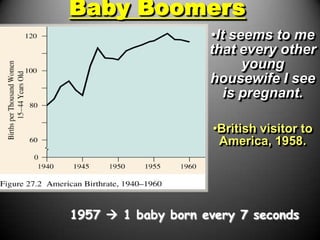
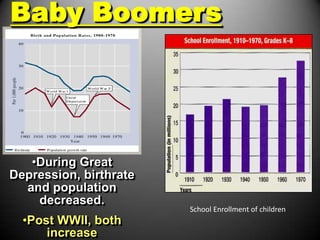
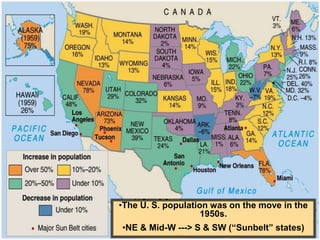
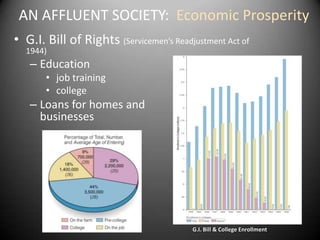
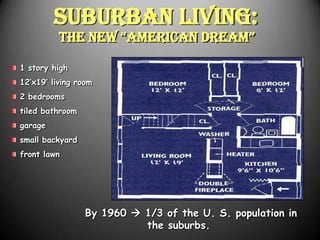
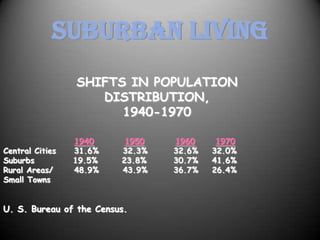
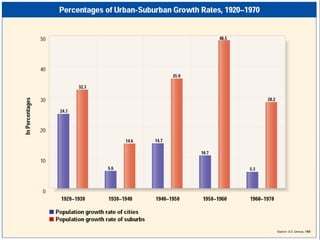
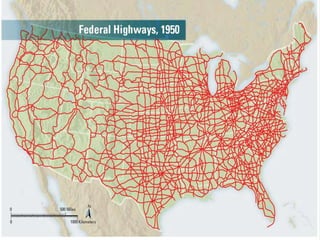
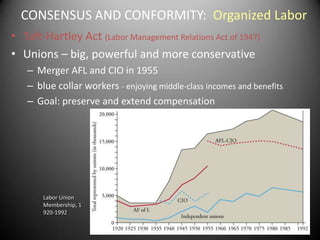
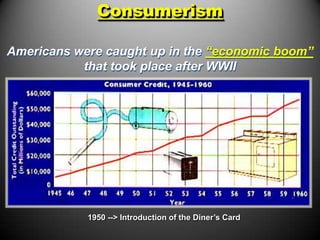
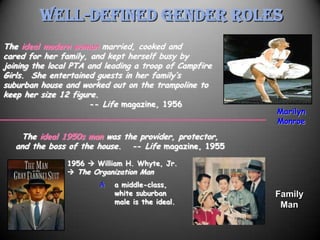
The 1950s were a time of economic prosperity and suburban growth fueled by the GI Bill, affordable housing, and increased car ownership. However, there were also social tensions as new youth and countercultures emerged while racial segregation continued. The postwar era saw a rise in mass consumerism and popular culture influenced by new technologies like television.