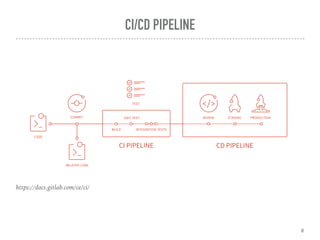
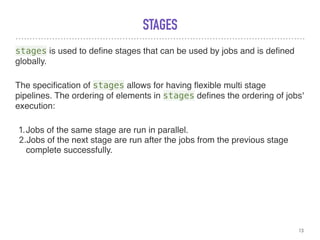
This document discusses GitLab Continuous Integration (GitLab CI/CD). It defines continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment. It explains that GitLab CI/CD uses pipelines made up of stages and jobs to test, build, and deploy code. Pipelines are configured using a YAML file. Jobs run on GitLab runners, which can execute jobs locally or using Docker. Benefits of GitLab CI/CD include integrated pipelines, Docker/Kubernetes integration, and not requiring plugins. The downside is that it is only available within GitLab.