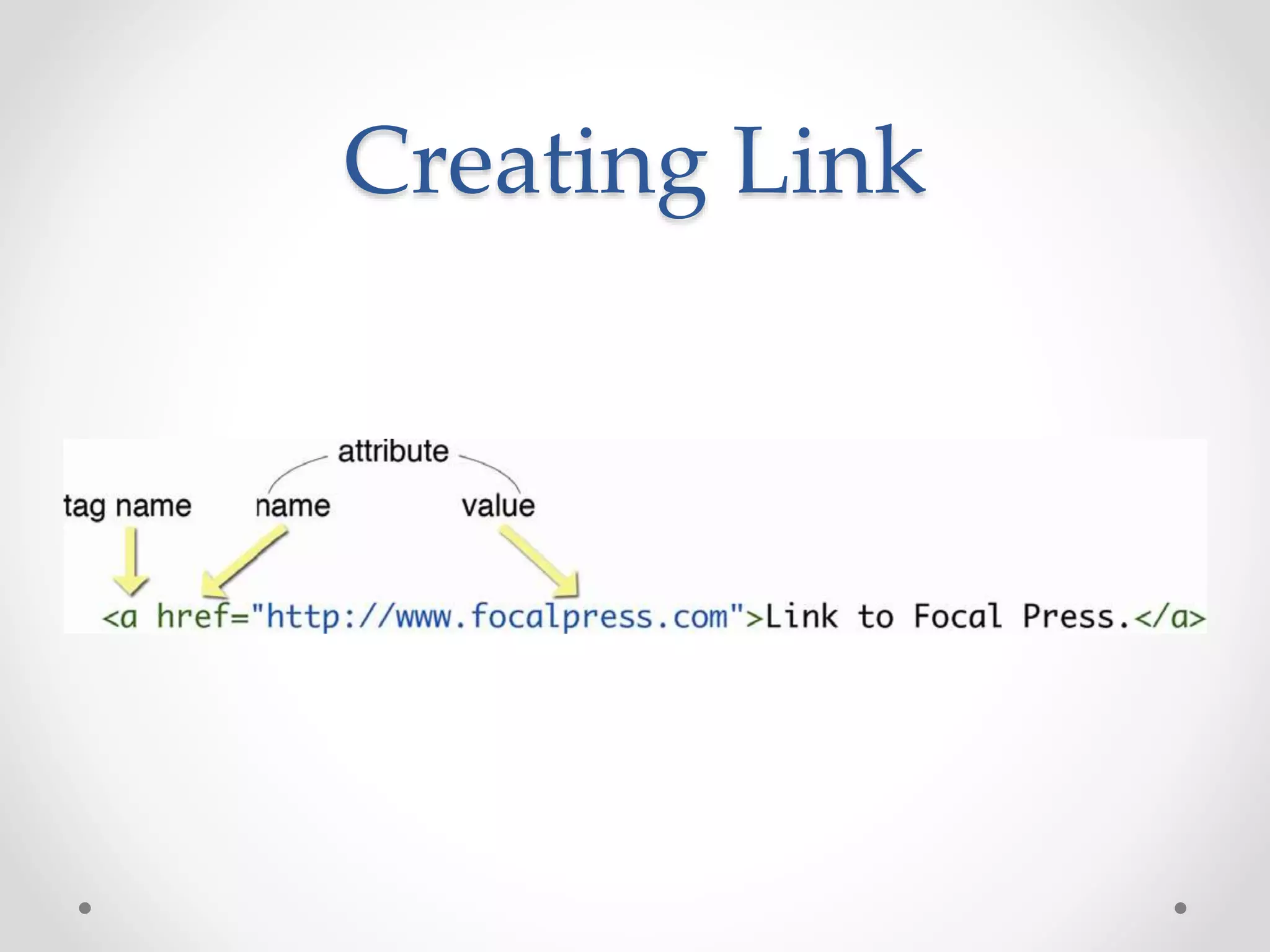
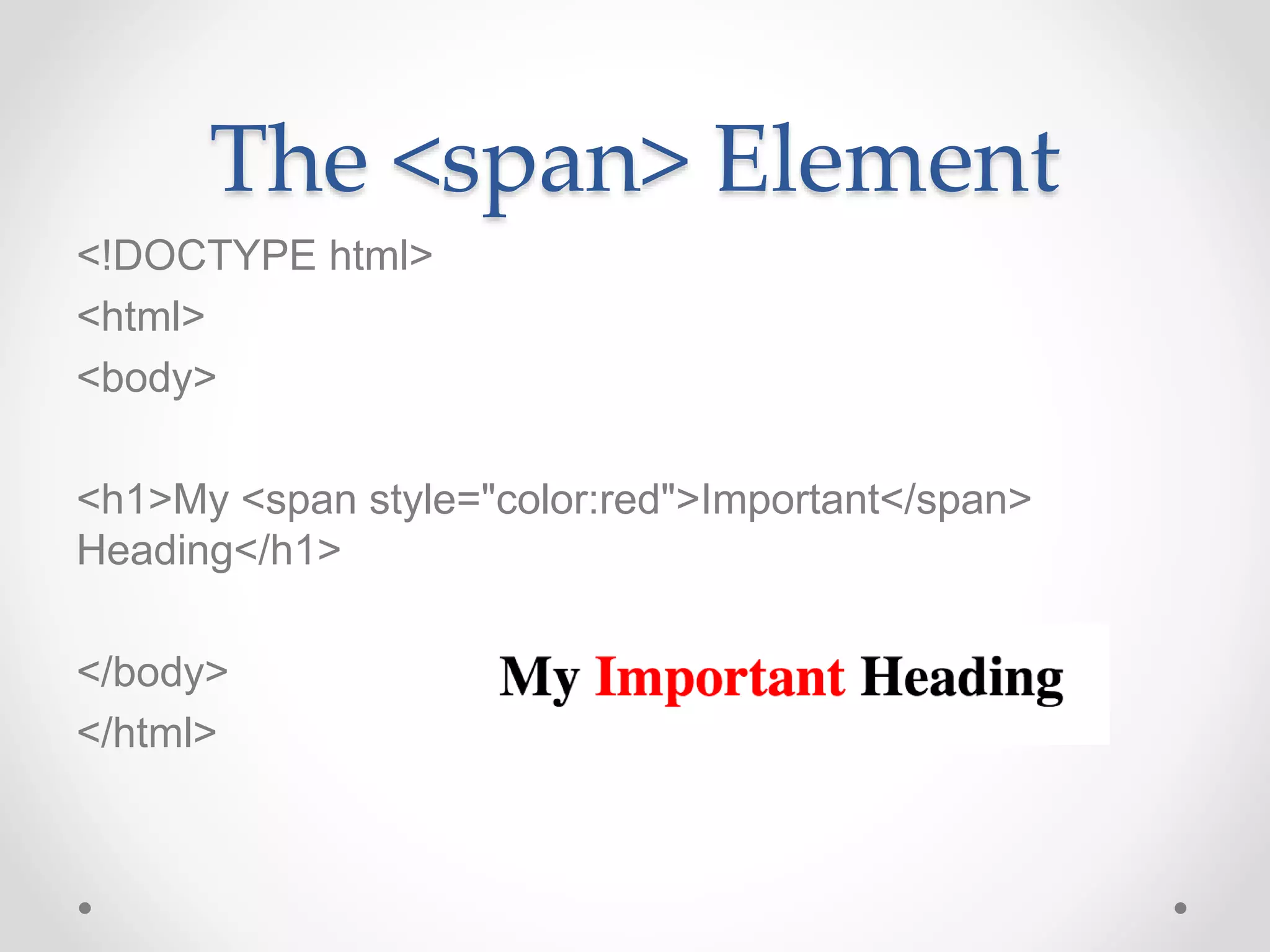
HTML Basics document provides an overview of HTML elements and tags used to format text and structure web pages. It discusses the basic structure of an HTML document including the <head>, <title>, and <body> sections. Common text formatting tags like <p>, <h1>-<h6>, <strong>, <em>, and <br> are demonstrated. Other elements covered include images, lists, links, and basic styling with inline CSS. The document serves as an introduction to basic HTML syntax and structure.