history
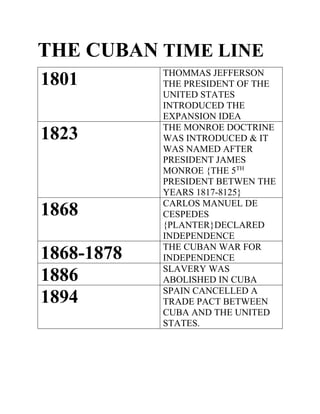
- 1. THE CUBAN TIME LINE 1801 THOMMAS JEFFERSON THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES INTRODUCED THE EXPANSION IDEA 1823 THE MONROE DOCTRINE WAS INTRODUCED & IT WAS NAMED AFTER PRESIDENT JAMES MONROE {THE 5TH PRESIDENT BETWEN THE YEARS 1817-8125} 1868 CARLOS MANUEL DE CESPEDES {PLANTER}DECLARED INDEPENDENCE 1868-1878 THE CUBAN WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE 1886 SLAVERY WAS ABOLISHED IN CUBA 1894 SPAIN CANCELLED A TRADE PACT BETWEEN CUBA AND THE UNITED STATES.
- 2. THE INDIGENOUS PEOPLE {KALINAGOUS, MAYANS, TAINOS} The Taino, Kalinago, and Mayan peoples were some of the most significant indigenous tribes that inhabited the Caribbean and Central America regions. These groups have a rich cultural heritage that still influences the world today. The Tanios were the first indigenous people in the Caribbean, with their civilization originating in the Greater Antilles. They were skilled at farming, hunting, and fishing, using the environment around them to produce food and resources. Their culture was highly organized, with a strong hierarchical structure and a focus on communal values. Taino society was highly religious, with a belief system that combined a reverence for nature, ancestor worship and the worship of spirits known as Zemis. The Kalinago, also known as the Caribs, inhabited the islands in the Lesser Antilles. They were known for their skills in warfare, seafaring, and trading. They lived in communal villages along the coast and were highly respected for their navigational skills.
- 3. The Kalinago's economy was dependent on the cultivation of cassava, a crop that allowed them to survive in difficult environments. They also were skilled craftspeople, producing intricate pottery and woven baskets. The Mayan people were one of the most advanced civilizations in the New World, having resided in modern-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras and El Salvador. They had a complex system of writing, mathematics, art, and science, with a calendar that was more accurate than any used in Europe at the time. Their society was highly organized, with extensive trade networks and a hierarchical class system. The Mayans were known for their impressive architecture, including the towering pyramids and intricate palaces that still draw visitors to the region today. Despite their unique qualities, these three groups shared several commonalities. For example, all three groups were skilled farmers who mastered various farming techniques to sustain their people. Furthermore, they all believed in a spiritual world and had a complex pantheon of gods and other supernatural beings. Finally, they all faced intense scrutiny and colonization by the Spanish Empire in the 16th century, which ultimately led to the decline of their cultures and way of life. In conclusion, the Tanios, Kalinago's, and Mayans were three of the most significant indigenous cultures of the Americas. Their
- 4. rich heritage of language, art, religion and science continue to influence the world today. Although many elements of their cultures were lost over time because of colonization and other external factors, the memory and legacy of these groups remain a treasured aspect of human history. What three qualities was the Kalinago chief expected to possess? To be a religious leader(priest) •To be a warrior •Had to have killed several enemy warriors or at least on Cacique with his bare hands. Three features of the raids which the kalinagos made against the Taino villages.
