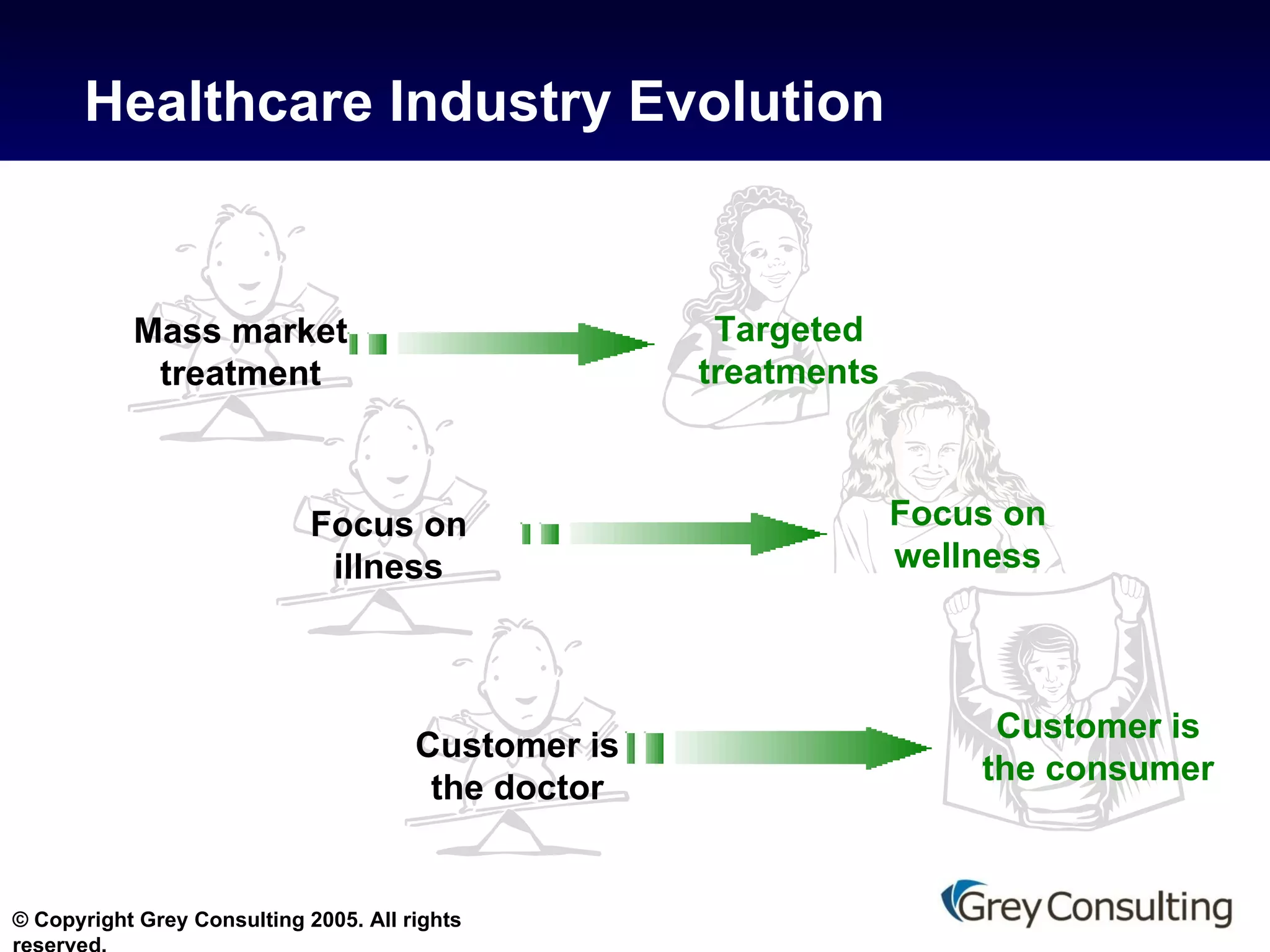
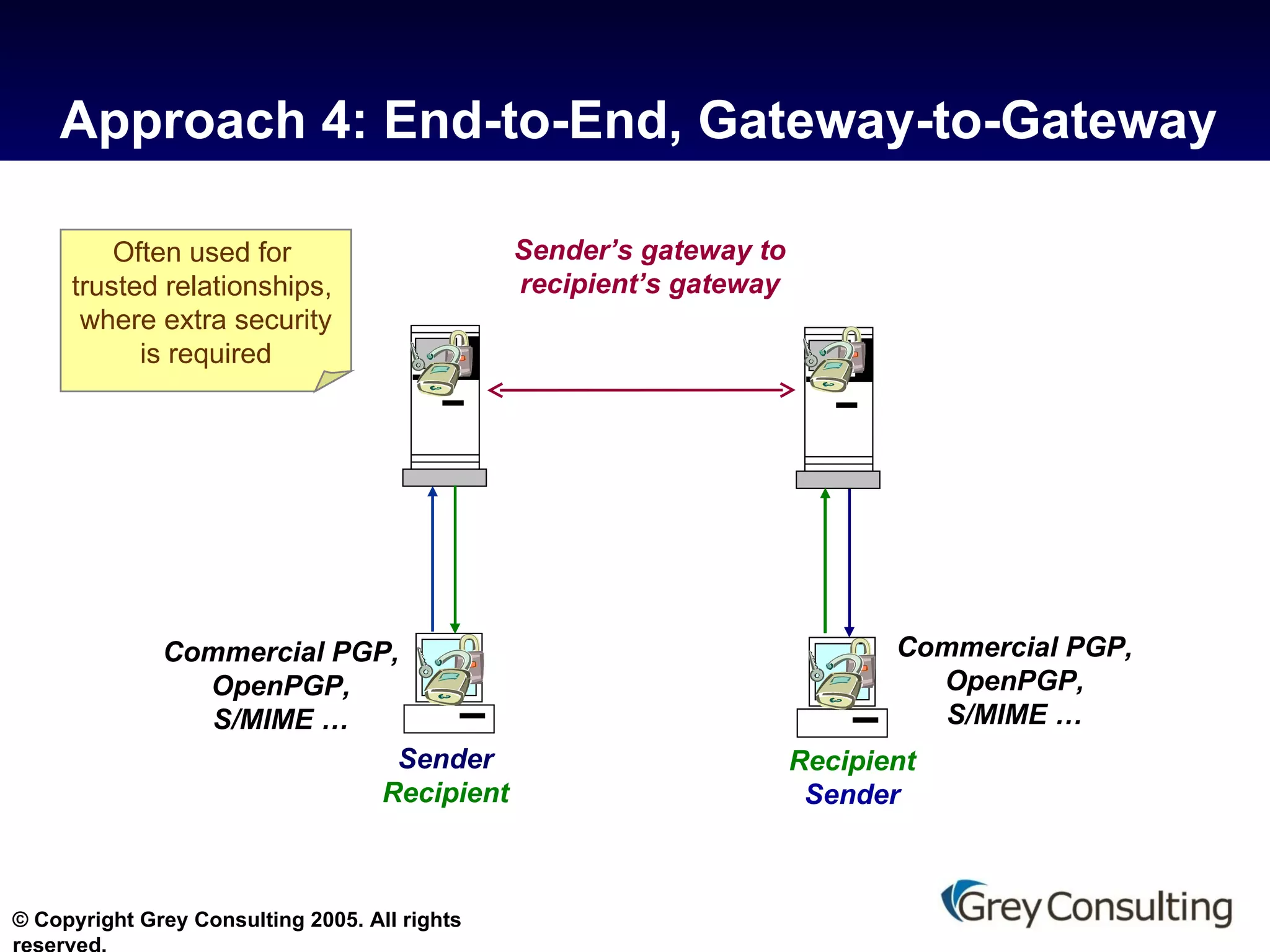
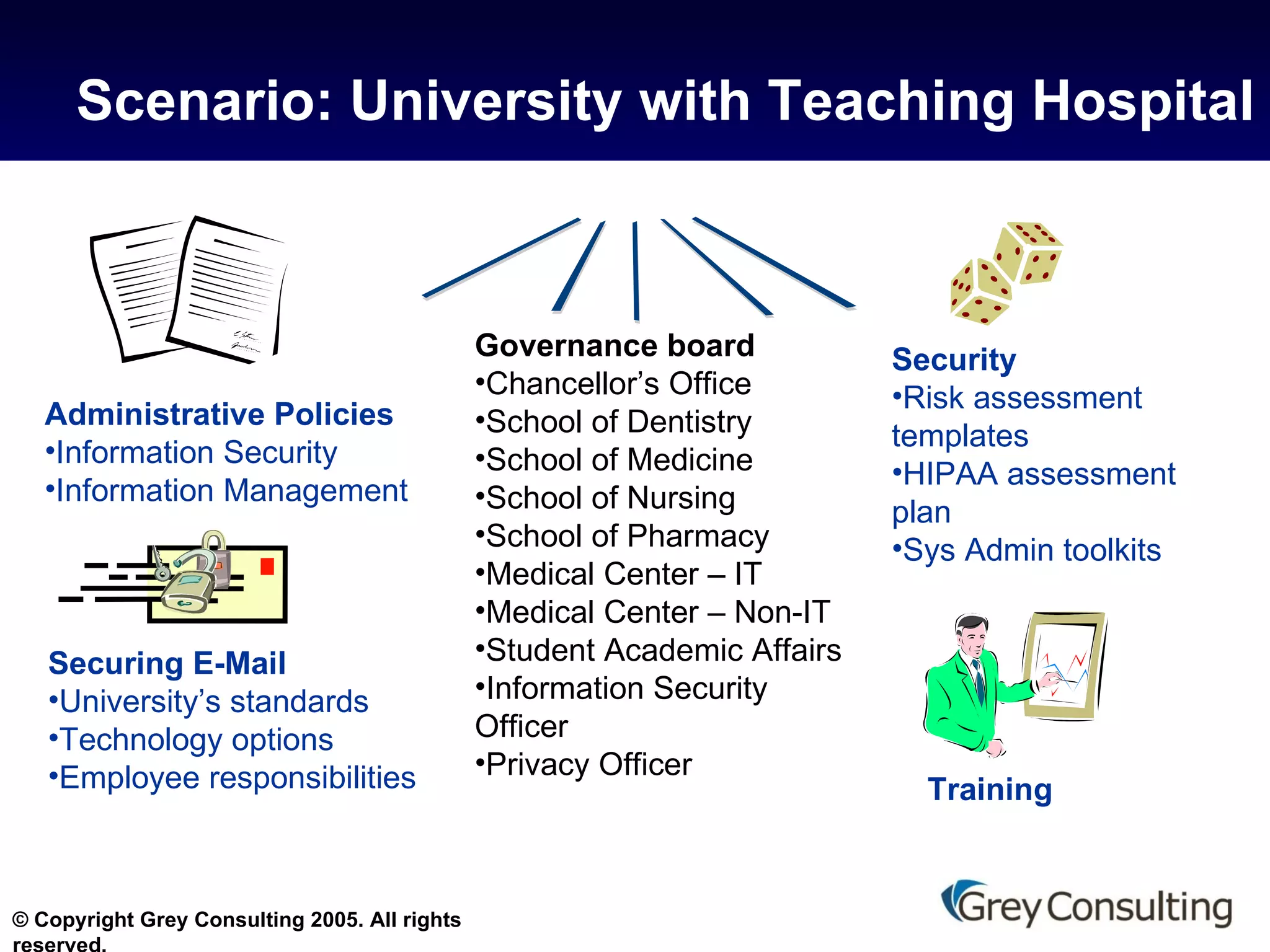
The document discusses the evolving role of email and messaging in healthcare, emphasizing compliance with HIPAA regulations and protecting patient health information (PHI). It outlines best practices for healthcare providers, including technology recommendations and employee training to enhance security and privacy. The document also highlights the need for continuous vulnerability assessments and the appointment of a privacy officer to ensure adherence to regulations.









