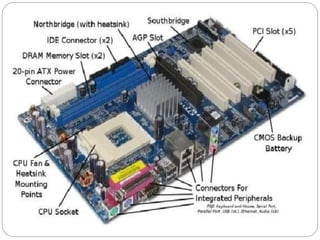
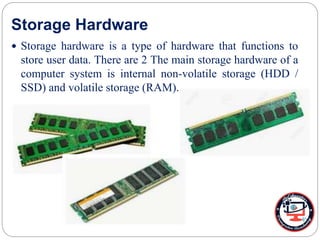
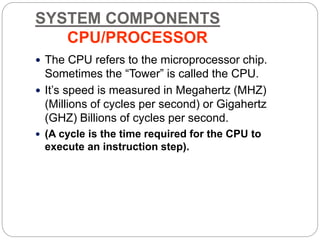
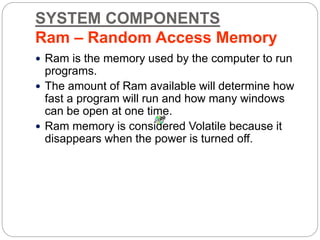
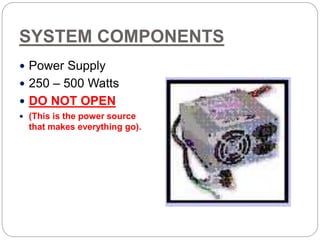
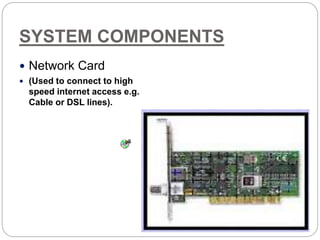
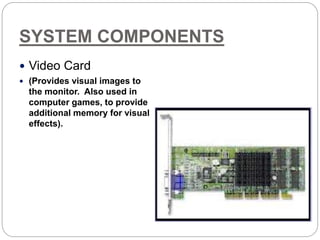
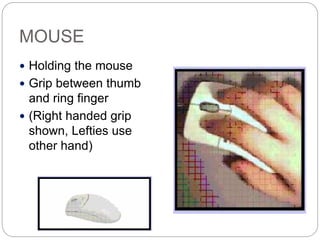
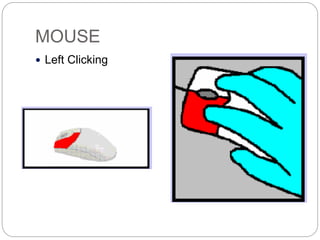
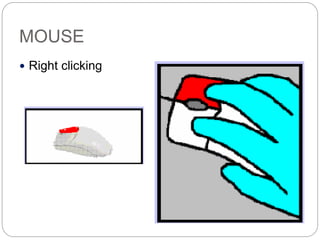
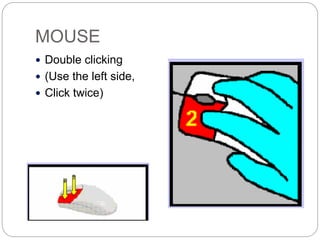
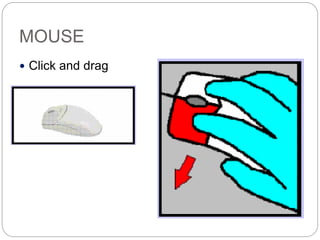
This document defines and describes computer hardware, its functions, and components. It discusses how hardware works with firmware to provide basic instructions, and describes the main types of hardware including processing hardware like the CPU, motherboard, VGA, and sound card. It also covers storage hardware, electrical hardware like the power supply, and peripheral devices. The key components of a computer system are defined along with their functions. Common hardware issues and precautions are also outlined.