- 5. Since the Kalinagos were warlike they made better weapons. They made use of bow and arrows. Fire- and poison-tipped arrows were used which was almost fatal to its victim. They also had many types of clubs and spears. •Taino men being killed •Taino woman being taken as slaves and raped to produce children. •Male prisoners were kept as prisoners and tied in a hammock near the roof of the cabet and after several days they were taken down and horribly tortured, those slaves who had the greatest courage were killed and consumed with reverence at religious ceremonies
- 10. The Taino, Kalinago (also known as Caribs), and Mayans are three distinct indigenous groups that developed in different regions of the Americas at different times. Here is some information on each group: The Taino: - The Taino people were one of the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean islands, including Cuba, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, and Hispaniola (which includes the modern-day countries of Haiti and the Dominican Republic). - The origins of the Taino people are not entirely clear, but it is believed that they may have migrated from South America as early as 4000 BCE and flourished in the Caribbean from about 600 to 1500 CE. - Taino homes were typically rectangular in shape and were constructed from wooden poles with thatched roofs made from
- 11. palm leaves. They were often situated near the water, and many Taino villages were built around a central plaza or marketplace. - The Taino people had a complex religion that involved the worship of various gods and goddesses related to nature and fertility. They also engaged in rituals and ceremonies that involved music, dance, and the consumption of a fermented beverage called casabe. The Kalinago: - The Kalinago people were one of the indigenous peoples of the Lesser Antilles in the eastern Caribbean, including modern-day Dominica, Saint Lucia, and Grenada. - The origins of the Kalinago people are unclear, but it is believed that they may have also migrated from South America around 1000 CE. - Kalinago homes were typically round in shape and were constructed from wooden poles with thatched roofs made from palm leaves. They were often situated on hilltops for defensive purposes, as the Kalinago were known to be fierce warriors. - The Kalinago people had a complex religion that involved the worship of various gods and goddesses related to nature and the afterlife. They also engaged in body modifications, such as filing their teeth and tattooing their bodies, as part of their cultural practices.
- 12. The Mayans: - The Mayan people were one of the indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica, which includes modern-day Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and Honduras. - The origins of the Maya are not entirely clear, but it is believed that they may have developed as early as 2000 BCE. Civilization reached its peak in the Classic Period, from about 250 to 900 CE. - Mayan homes were typically rectangular in shape and were constructed from limestone or adobe bricks with thatched roofs made from palm leaves. The Mayans built elaborate cities and temple complexes that were highly developed in terms of art, mathematics, astronomy, and engineering. - The Mayans had a complex religion that involved the worship of various gods and goddesses related to nature, time, and the cycles of the cosmos. They also developed a hierarchical social structure, with priests and rulers occupying the highest positions of power. Overall, each of these indigenous groups developed unique cultures, languages, and ways of life that were shaped by their specific geographic and historical contexts.
- 13. Sure, the Taino people of the Caribbean islands used various natural materials to construct their houses. Some of the most used materials were: 1. Wood - Taino houses were primarily constructed by using wooden poles for support and framing. The poles were sometimes covered with woven straw or reeds to form walls. 2. Leaves - Large leaves, such as the fronds of the palm tree or banana leaves, were used to create thatched roofs for Taino homes. 3. Mud and Clay - The Taino people also used cured mud and clay to create walls for their homes. After being mixed with water and dried, the mud walls provided both insulation and protection from the elements. 4. Stone - Taino homes were often built with stones, especially in areas that were more prone to natural disasters such as hurricanes. The stones were stacked to make walls, and in some cases, were used to create foundations for the homes.
- 14. RESISTANCE AND REVOLTS BIRBICE REVOLT {1763} LEADRER: COFFY {AN AFRICAN BORN SLAVE} CAUSES- * THE HARSH TREATMENT THE SLAVES RECIEVED FROM THE WHITES/ PLANTERS * THE WANTED A PLACE WHERE THE COULD LIVE IN FREEDOM. Berbice was a "death trap" for European soldiers. Nevertheless, the Dutch prevailed due to the rebels' inability to access global trade, European fire power and supplies, dissension among the rebels, and support from Amerindian.