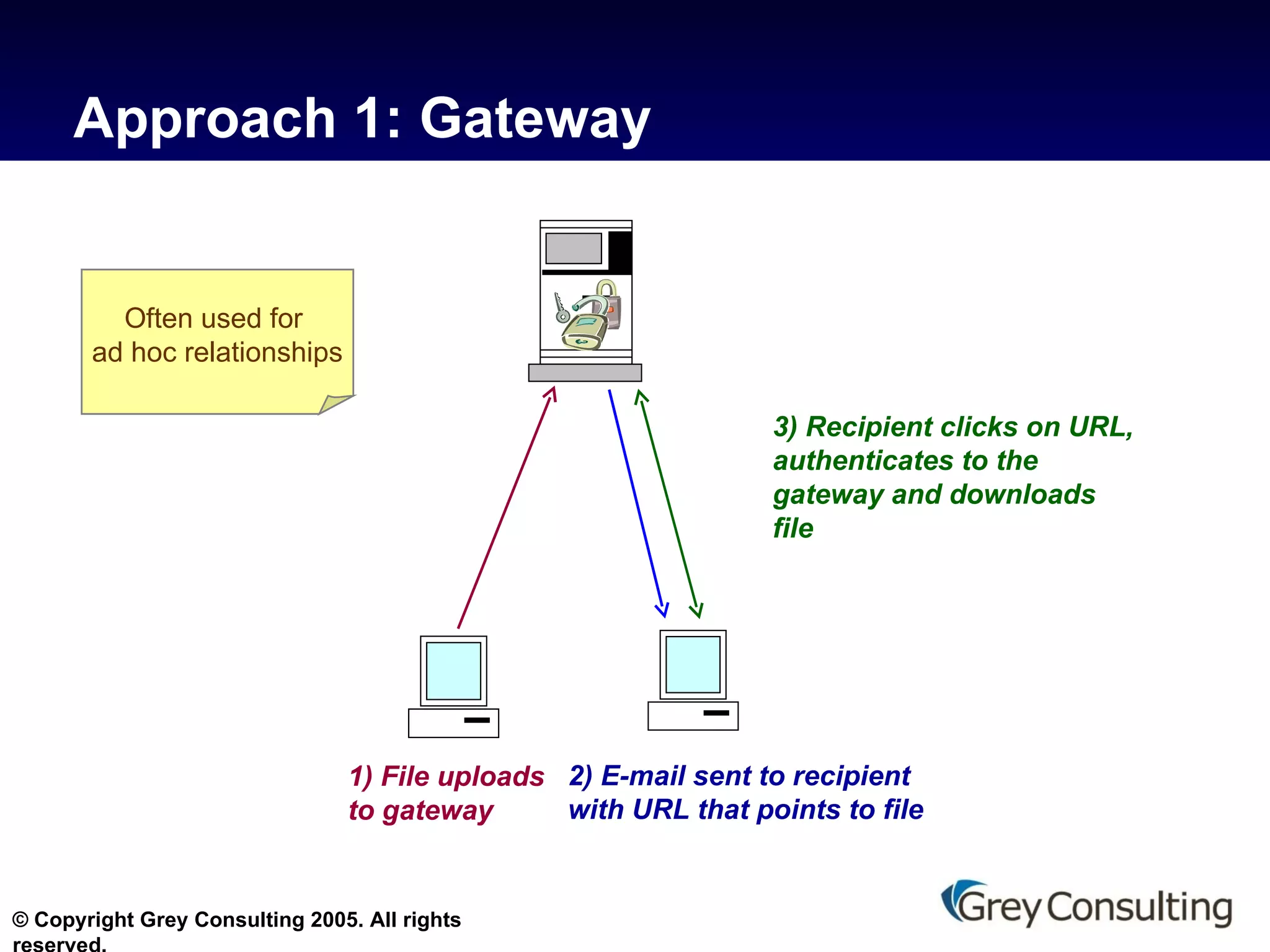
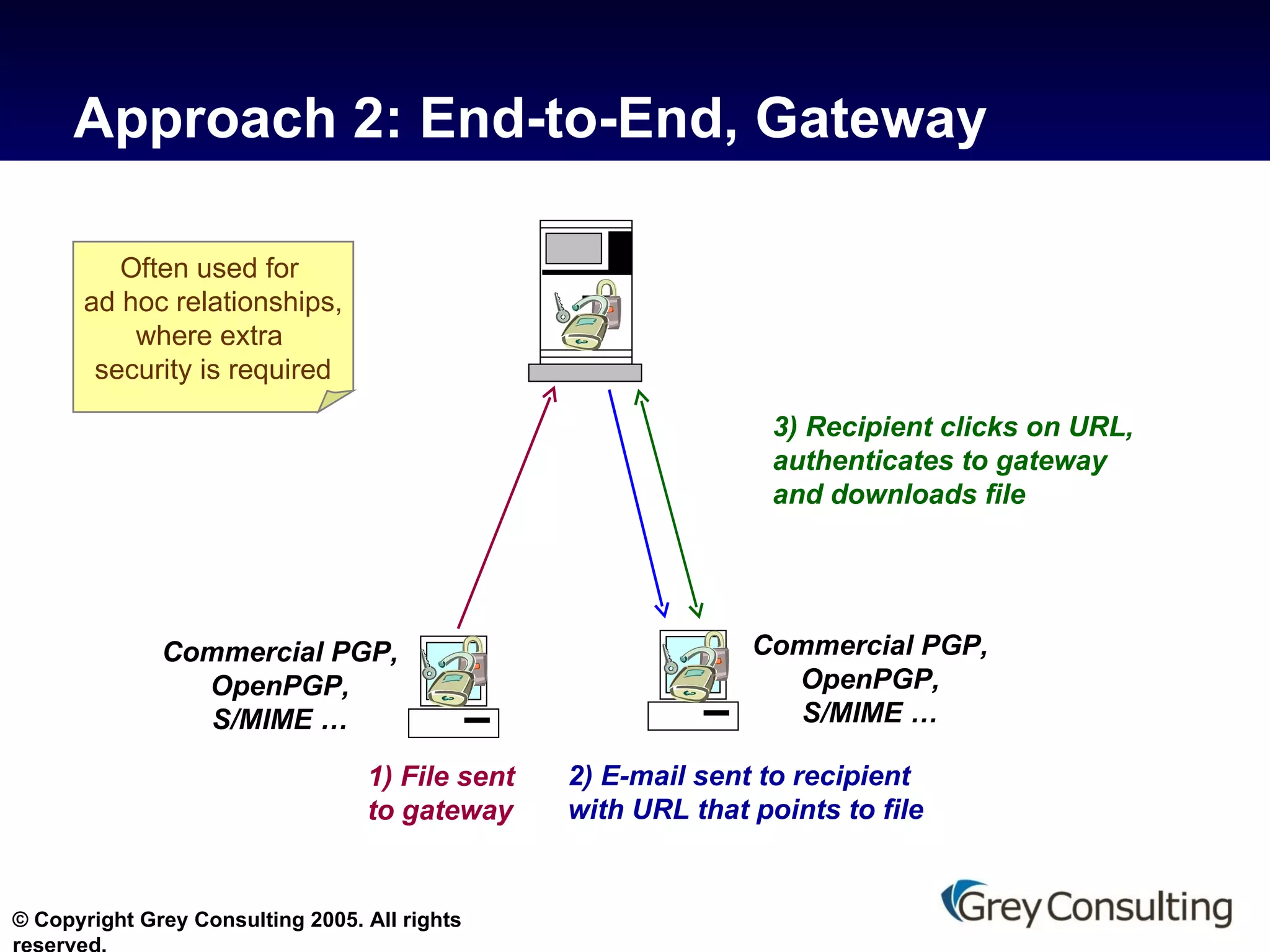
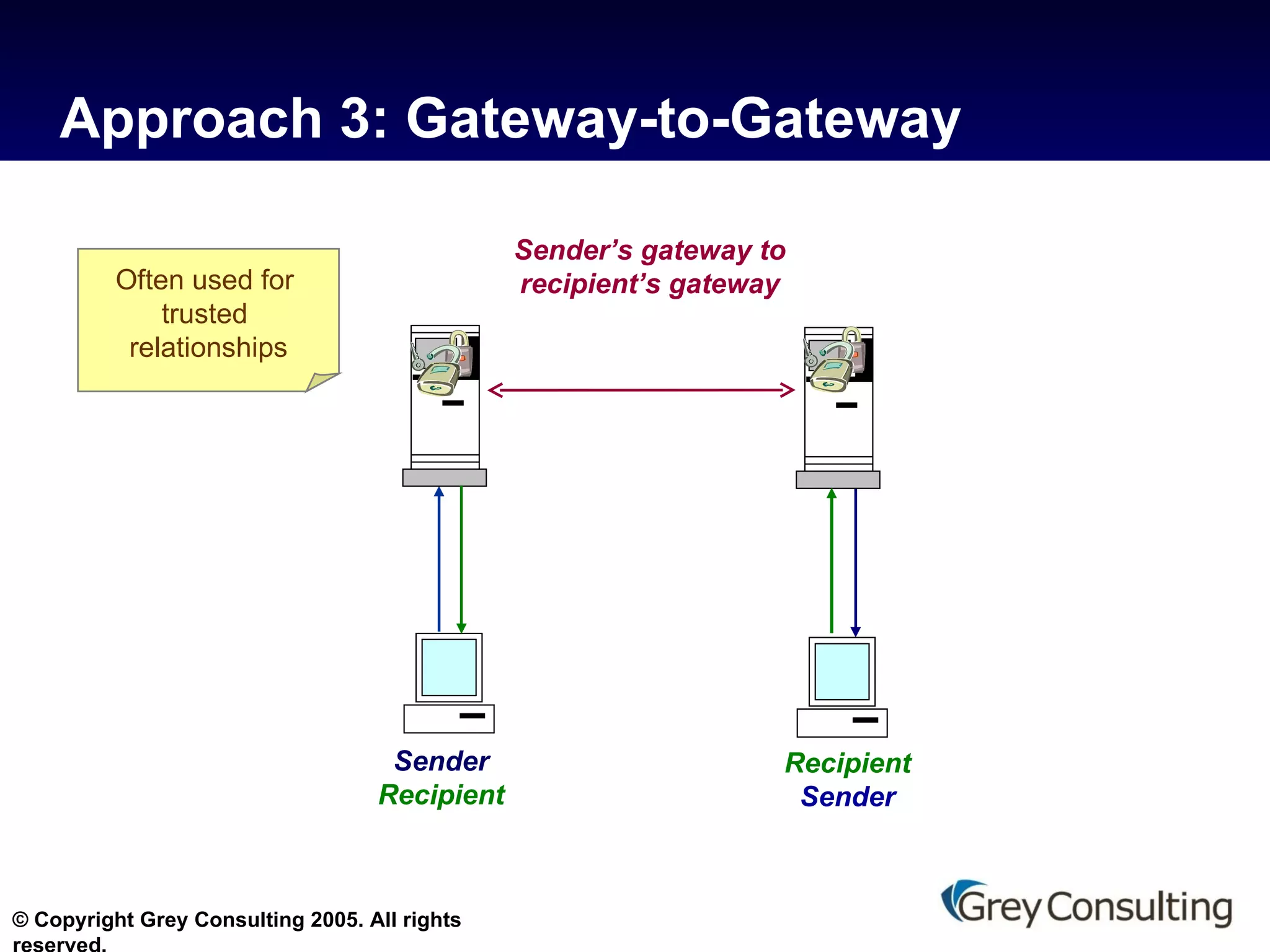


![For further information on this topic, contact Grey Consulting [email_address] 845.531.5050 www.grey-consulting.com making messaging and collaboration work](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hipaa-and-email-protecting-phi-10856/75/HIPAA-and-E-Mail-Protecting-PHI-18-2048.jpg)