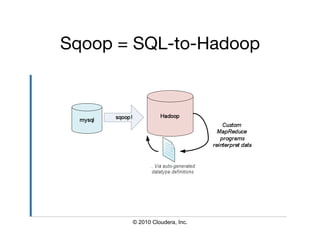
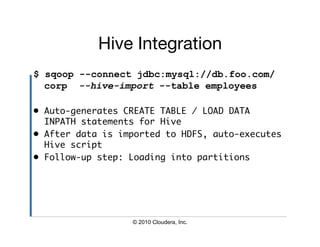
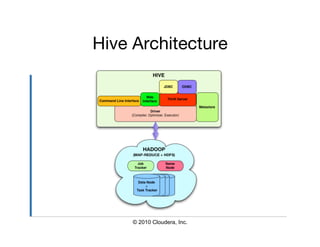
The document provides an overview of Hive, a data warehousing infrastructure built on Hadoop that allows for querying and managing large datasets. It covers its architecture, data models, installation instructions, configuration, and command-line interface functionalities. Hive is open source, supports rapid ad-hoc queries, and is suitable for handling vast amounts of data while providing a high-level querying interface.




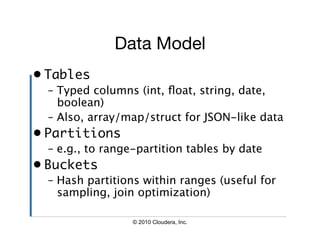
![Column Data Types
CREATE TABLE t (
s STRING,
f FLOAT,
a ARRAY<MAP<STRING, STRUCT<p1:INT,
p2:INT>>);
SELECT s, f, a[0][‘foobar’].p2 FROM t;
© 2010 Cloudera, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hive-user-meeting-march-2010-cloudera-quickstart-100325151728-phpapp01/85/Hive-Quick-Start-Tutorial-7-320.jpg)
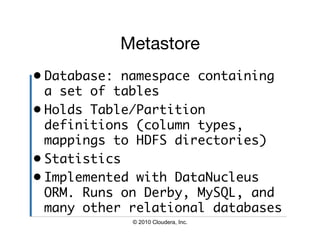










![Hive CLI Commands
• Set a Hive or Hadoop conf prop:
– hive> set propkey=value;
• List all properties and values:
– hive> set –v;
• Add a resource to the DCache:
– hive> add [ARCHIVE|FILE|JAR]
filename;
© 2010 Cloudera, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hive-user-meeting-march-2010-cloudera-quickstart-100325151728-phpapp01/85/Hive-Quick-Start-Tutorial-19-320.jpg)