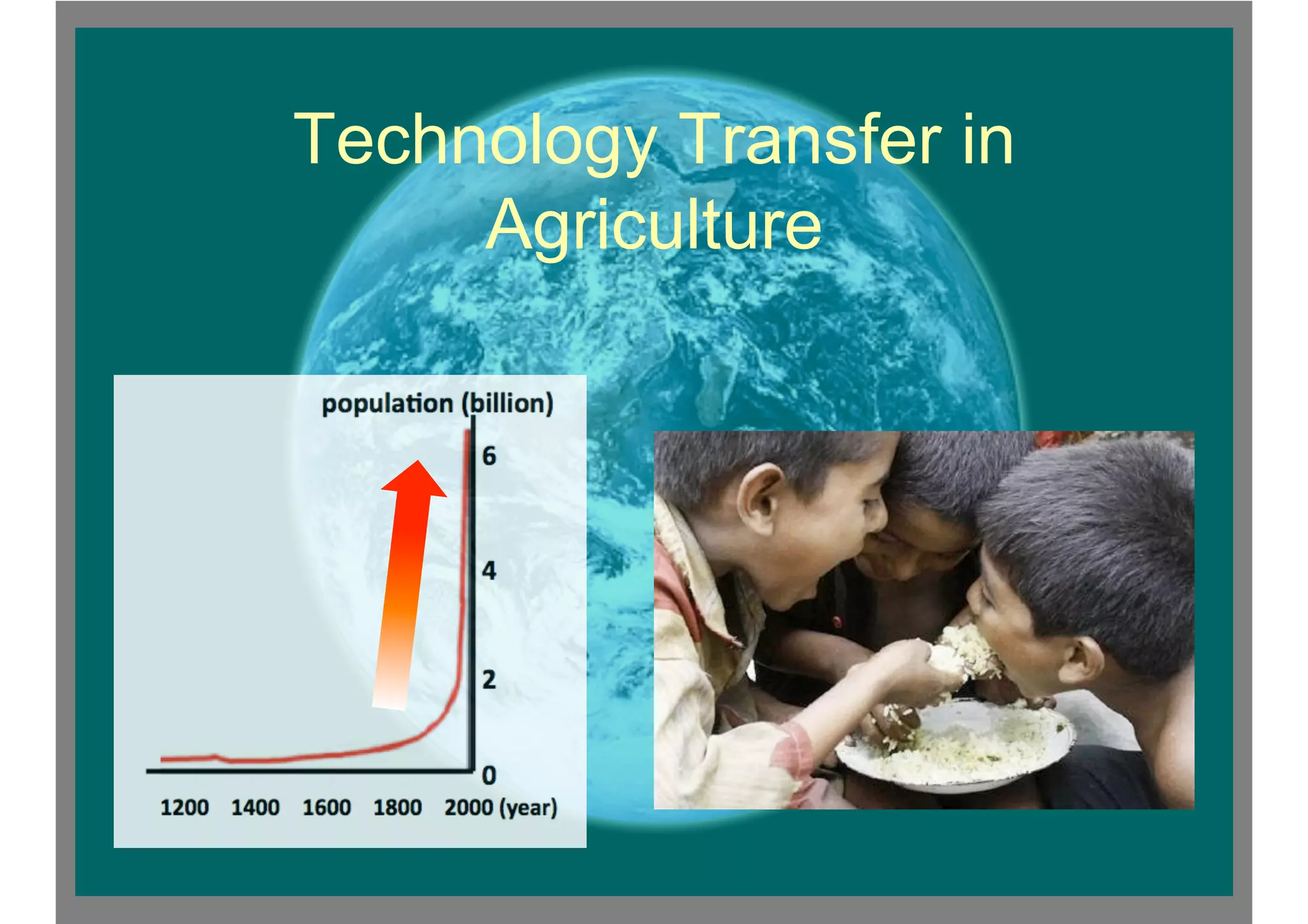
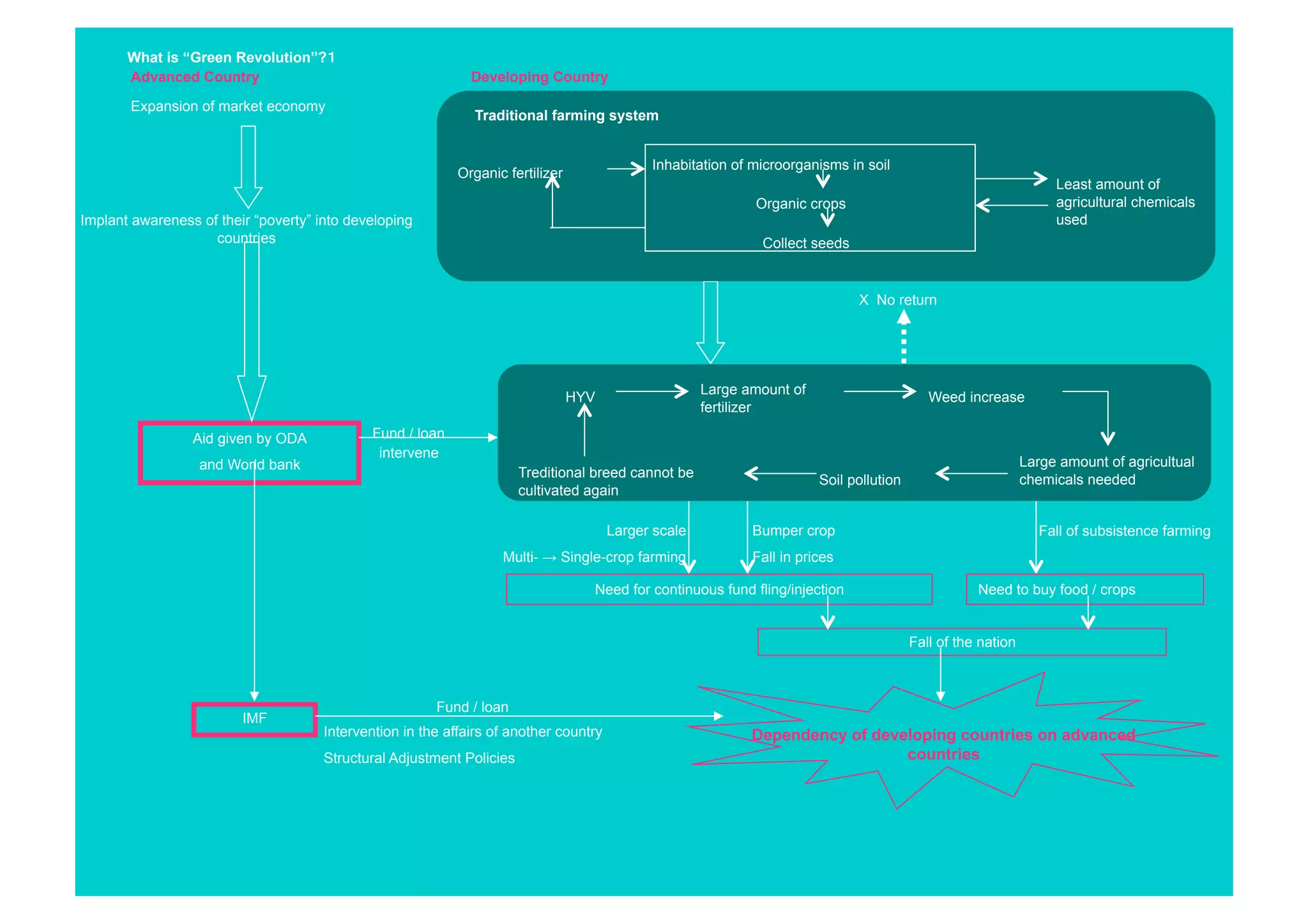
The document summarizes the introduction and spread of the Green Revolution in India. It describes how Norman Borlaug developed high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice with support from the Rockefeller Foundation. These varieties were introduced in India in the 1960s through a collaboration between the Ford Foundation and Indian government. Punjab was the initial site due to reliable water supply and agricultural success. The introduction of HYVs led to increased crop production and self-sufficiency in grains for India. However, it also caused environmental problems from overuse of fertilizers and pesticides. The Green Revolution impacted local communities and increased inequality among farmers.