- 15. Why did the Berbice Revolt fail? Answer and Explanation: The Berbice Revolt failed due to divisions among the rebels and a failure to seize on momentum. In February of 1763, a slave revolt began on the Magdalenenburg plantation in Berbice (Dutch Guyana), and this caught the outnumbered white minority and Dutch government by surprise. BARBADOS REVOLT/ BUSSA REVOLT 1816 LEADERS: BUSSA JACK & FRANKLIN CAUSES- *MISINTERPRETATION OF THE REGISTRATION BILL *ACTIVITIES OF THE NON- CONFORMIST CHURCH
- 16. * DESIRE OF FREEDOM *HARSH TREATMENTS RECEIVED FROM THE WHITE PLANTERS EFFECTS- * ECONOMIC: DISTRUCTION OF CANEFIELD AND ESTATE * SOCIAL- DEATHES {144 ENSLAVED AFRICANS DIED, INCLUDING BUSSA AND 1 WHITE DIED ALSO} OUTCOME:214 PERSONS WERE EXECUTED AND 100 EXITED TO SIERRA LEONE. THE MISSIONARIES WERE PERSECUTED AND CHAPELS WERE DAMAGED. HAITIAN REVOLUTION 1791 LEADER- TOUSSAINT LOUVETURE
- 17. Who were the leaders of the revolution in Haiti? Napoleon sent General Charles Leclerc to overthrow him and restore French rule, but Haitians, led by Jean-Jacques Dessalines and Henry Christophe, prevailed over the French, and Dessalines declared Haiti independent in 1804. CAUSES THE MULATOES FUSTRATED ASPIRATIONS ,THE BRUTALITY OF SLAVE OWNERS AND THE INSPIRATION OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION. CONSEQUENCES- First, the warfare of the Haitian Revolution destroyed the capital and infrastructure of the economy. Second, Haiti lacked diplomatic and trade relations with other nations. Third, Haiti lacked investment, both foreign and domestic investment. THE CHRISTMAS REBELLION 1831
- 18. IT TOOK PLACE ON THE KESINGTON ESTATE IN ST. JAMES LEADER SAMUEL SHARP CAUSES- *SLAVES BELIEVED THAT EMANCIPATION WAS BEING WITH HELD * THE SALVES WANTEND TO BE PAID FOR THEIR LABOUR ON THE PLANTATION *THE ACTIVITIES OF THE NON- CONFORMIST CHURCH OUTCOME- *DURING THE REBELION 100 SLAVES WERE KILLED ALONG WITH 10 WHITES *AFTER THE REBELLION 100 SLAVES WERE EXECUTED ALONG WITH SAMUEL SHARP
- 19. *ANOTHER 100 SLAVES WERE FLLOGED * THE CAHPELS WERE DISTROYED MISSIONARIES: WILLIAM KNIBB, BURCHELL & PFEIFFER THE DEMERAR REVOLT 1823 CAUSE- Poor treatment, (mistaken) belief that Parliament had emancipated the slaves CONSEQUENCE - *The largely non- violent rebellion was brutally crushed by the colonists under Governor John Murray. They killed many slaves: estimates of the toll from fighting range from 100 to 250. After the insurrection was put down, the government sentenced another 45 men to death, and 27 were executed.
- 20. RESON FOR THE FAILURE OF THE REVOLT: Large numbers of Christian slaves refused to rebel and helped suppress those who rose. Other enslaved people confronted their owners and the military forces sent against them. The name of two enslaved women who were leaders of revolts in the Caribbean- * * why planters regarded women as being the fiercest, most troublesome, and ungovernable of all enslaved people? * Because they would often kill their unborn children to avoid the white's bloodline * Some would rather sleep with whites just so their children could be free.
- 21. *They were scheming like women today
- 23. US AND CUBA History Group Essay- Examine Five Policies of the Castro Revolution 1959-1962 and explain how each impacted Cuba. Introduction
- 24. The Castro Revolution of 1959-1962 had policies such as political economic and social policies that made a great impact on the Cuban Society both positively and negatively. Economic policies can be defined as a country setting levels of taxation, budgets and such in a country's economy. Social policies are the term given to government policies, actions, programs or initiatives that are intended to improve upon social problems The US had interest in Cuba because of their geographical location which was south of Florida, and it could hold a military base that could protect USA back yard. They also had investments in Cuba such as: railways, mining, tobacco and sugarcane factories. During Batista’s rein as president of Cuba
- 25. he indulged in corruption which in most instances didn’t benefit the people of Cuba. In such instances was him giving USA the power to intervene in Cuba’s relations. Hence, nationalism encouraged many like Castro to fight against capitalism and US. In the process getting rid of Batista’s regime. Throughout this essay five main points will be discussed- Give five ways/policies of the Castro revolution 1959-1962 and how they impacted Cuba. 1. Land Reform - Economic 2. Health care- Social 3. Education- Social. 4. Housing- Social. 5. Nationalism- Economic 6. Getting rid of capitalism and turning the economic into a communist country
- 26. ◦ Body Of Essay There was a band in large scale private land holding. The government seized large landholdings owned by wealthy landowners and redistributed them to landless peasants. The goal was to create a more equitable distribution of land and reduce the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few. The impact of land reform was significant, as it provided many peasants with access to land, which allowed them to become self-sufficient and earn a living through agriculture. However, the reform also had some negative consequences, such as the displacement of some landowners and the disruption of the agricultural sector. Healthcare was another area of reform, and the Castro government invested heavily in
