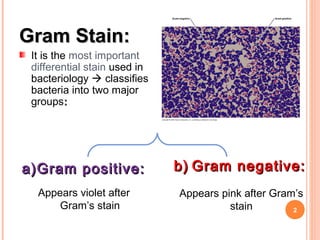
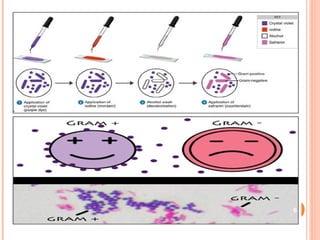
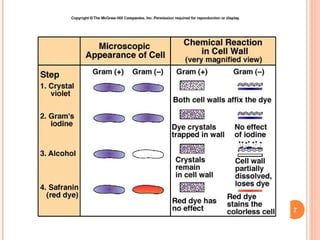
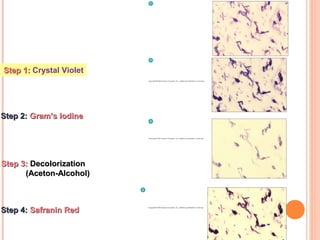
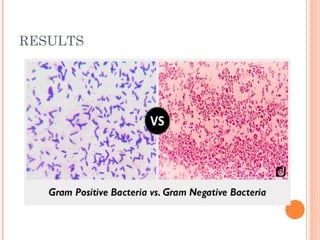
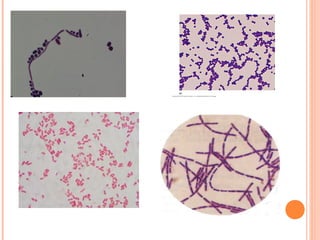
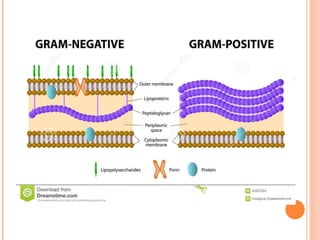
The document provides information about the Gram stain procedure and its importance in bacteriology. It describes how the Gram stain technique classifies bacteria into two groups - Gram positive and Gram negative - based on whether they appear violet or pink after staining. Key steps include fixing a smear, staining with crystal violet and iodine, decolorizing with alcohol or acetone, and counterstaining with safranin. The principle is that Gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer that retains the primary stain, while Gram negative bacteria have a thin layer that is decolorized, taking up the counterstain instead. The Gram stain is a critical first step in bacterial identification and diagnosis.