This document reviews the inverse scattering series internal multiple attenuation algorithm for land data, highlighting its sensitivity to reference velocity and the importance of accurate near-surface velocities. Two analytic examples demonstrate the algorithm's capability in handling 1D normal and non-normal incidence without requiring actual velocity. The findings emphasize that conventional methods may fail under certain assumptions, making the inverse scattering method more effective for internal multiple suppression in land data.







![On-shore research project I - internal multiple attenuation algorithm MOSRP07
Suppose we choose the wrong reference velocity c0. The new vertical wave number becomes kz =
2ω/c0, and the new pseudo depths are za = c0t1/2 and zb = c0t2/2.
Equation (35) can be rewritten as
b1(z) = R1δ(z − za) + R2T1T1δ(z − zb). (39)
Substituting (44) into the third integral of (32), we have
∞
z2+
dz3eikzz3 [R1δ(z3 − za) + R2T1T1δ(z3 − zb)]
= R1eikzza
H(za − (z2 + )) + R2T1T1eikzzb
H(zb − (z2 + )),
(40)
where H is the Heaviside function. The second integral becomes
z1−
−∞
dz2e−ikzz2 [R1δ(z2 − za) + R2T1T1δ(z2 − zb)]
· [R1eikzza
H(za − (z2 + )) + R2T1T1eikzzb
H(zb − (z2 + ))]
= R2
1eikz(za−za)
H(za − (za + ))H((z1 − ) − za)
+ R1R2T1T1eikz(za−zb)
H(za − (zb + ))H(z1 − − zb)
+ R1R2T1T1eikz(zb−za)
H(zb − (za + ))H(z1 − − za)
+ R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eikz(zb−zb)
H(zb − (zb + ))H(z1 − − zb).
(41)
The underlined Heaviside function in (41) are zero due to H(< 0) = 0. The remaining third term
is
R1R2T1T1eikz(zb−za)
H(zb − (za + ))H(z1 − − za). (42)
Therefore,
b3IM (kz) =
∞
−∞
dz1eikzz1 [R1δ(z1 − za) + R2T1T1δ(z1 − zb)]
· [R1R2T1T1eikz(zb−za)
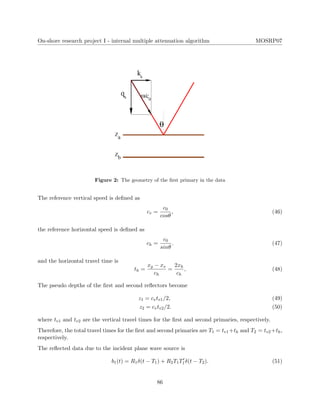
H(zb − (za + ))H(z1 − − za)]
= R2
1R2T1T1eikz(zb−za+za)
H(zb − (za + ))H(za − − za)
+ R1R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eikz(zb−za+zb)
H(zb − (za + ))H(zb − − za)
= R1R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eikz(2zb−za)
= R1R2
2T2
1 T1
2
ei(2ω/c0)(2c0t2/2−c0t1/2)
= R1R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eiω(2t2−t1))
.
(43)
Note that the underlined term H(− ) = 0, and H(> 0) = 1.
84](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hsu-weglein-2008-150410121310-conversion-gate01/85/Reference-velocity-sensitivity-for-the-marine-internal-multiple-attenuation-algorithm-analytic-examples-Arthur-B-Weglein-8-320.jpg)

![On-shore research project I - internal multiple attenuation algorithm MOSRP07
Fourier transforming into the frequency ω domain gives
b1(ω) = R1eiωT1
+ R2T1T1eiωT2
= R1eiω(tv1+th)
+ R2T1T1eiω(tv2 +th)
= [R1ei( 2ω
cv
)(
cvtv1
2
)
+ R2T1T1ei( 2ω
cv
)(
cvtv2
2
)
]e
i( 2ω
ch
)(
chth
2
)
.
(52)
Equation (52) can be rewritten as
b1(kh, kz) = [R1eikzz1
+ R2T1T1eikzz2
]eikhxh
. (53)
Fourier transforming b1 over xh, we find
b1(kh, kz) = [R1eikzz1
+ R2T1T1eikzz2
]δ(kg − ks). (54)
Inverse Fourier transforming equation (53) over kz gives
b1(kh, z) = [R1δ(z − z1) + R2T1T1δ(z − z2)]δ(kg − ks) (55)
Substituting equation (55) into the third integral of equation (23), we have
∞
z2+
dz3eikzz3 [R1δ(z3 − z1) + R2T1T1δ(z3 − z2)]δ(k2 − ks)
= [R1eikzz1
H(z1 − (z2 + )) + R2T1T1eikzz2
H(z2 − (z2 + ))]δ(k2 − ks).
(56)
The second integral is
z1−
−∞
dz2e−ikzz2 [R1δ(z2 − z1) + R2T1T1δ(z2 − z2)]δ(k1 − k2)
·[R1eikzz1
H(z1 − (z2 + )) + R2T1T1eikzz2
H(z2 − (z2 + ))]δ(k2 − ks)
= R2
1eikz(z1−z1)
H(z1 − (z1 + ))H((z1 − ) − z1)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
+ R1R2T1T1eikz(z1−z2)
H(z1 − (z2 + ))H((z1 − ) − z2)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
+ R1R2T1T1eikz(z2−z1)
H(z2 − (z1 + ))H((z1 − ) − z1)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
+ R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eikz(z2−z2)
H(z2 − (z2 + ))H((z1 − ) − z2)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks).
(57)
The underline Heaviside functions are zero. The remaining third term is
[R1R2T1T1eikz(z2−z1)
H(z2 − (z1 + ))H((z1 − ) − z1)]δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks). (58)
Therefore,
b3(kh, kz) =
∞
−∞
dz1e−ikzz1 [R1δ(z1 − z1) + R2T1T1δ(z1 − z2)]δ(kg − k1)
·[R1R2T1T1eikz(z2−z1)
H(z2 − (z1 + ))H((z1 − ) − z1)]δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
= R2
1R2T1T1eikz(z2−z1+z1)
H(z2 − (z1 + ))H((z1 − ) − z1)δ(kg − k1)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
+ R1R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eikz(z2−z1+z2)
H(z2 − (z1 + ))H(z2 − − z1)δ(kg − k1)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
= R1R2
2T2
1 T1
2
eikz(2z2−z1)
δ(kg − k1)δ(k1 − k2)δ(k2 − ks)
(59)
87](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hsu-weglein-2008-150410121310-conversion-gate01/85/Reference-velocity-sensitivity-for-the-marine-internal-multiple-attenuation-algorithm-analytic-examples-Arthur-B-Weglein-11-320.jpg)


