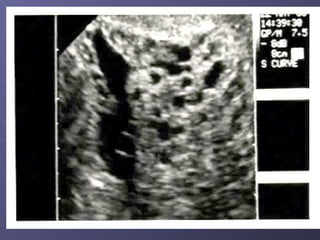
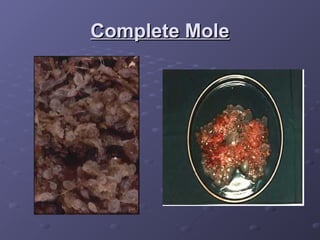
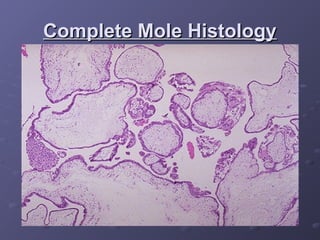
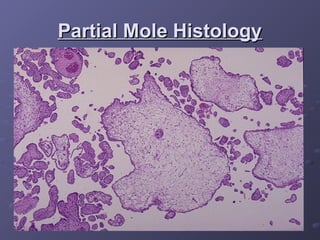
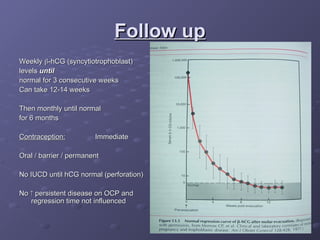
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a group of rare tumors that develop in the uterus during or after pregnancy, primarily from trophoblastic tissue. Most types of GTD, including molar pregnancies, are noncancerous and highly treatable. Symptoms may include excessive uterine enlargement, vaginal bleeding, and nausea. Treatment options are available, and in the majority of cases, GTD can be cured.