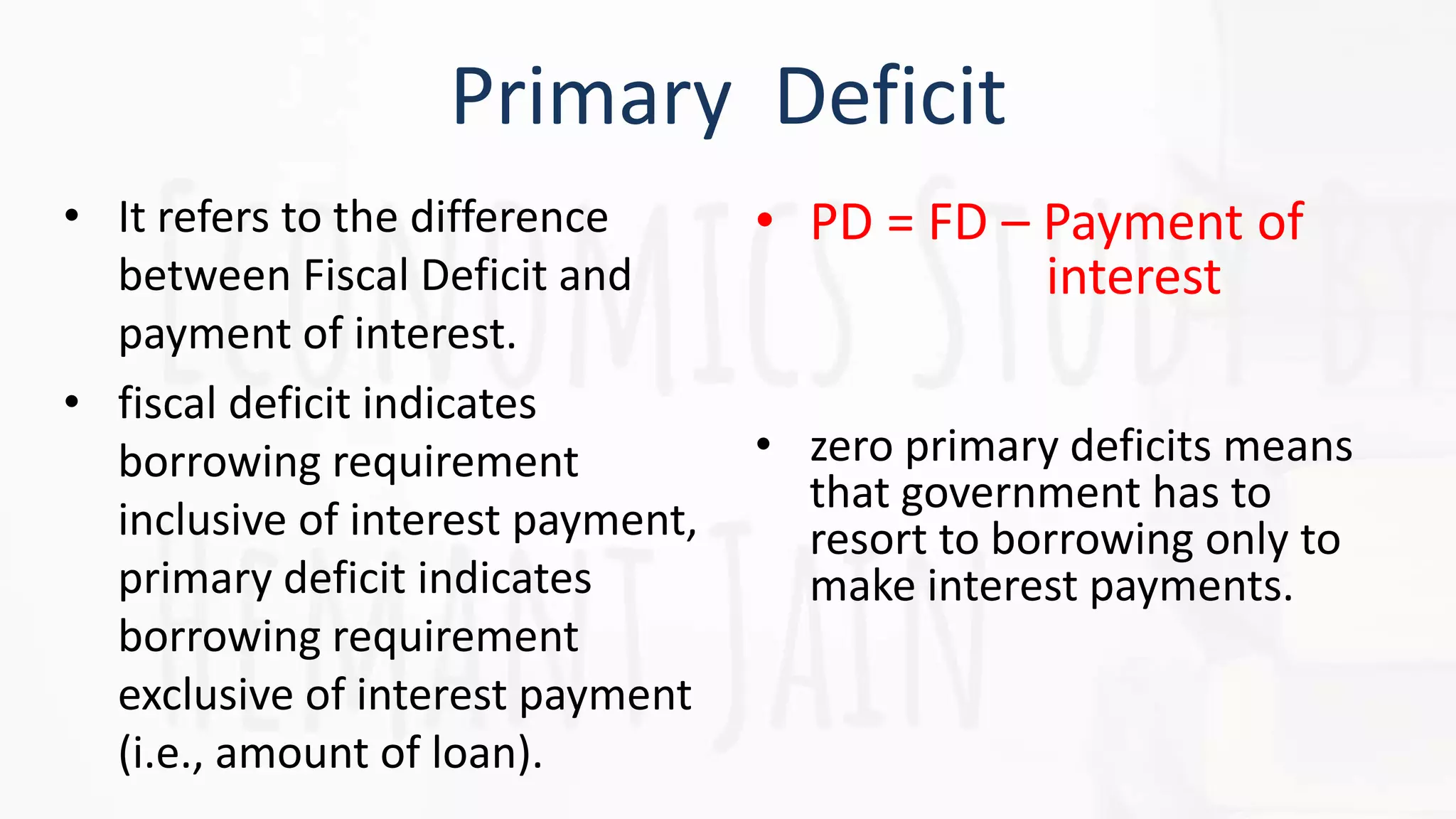
The document provides a detailed overview of government budgeting, covering its definition, objectives, classifications, and types of budget deficits. It highlights the role of the budget in promoting economic stability, GDP growth, income and wealth redistribution, and resource allocation. The document also explains the implications of different types of budget receipts and expenditures, as well as the concepts of revenue and fiscal deficits.