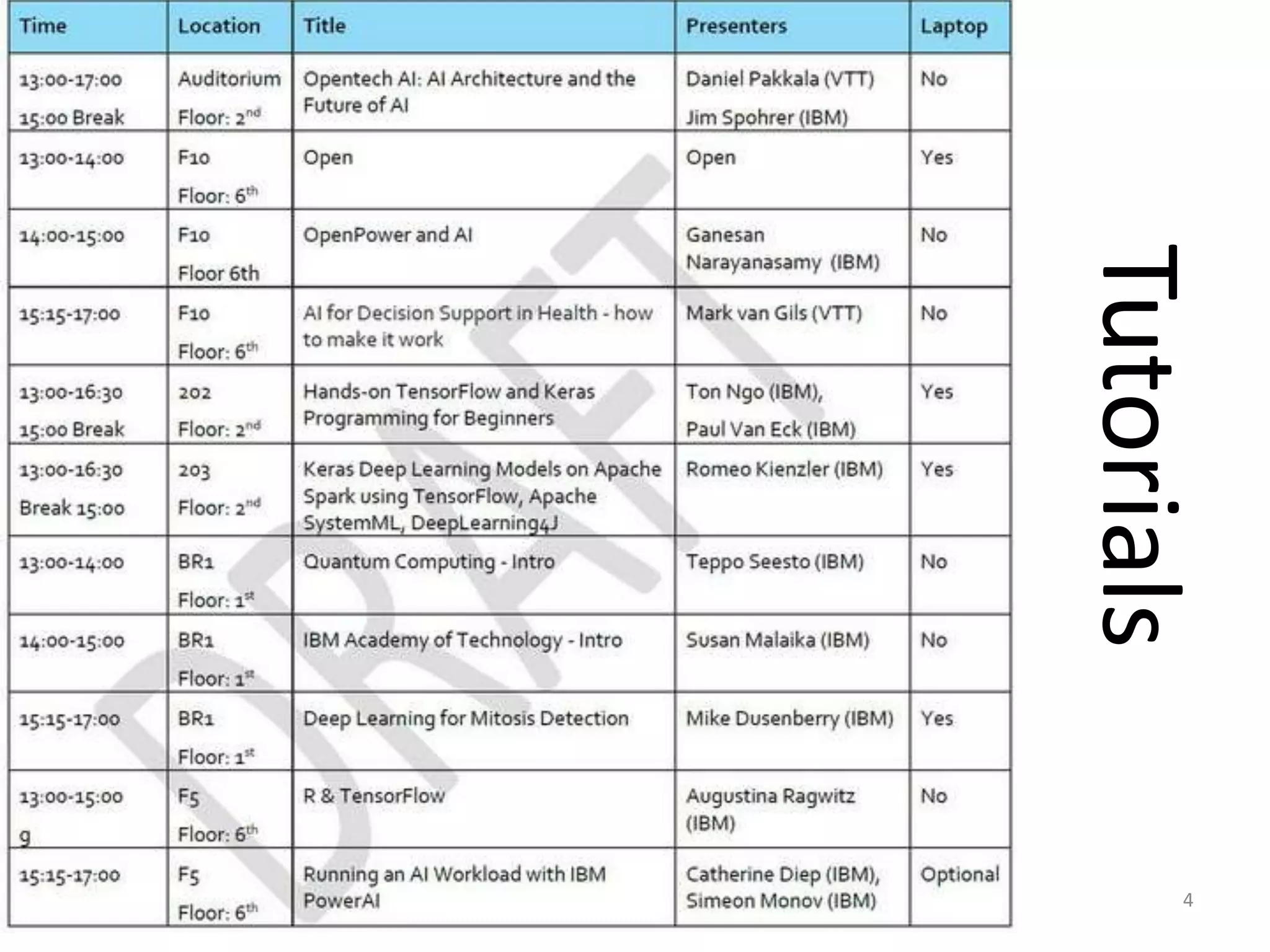
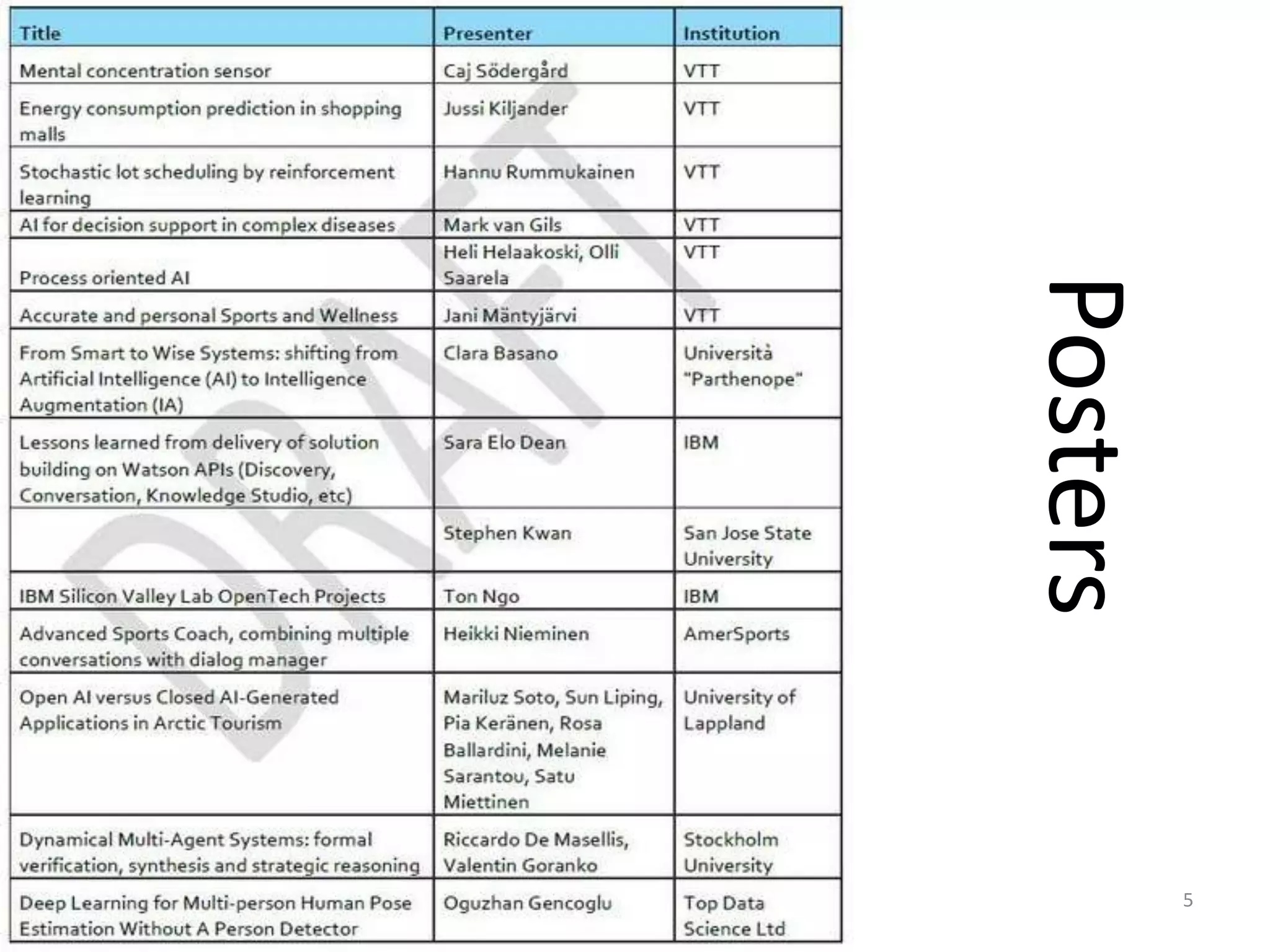
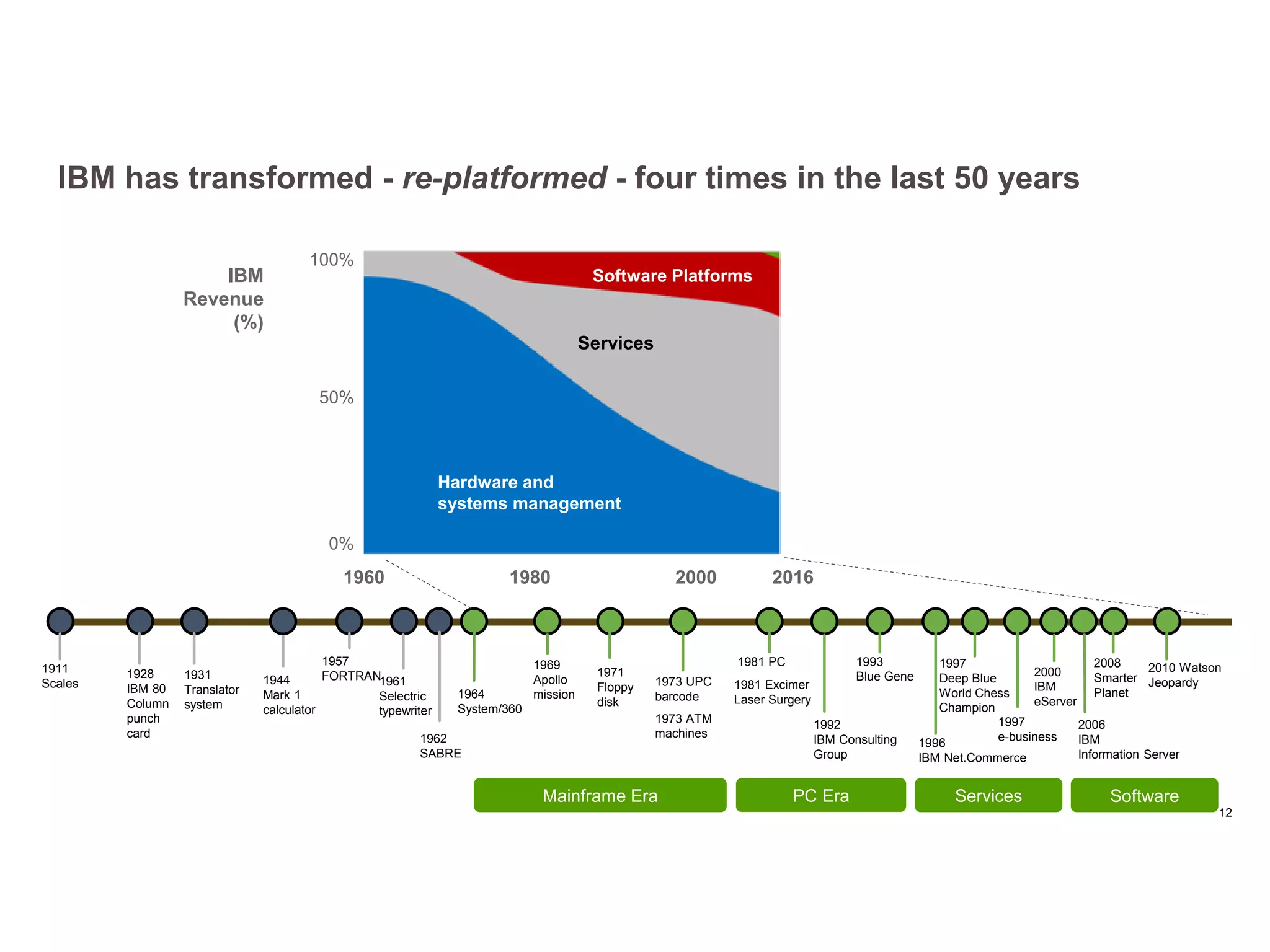
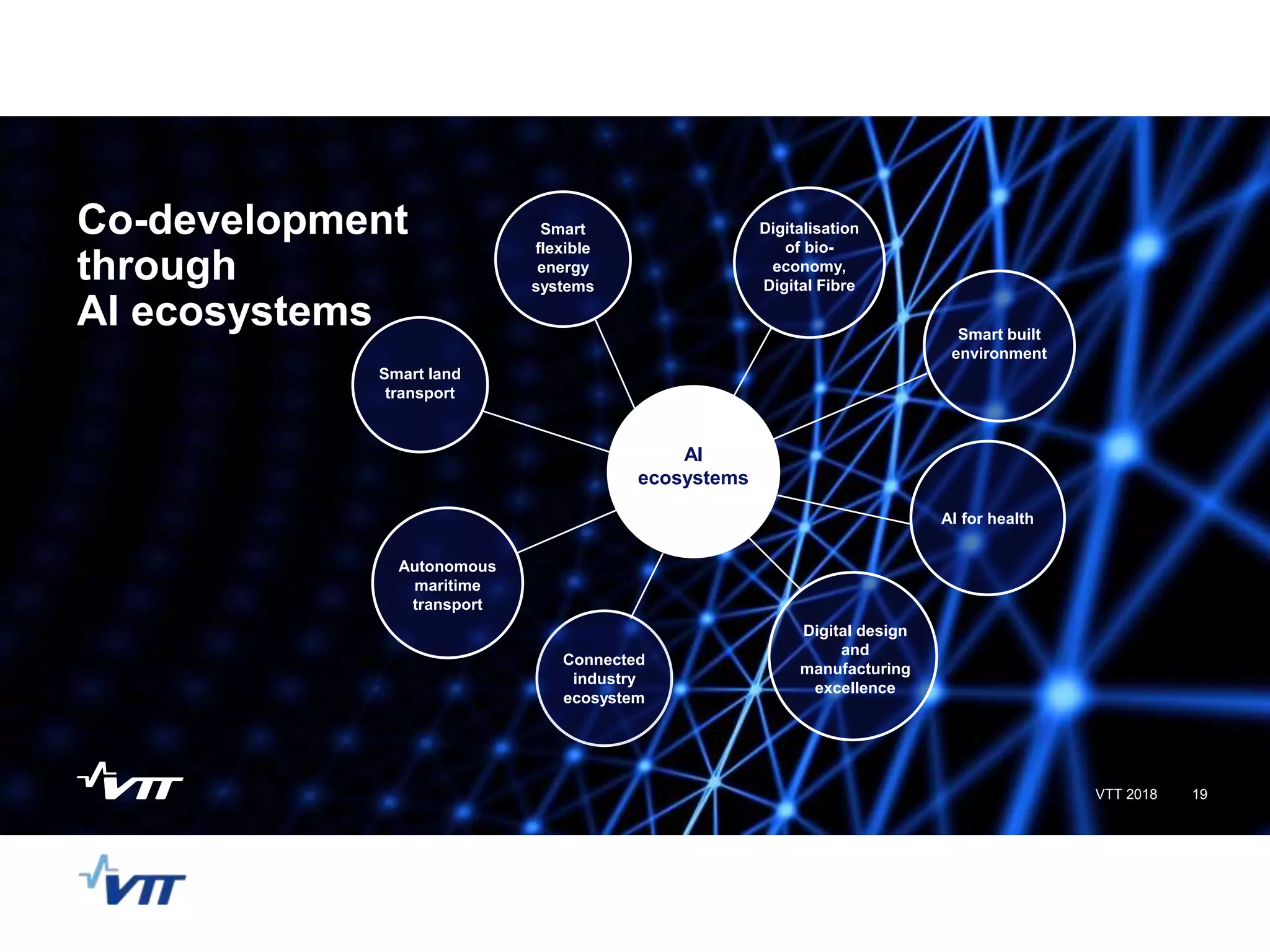