- 27. building a comprehensive healthcare system. The government established hospitals, clinics and trained medical personnel. The result was a significant improvement in the health of the population, particularly in rural areas, where access to healthcare was limited. The impact of the healthcare system was significant, as it provided access to quality healthcare to all Cubans, regardless of their income. Education was also a key area of reform, and the government invested heavily in providing access to education to all Cubans. The government established schools and universities and provided free education to all citizens. The result was a significant increase in literacy rates and the development of a highly educated
- 28. workforce. The impact of the education system was significant, as it provided access to education to all Cubans, regardless of their income. Housing was another area of reform, and the government implemented policies to provide affordable housing to all Cubans. The government-built thousands of new housing units and implemented policies to make homeownership accessible to all. The impact of the housing policies was significant, as it provided affordable housing to many Cubans who were previously living in substandard conditions. Nationalism was a key component of the Castro Revolution, and the government implemented policies to promote Cuban
- 29. culture and identity. The government promoted the use of the Spanish language and the celebration of Cuban traditions and holidays. The impact of nationalism was significant, as it helped to create a sense of unity and pride among the Cuban people. The Castro government also implemented policies to move towards socialism and get rid of capitalism. The government nationalized many industries, including sugar, tobacco, and mining, and implemented policies to promote collective ownership and control of the means of production. The impact of these policies was significant, as it led to the creation of a more socialist economy and reduced the influence of foreign corporations in Cuba.
- 30. In conclusion, the Castro Revolution of 1959-1962 brought about significant changes in Cuba, impacting various aspects of Cuban society. The reforms implemented in land reform, healthcare, education, housing, nationalism, and the move towards socialism had both positive and negative consequences, but overall, they helped to create a more equitable and just society in Cuba. The revolution left a lasting impact on Cuba, shaping the country's history and identity Answer ONE question only from this section. All essays in this section must be well developed with a clear introduction and conclusion. Points must be supported
- 31. with relevant details and examples. Marks will be awarded for good organization and correct grammar, spelling and punctuation. Theme 7 – The United States in the Caribbean, 1776 - 1985 Question 7 Examine FIVE ways in which USA impacted Cuba up to 1959. Include economic, social and political impact. Total 25 marks Introduction Hypothesis/ Thesis Statement – United States intervention into Cuba had both
- 32. negative and positive impact socially, politically and economically up to 1959. Background information – Reasons for USA intervention in the Caribbean (Manifest Destiny, Setting up of naval bases, investments and trading) Definition of key terms – social, economic and political Points to be discussed Positive impact 1st point USA invested in Cuba’s sugar, mining and tourism industry creating employment. (Economic)
- 33. 2nd point USA implemented programs to deal with sanitation and health care (social) Negative Impact 3rd point Tourism especially in Havana caused increase in crime and violence (gambling, prostitution, theft) (social) 4th point The introduction of the Platt Amendment that curtailed political activities to some extent. 5th point Using Cuba’s land for military bases in Guantanamo Bay (political) Body of Essay
- 34. 1st point USA invested in Cuba’s sugar, mining and tourism industry creating employment. (Economic) Give supporting information showing the prosperity of the sugar, mining and tourism industry and how each benefitted Cuba economically. 2nd point USA implemented programs to deal with sanitation and health care (social) Give supporting information on programs to deal with sanitation and health care and how they benefitted Cuba socially.
- 35. 3rd point Tourism especially in Havana caused increase in crime and violence (gambling, prostitution, theft) (social) Give supporting information on how gambling, prostitution, theft among others affected the Cubans negatively and socially. 4th point the introduction of the Platt Amendment that curtailed political activities to some extent. Give supporting information by outlining the clauses of the Platt amendment and explain how they affected the Cubans.
- 36. 5th point Using Cuba’s land for military bases at Guantanamo Bay. Give supporting information by outlining the reasons for the military bases and how they affected Cuba. Conclusion Synopsis of entire essay.