This document provides an overview of key concepts for understanding HTML and web development, including:
- The Internet is a worldwide collection of computer networks that connects millions of computers, while the World Wide Web consists of linked multimedia documents accessed via the Internet.
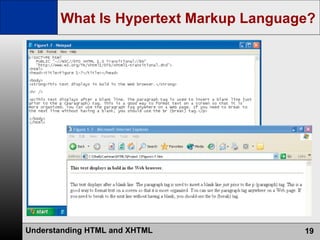
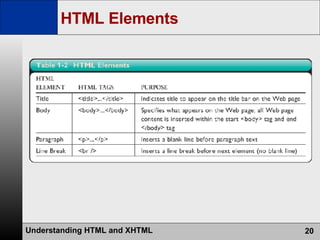
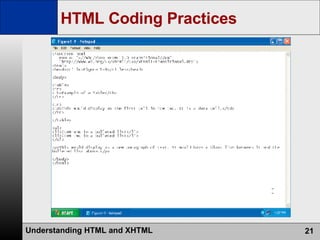
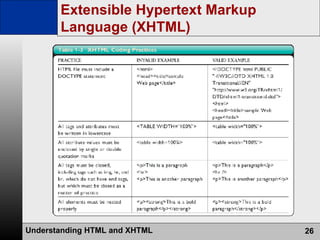
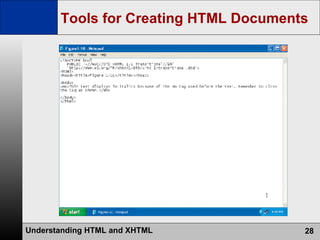
- HTML is the authoring language used to create web pages, which are stored on and served from web servers. Web browsers display web pages to users.
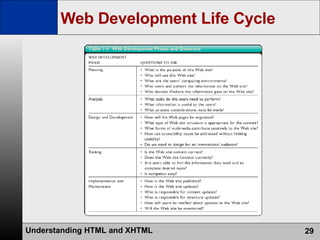
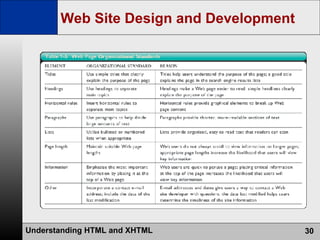
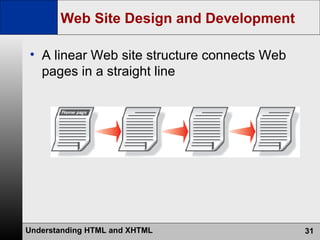
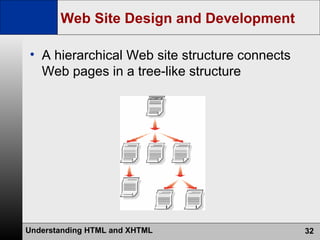
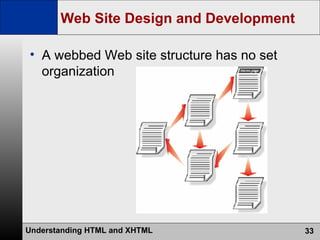
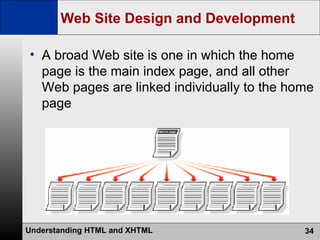
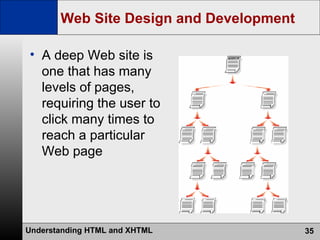
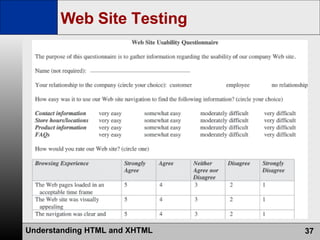
- The web development process involves creating pages using HTML, CSS, and scripts, testing pages, and refining the site structure and design based on a development lifecycle.
- Key topics covered are HTML tags and elements, CSS, DHTML, XHTML, development tools, and usability testing.