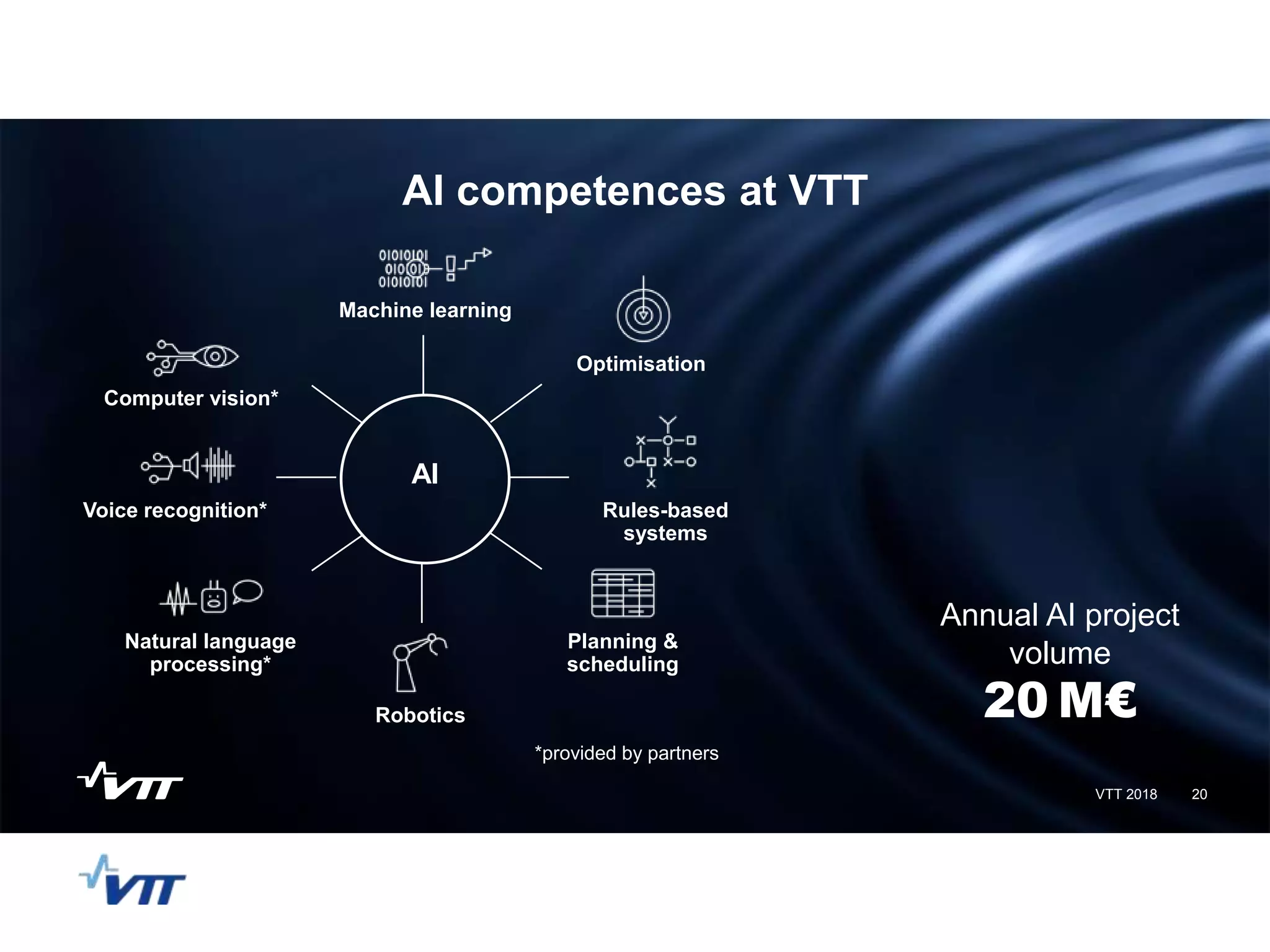
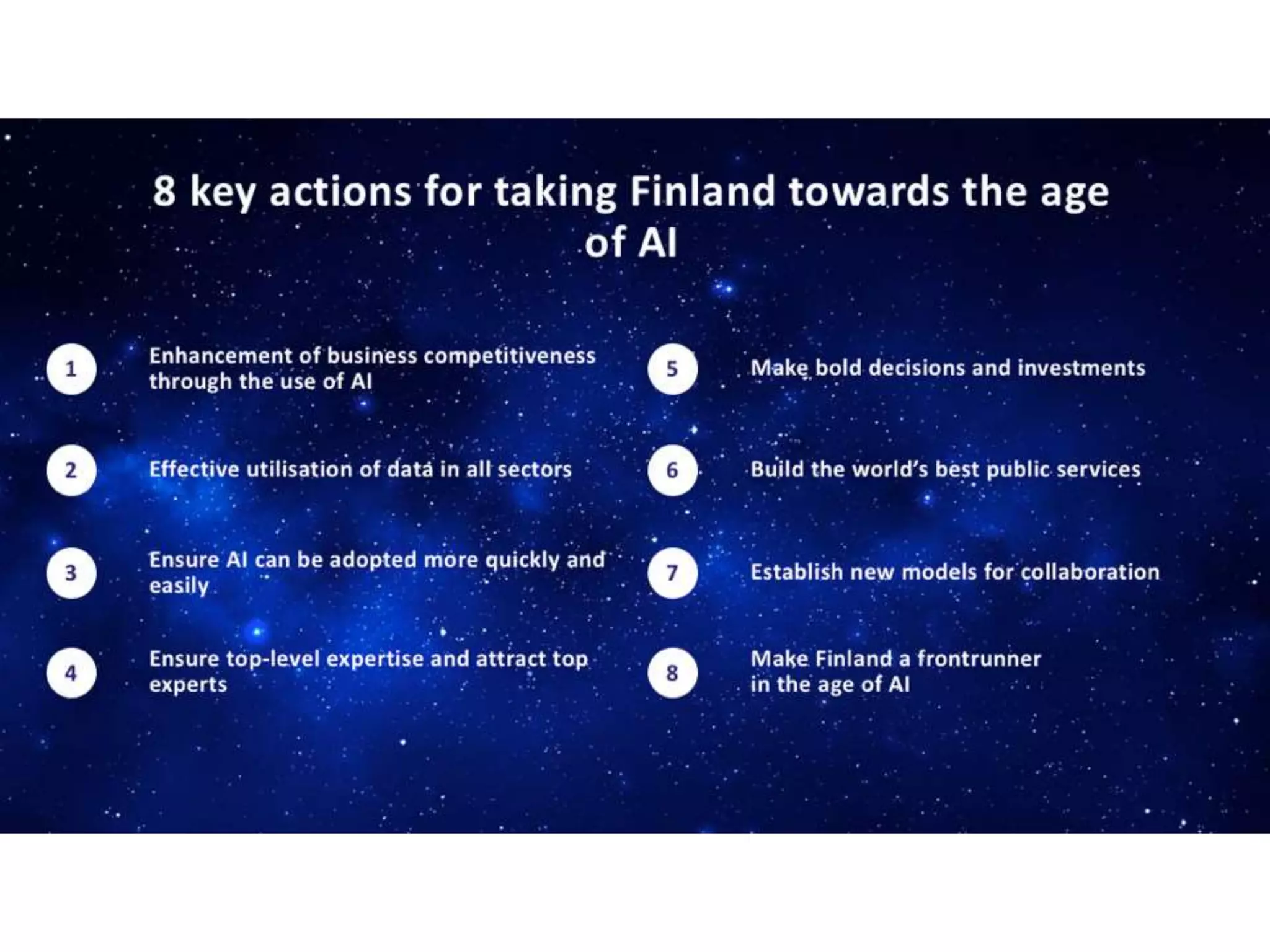
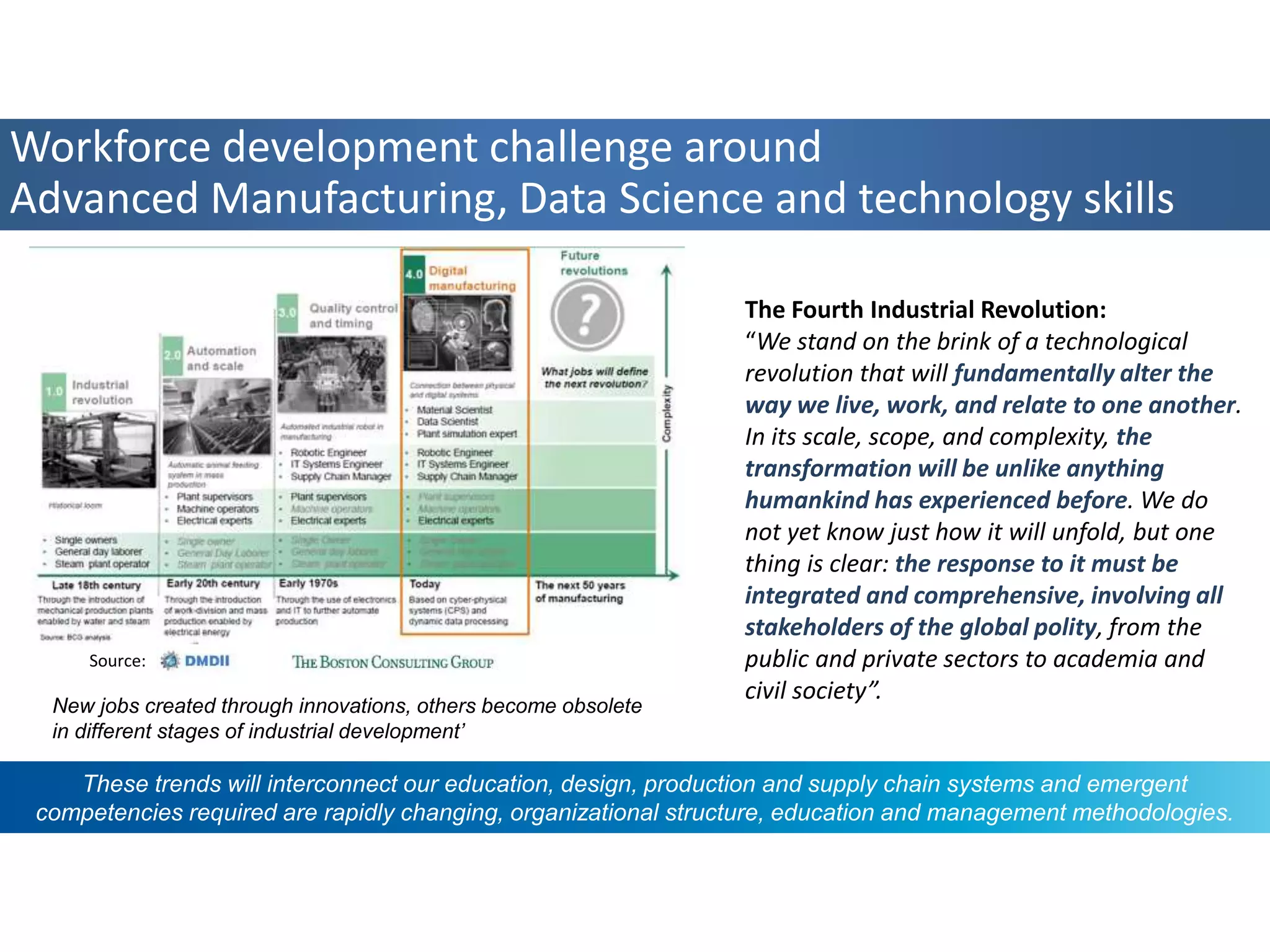
