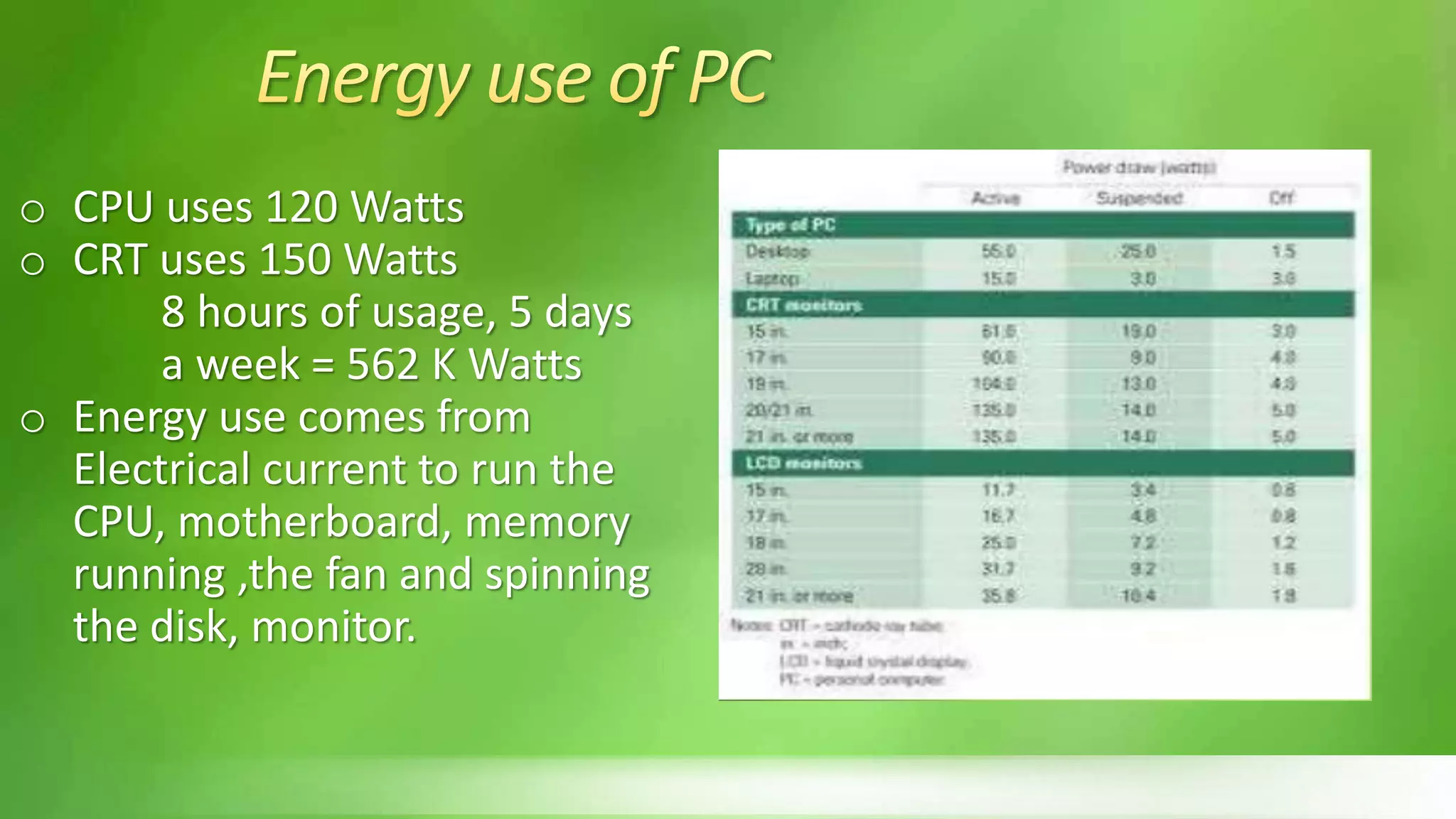
The document discusses green computing and provides information on the topic in multiple sections. It defines green computing as the environmentally responsible use of computers and related resources through implementing energy efficient technologies and reducing resource consumption and electronic waste. It discusses that computer energy use can be wasteful if left on when not in use. It also outlines four aspects of green computing: green use, green disposal, green design, and green manufacturing. Examples of green computing initiatives like Energy Star and thin clients are also summarized.