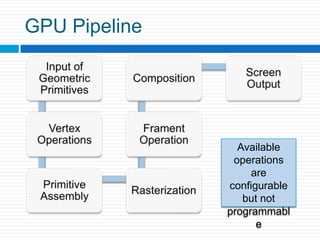
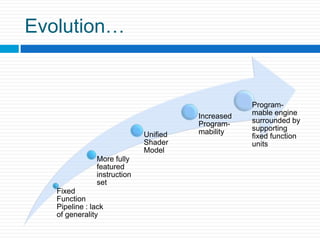
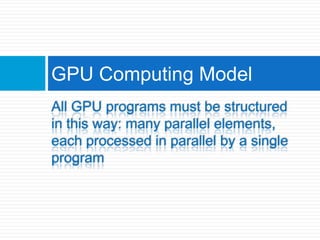
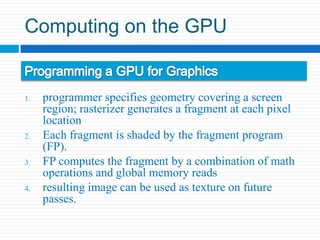
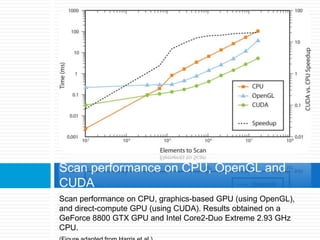
Graphics processing units (GPUs) are increasingly being used for general-purpose computing applications due to their highly parallel and programmable nature. GPU computing uses the GPU alongside the CPU in a heterogeneous model, with the sequential CPU portion handling control flow and passing data to the GPU for parallel intensive computations. GPUs have evolved from fixed-function processors into fully programmable parallel processors. Many applications that require large amounts of parallelism and throughput can benefit from offloading work to the GPU. GPU architectures provide a high degree of parallelism through multiple stream processors that can execute the same instructions on different data sets. Software environments like CUDA and OpenCL allow general-purpose programming of GPUs for applications beyond graphics. Future improvements may include