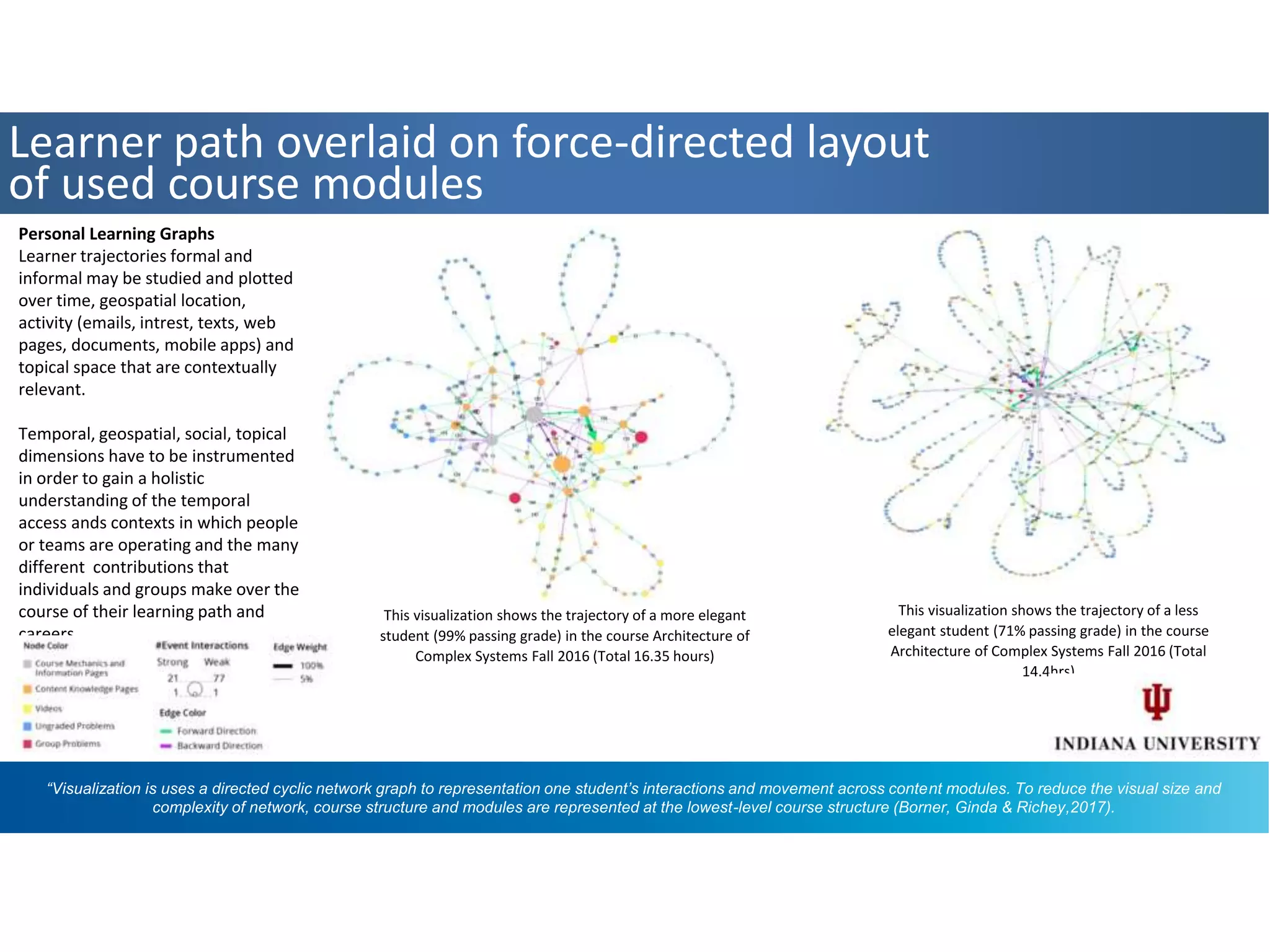
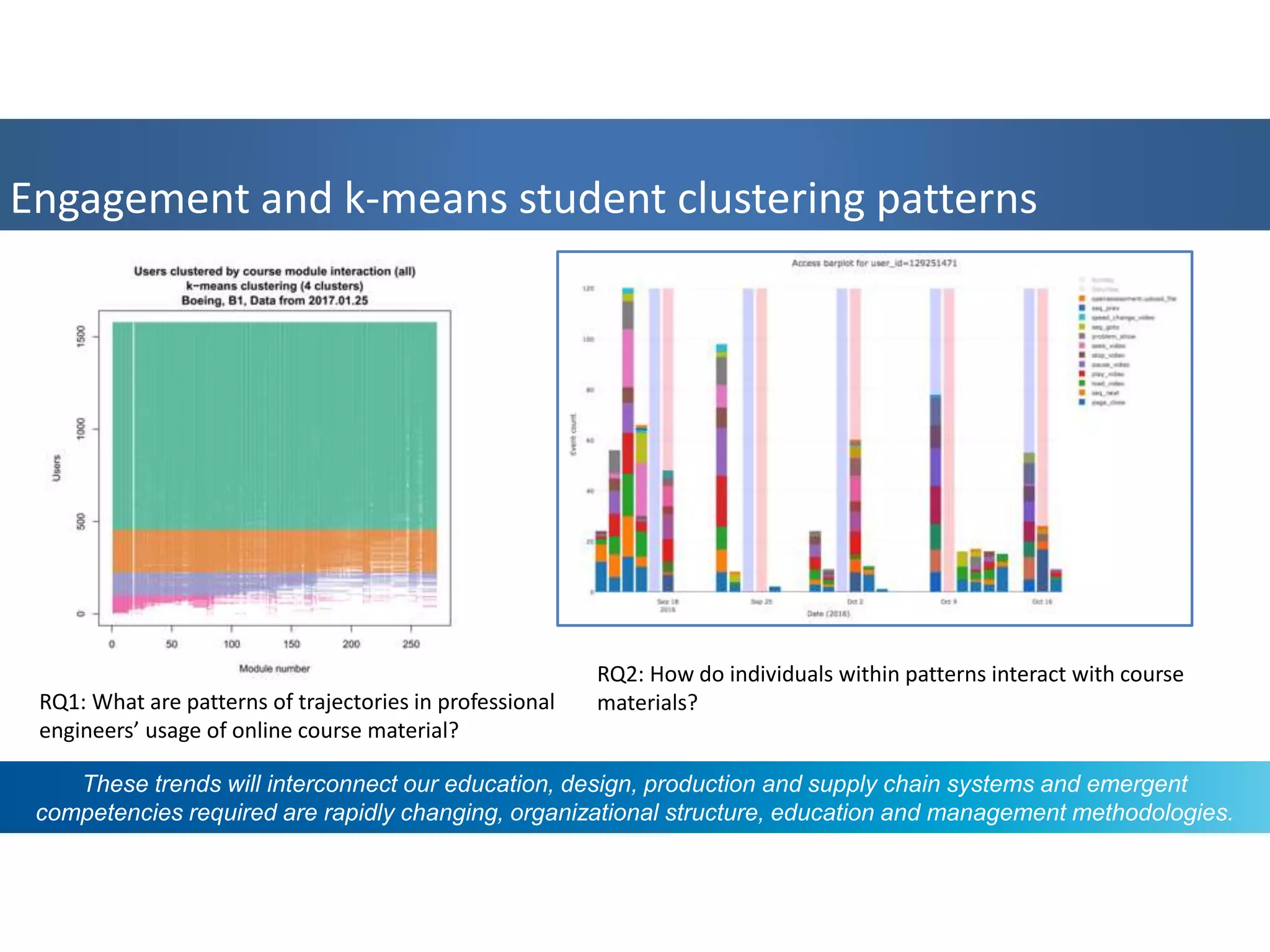
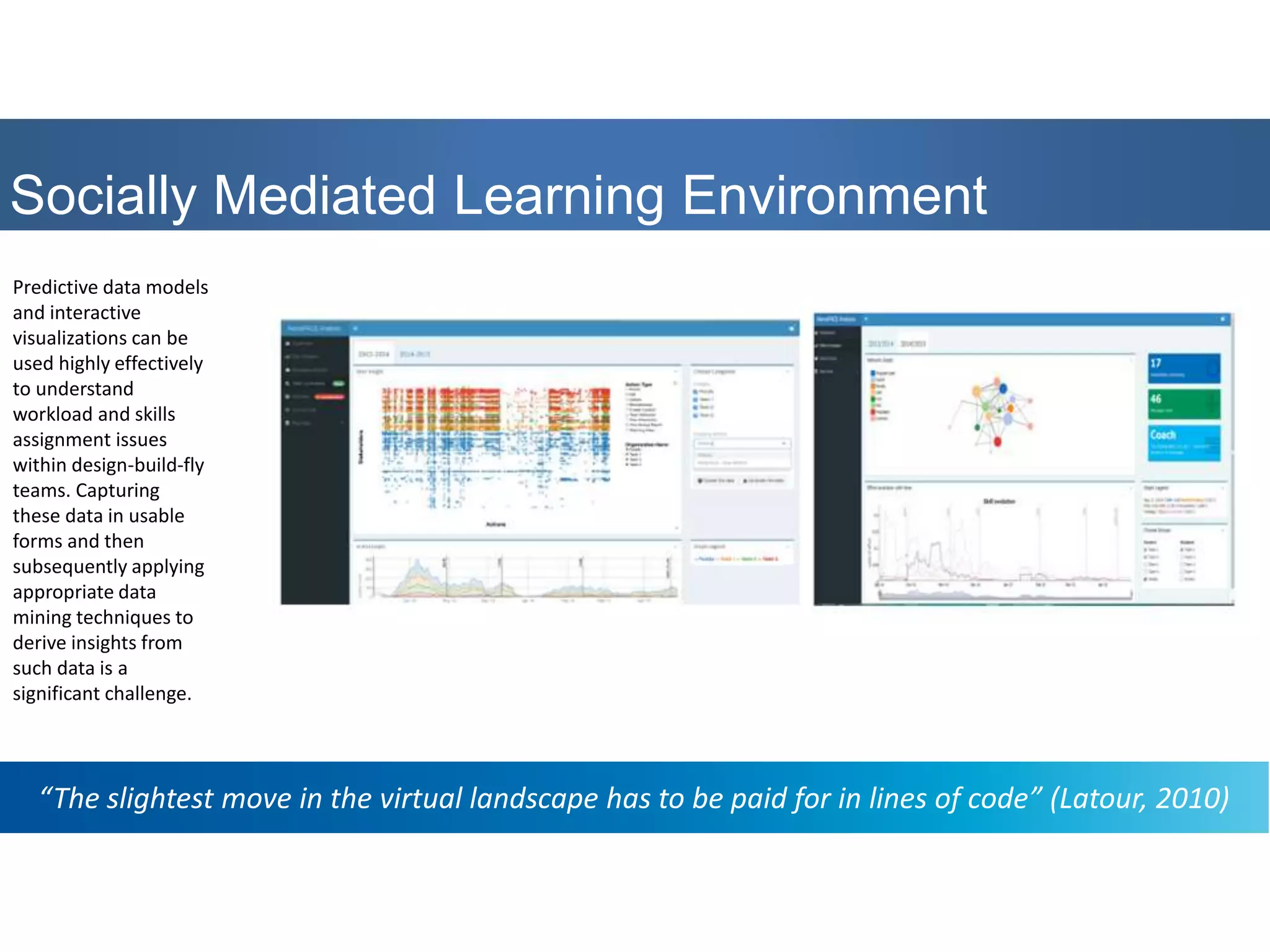
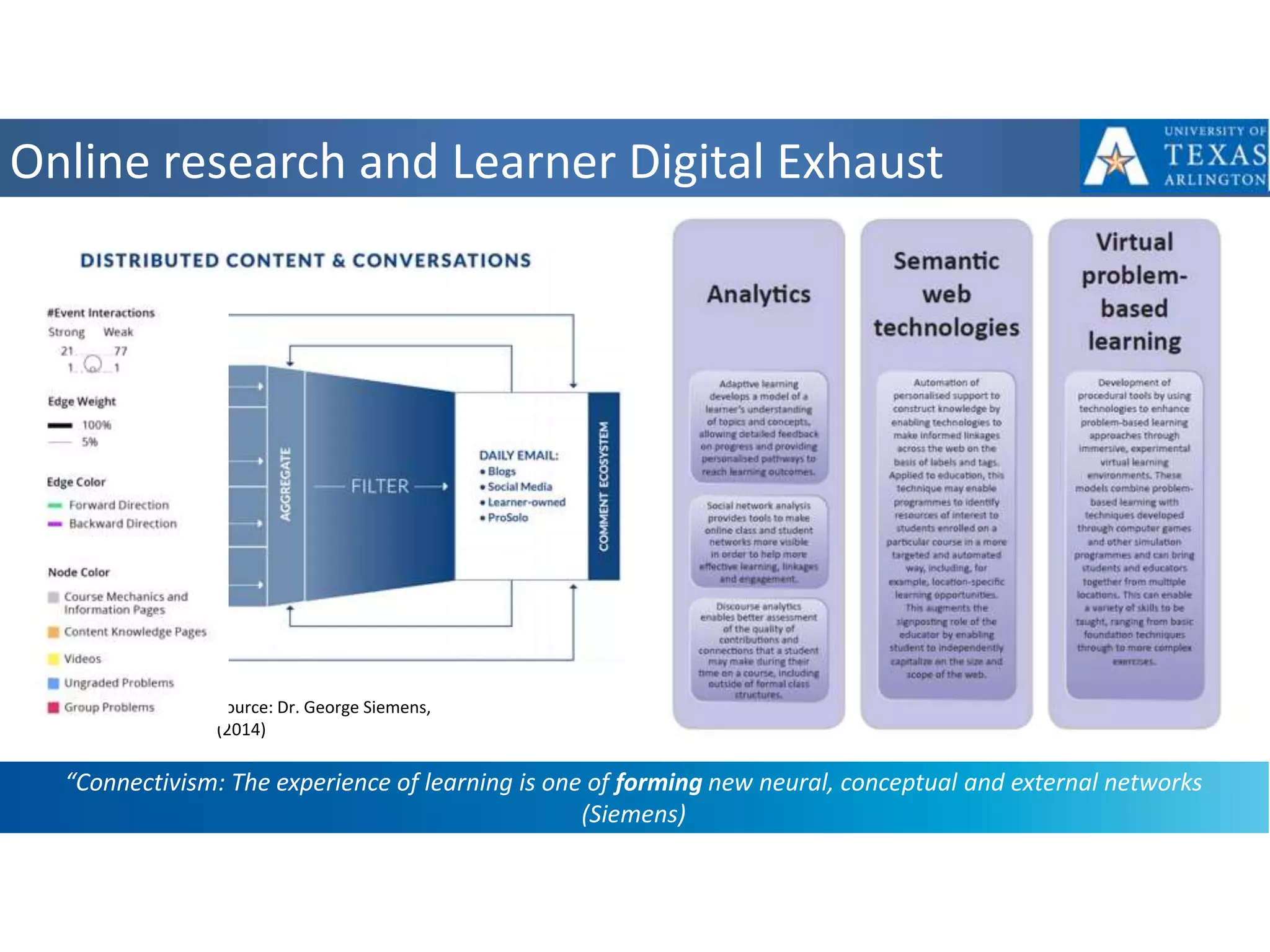
