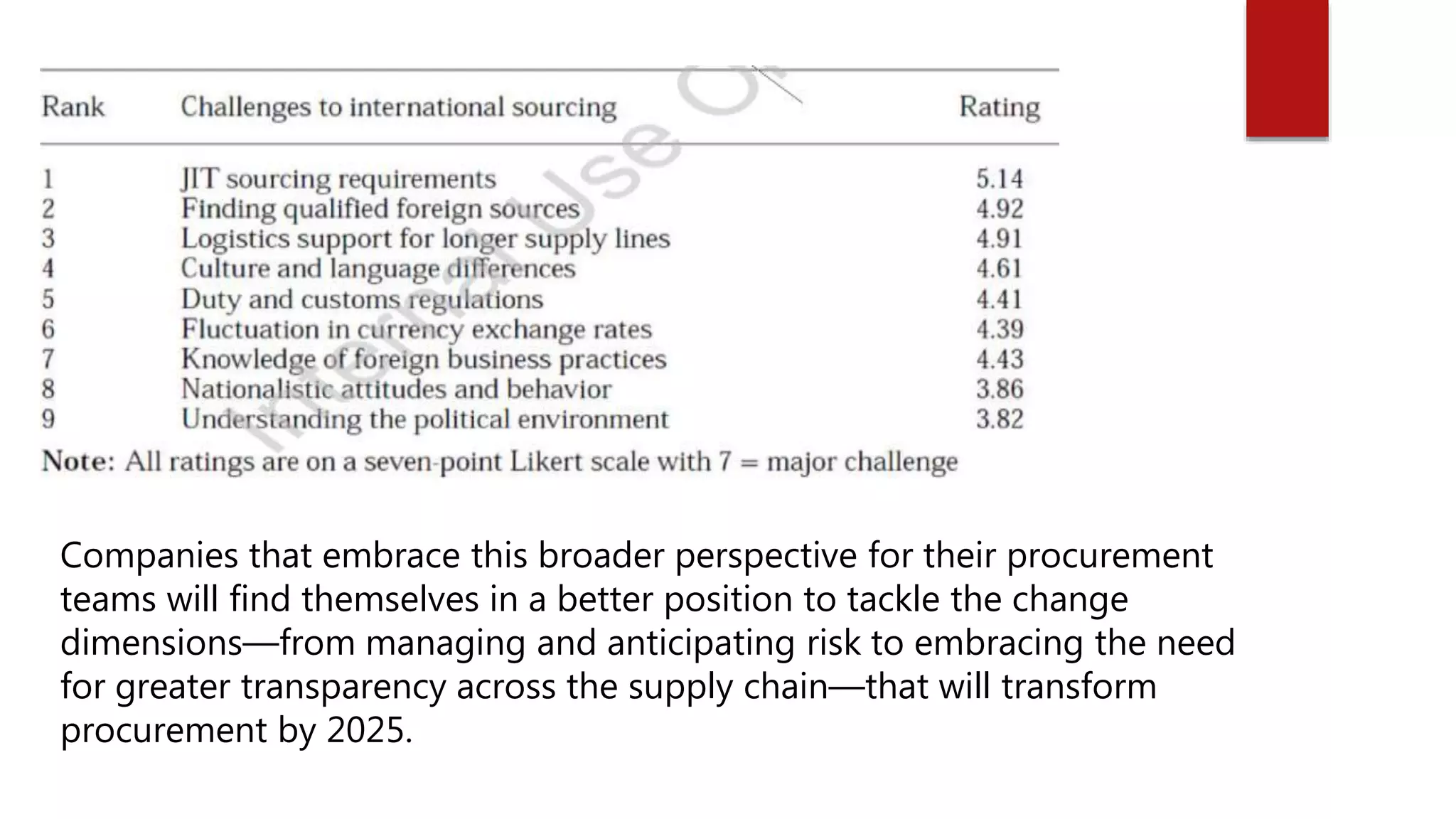
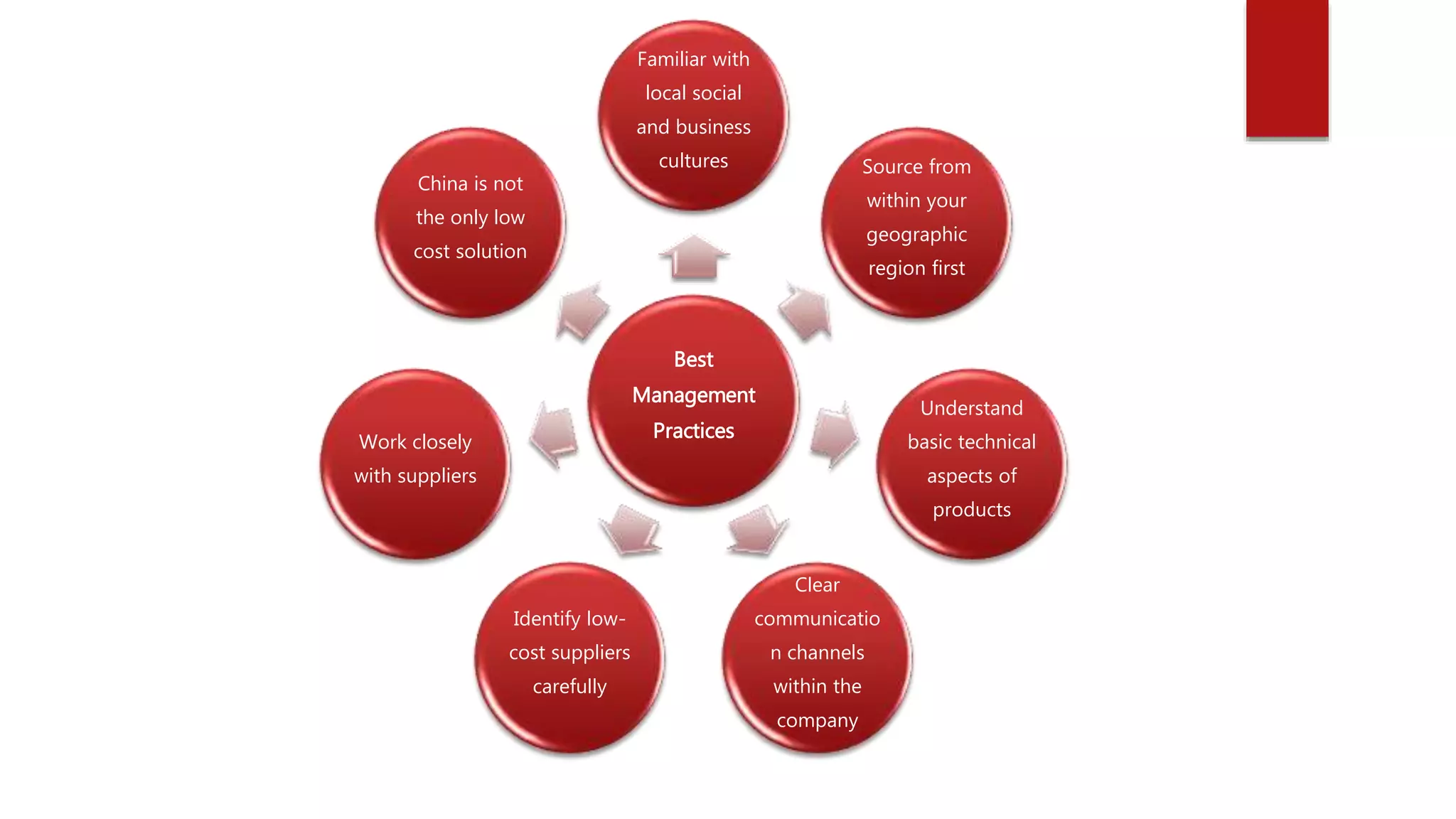
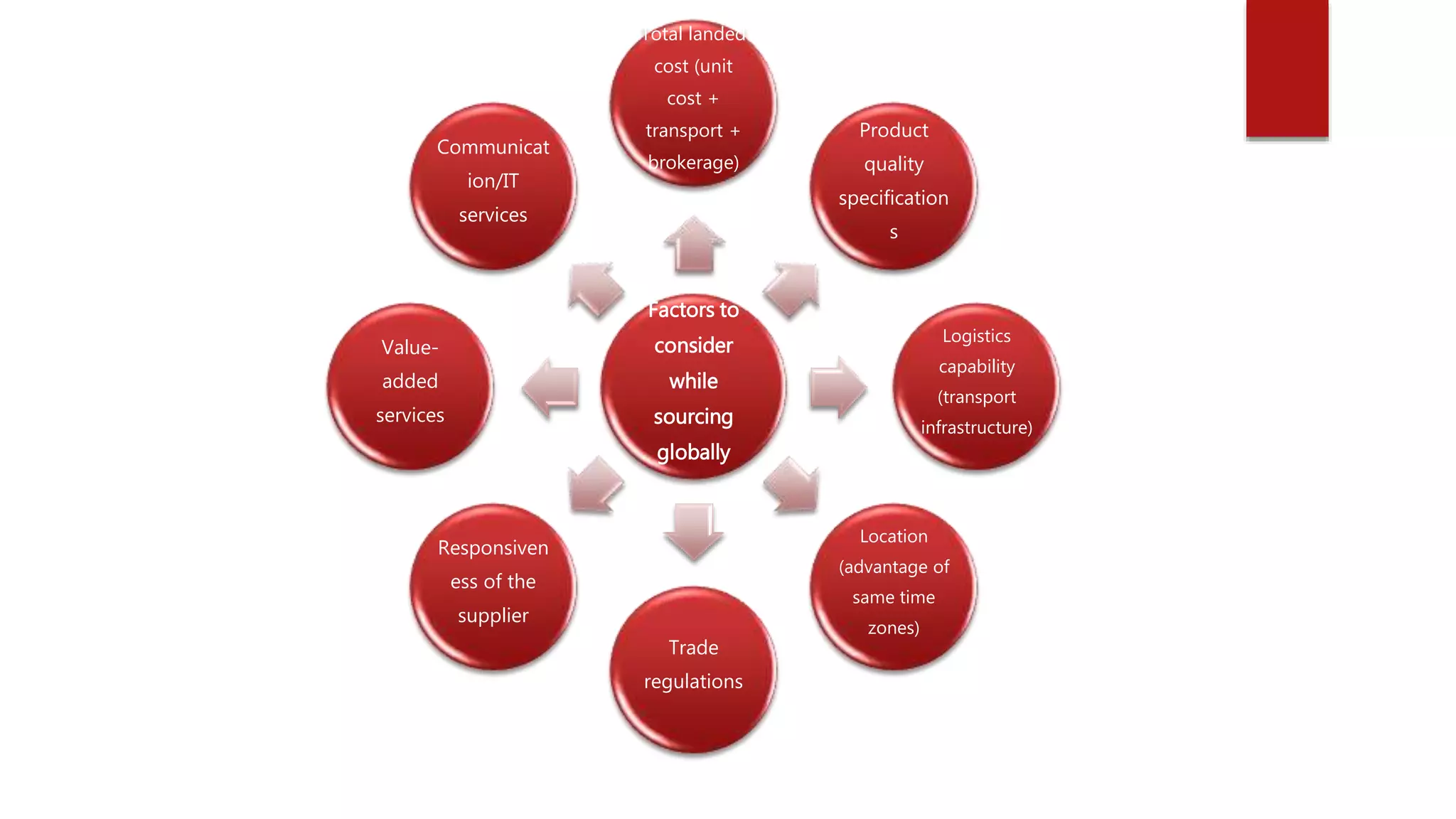
The document discusses inventory management and logistics costs in global sourcing processes. It provides insights into global sourcing strategies used by multinational corporations. Some key challenges to global sourcing mentioned include sustainability concerns, developing expertise in local emerging markets, and developing the necessary human resource capabilities to support global sourcing efforts. Factors influencing global sourcing decisions include product characteristics, organizational characteristics, and country characteristics. The total cost of ownership model can help evaluate sourcing and logistics strategies based on these factors.