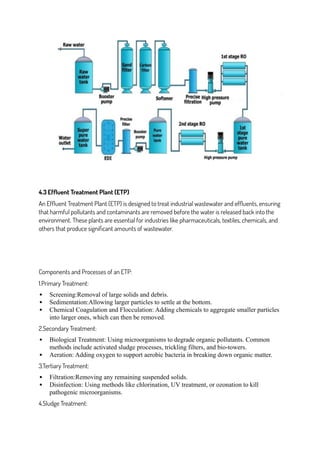
The document is an internship report detailing Mr. Min Prasad Subedi's training at Asian Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. in Nepal, conducted as part of his Bachelor of Pharmacy requirements. It covers various departments such as production, quality control, and research and development, emphasizing the integration of theoretical knowledge with practical experiences. The internship focused on manufacturing processes, quality assurance, and the importance of documentation and compliance with GMP standards in the pharmaceutical industry.