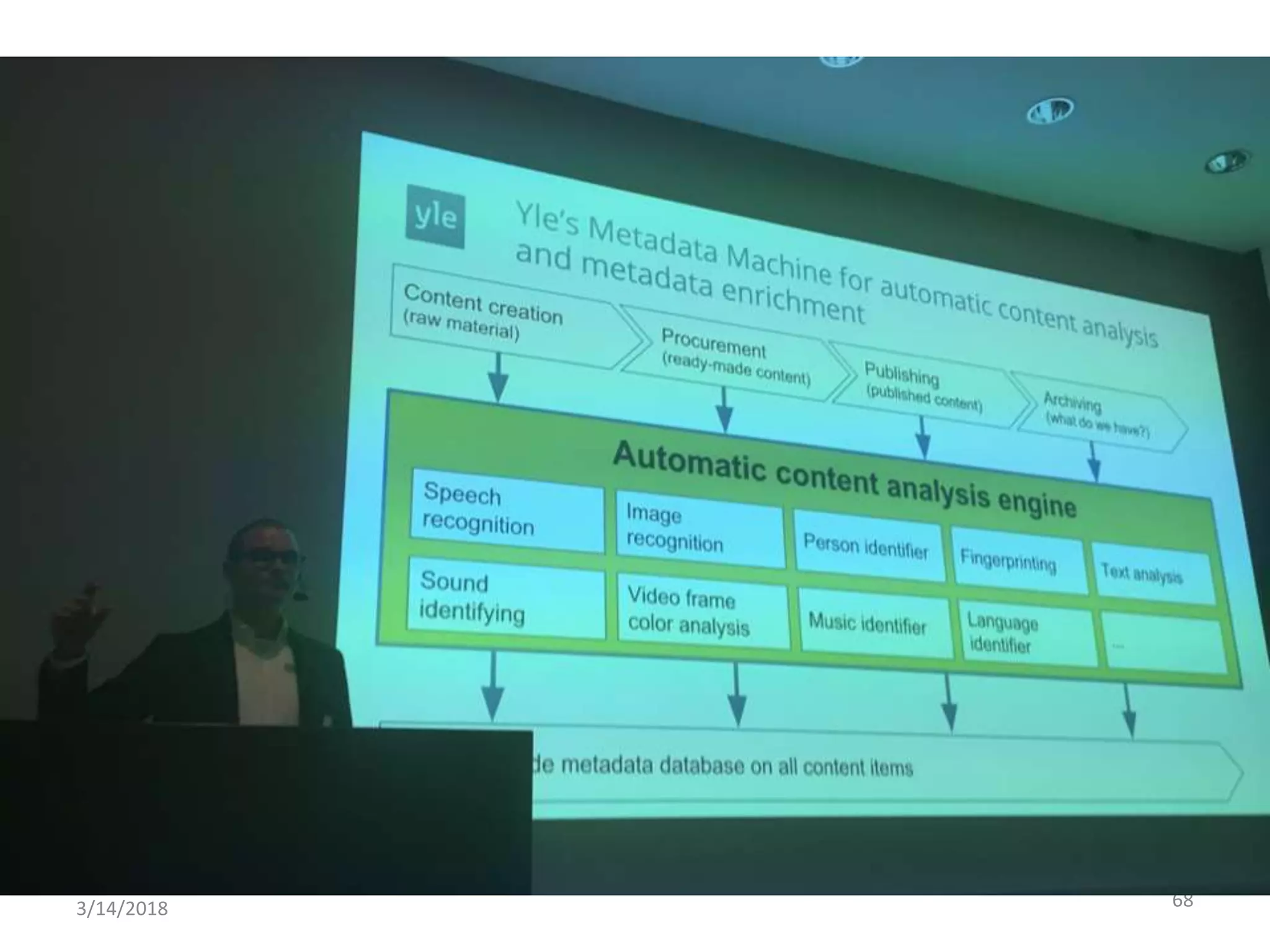
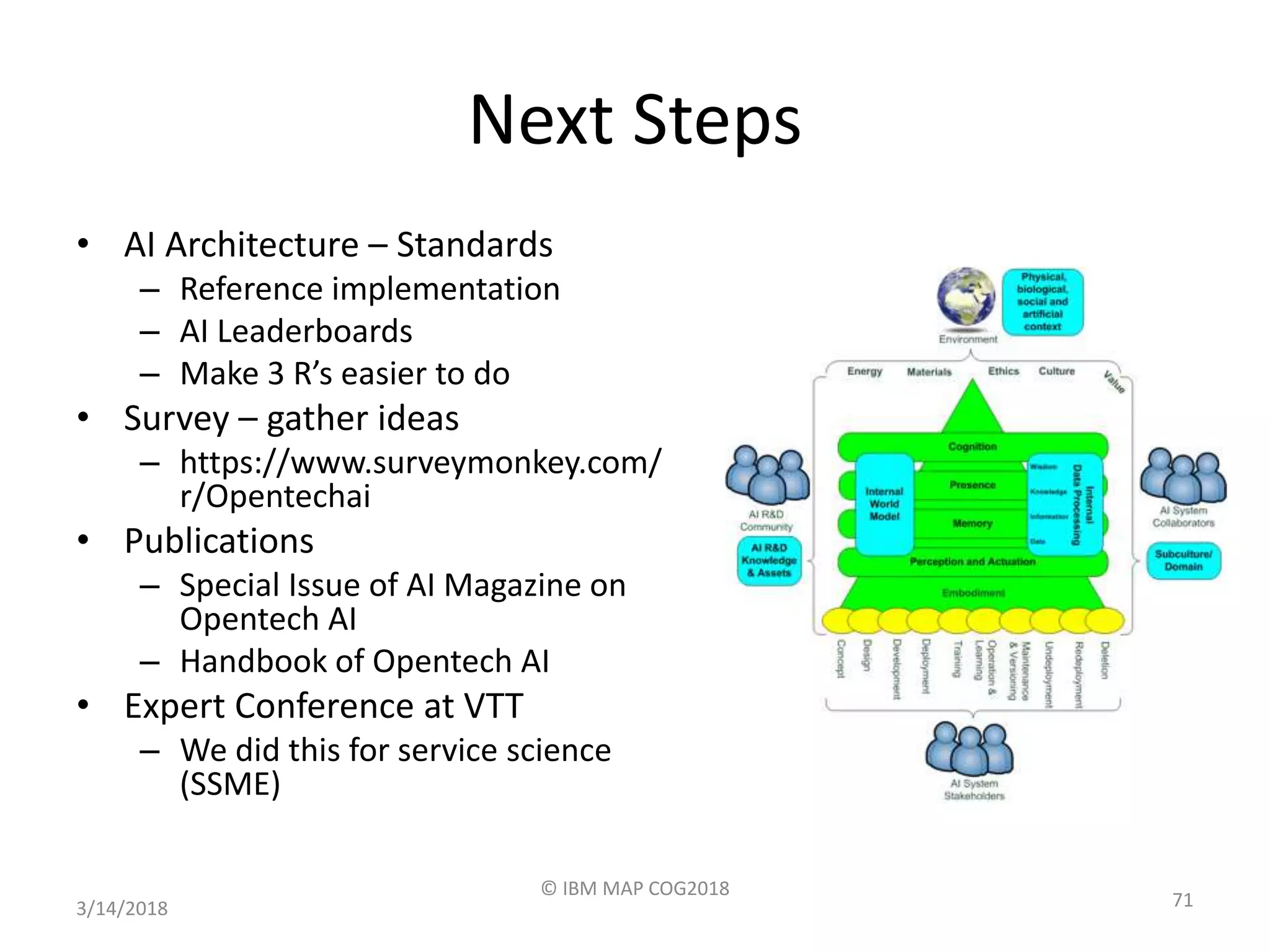
The panel discussed applications of AI and how multidisciplinary competencies are needed. Kalle Kantola of VTT discussed how AI needs supporting technologies like data, cybersecurity and IoT to realize value through applications. He provided an example of a pulp mill optimization that saved significant costs through quality control. Robin Burgener of 20Q.net discussed the history of 20Q and how it understands concepts differently than humans. Michael Richey of Boeing talked about the need for personalized learning given the exponential growth of information and different learning styles, and how Boeing supports advancing personalized learning.