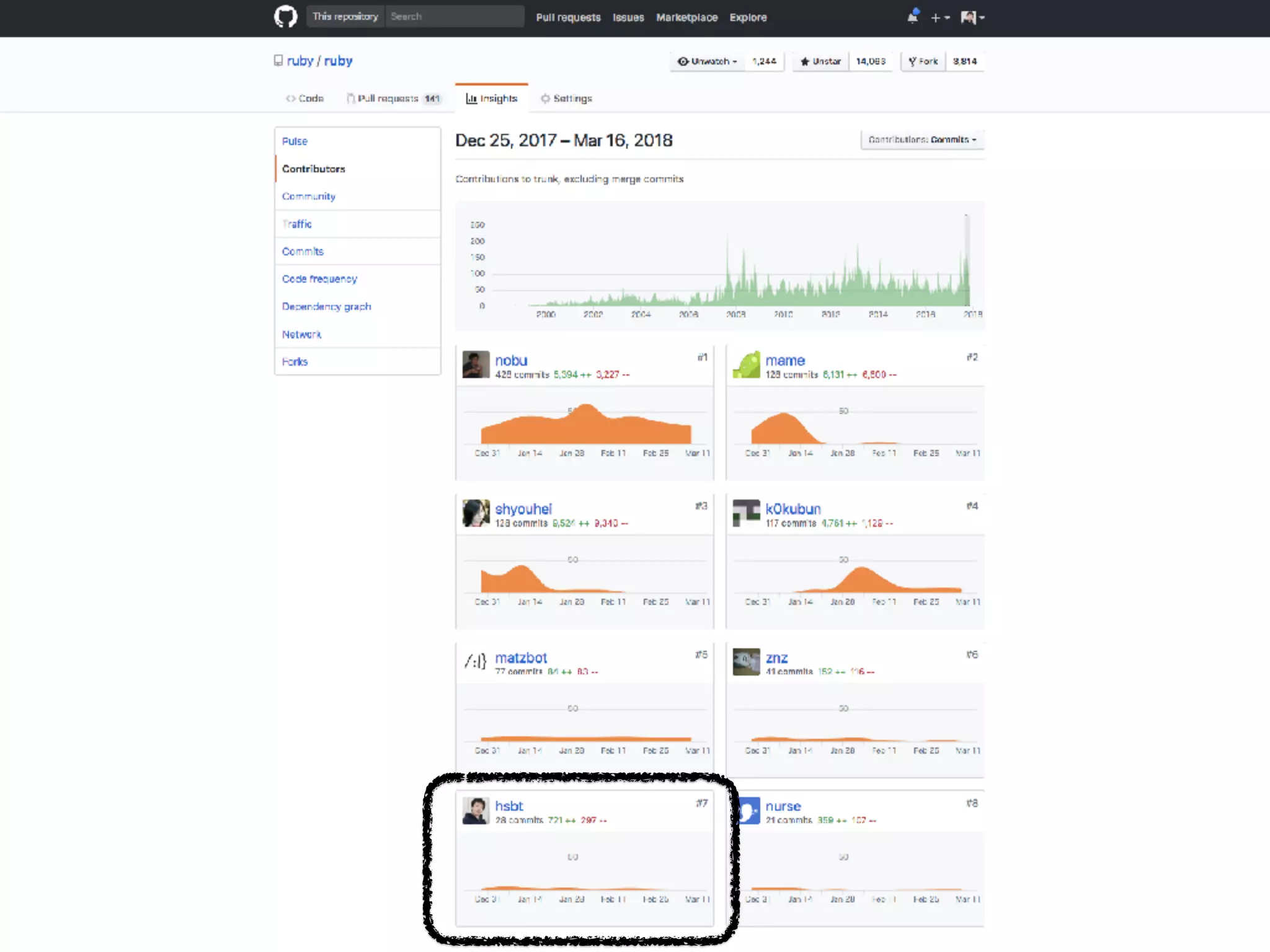
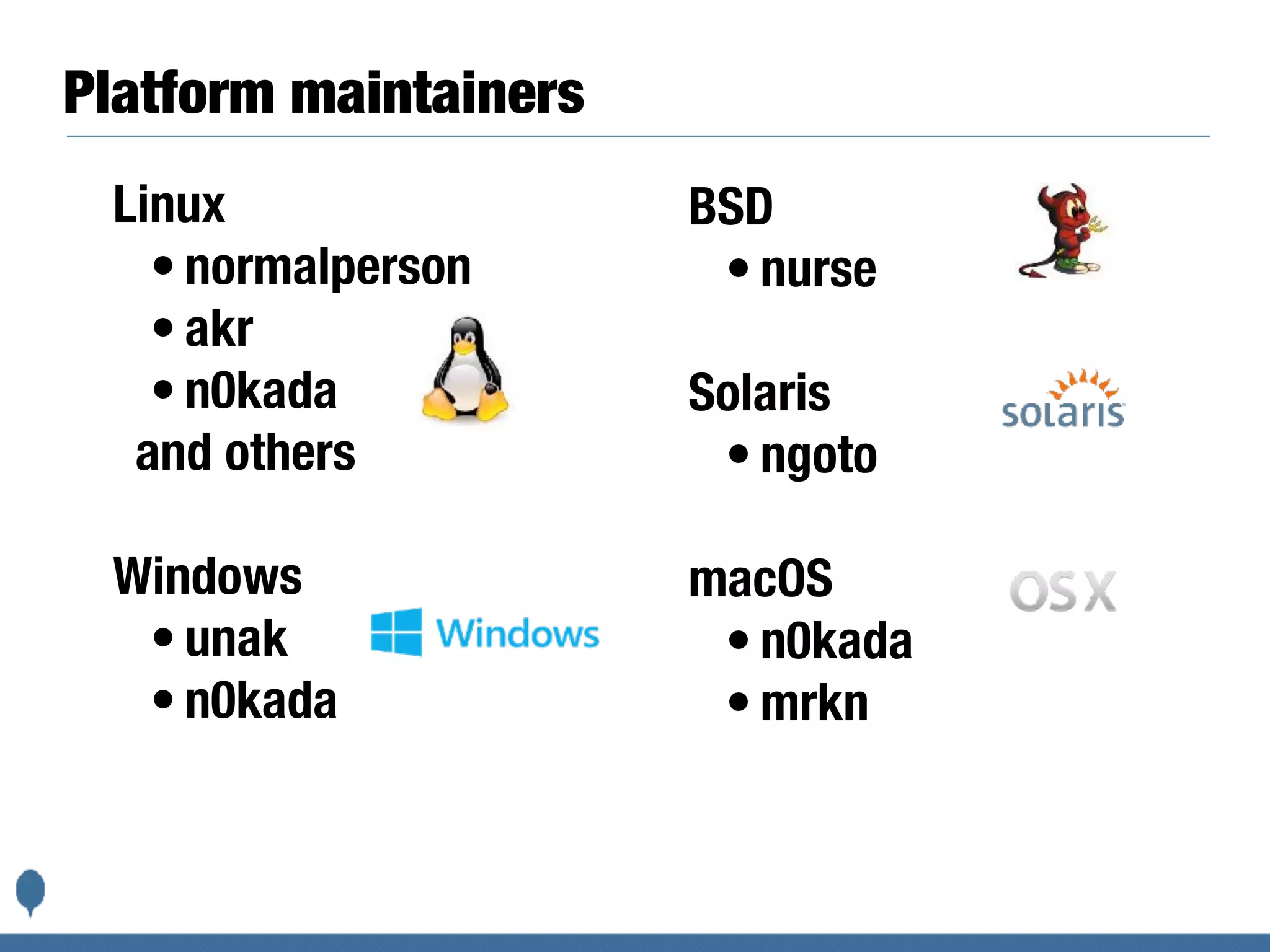
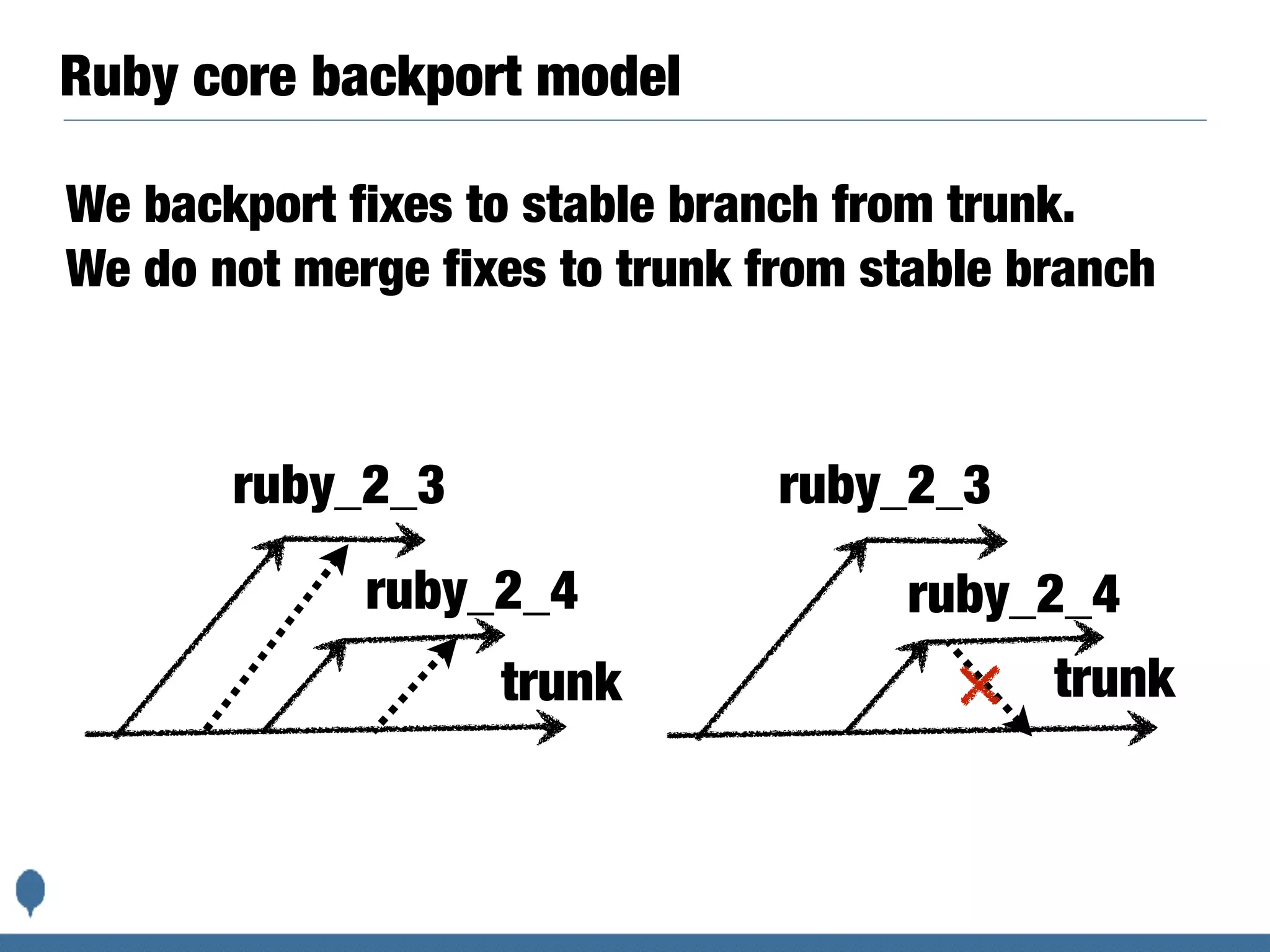
The document discusses how the Ruby programming language is developed and released. It describes the Ruby core team and committers, release cycles, backporting fixes, testing on various platforms via Ruby CI, packaging and distributing releases, handling security issues, and the *.ruby-lang.org domains. It also discusses moving the source code repository from Subversion to Git and migrating development tools and processes.


![self.introduce
=> {
name: “SHIBATA Hiroshi”,
nickname: “hsbt”,
organizations: [“pepabo”, “ruby”, “rubygems”,
“asakusarb”],
commit_bits: [“ruby”, “rake”, “rubygems”, “bundler”,
“rdoc”, “psych”, “ruby-build”, “railsgirls”, “railsgirls-
jp”, …],
sites: [“hsbt.org”, “ruby-lang.org”, “rubyci.org”,
“railsgirls.com”, “railsgirls.jp”],
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20180316-rubyconfph2018-4x3-180316094733/75/How-to-distribute-Ruby-to-the-world-3-2048.jpg)