Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times


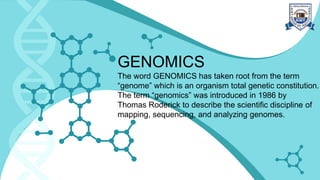

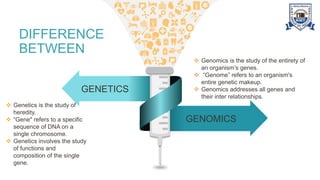
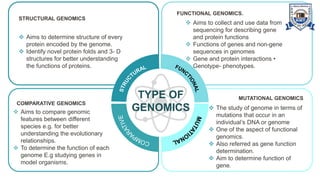

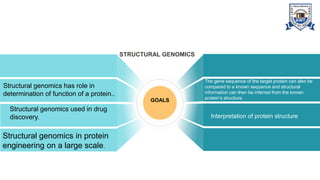
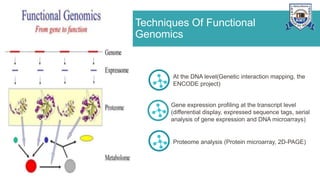
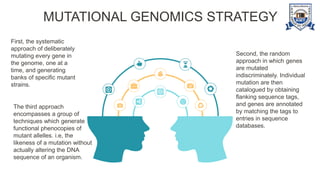

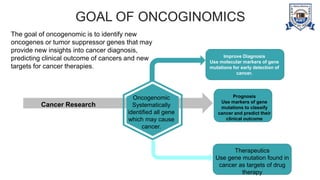
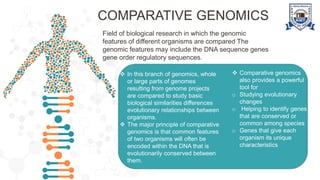
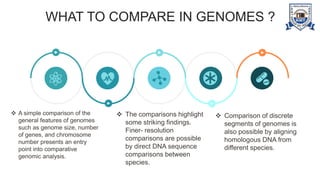
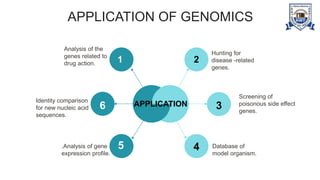

This document provides an overview of genomics, including definitions, key differences between genetics and genomics, and different types of genomics such as structural genomics, functional genomics, comparative genomics, and mutational/oncogenomics. It defines genomics as the study of an organism's entire genome and its functions, compared to genetics which focuses on individual genes. The types of genomics are described as studying protein structures (structural), gene functions (functional), comparing genomes across species (comparative), and characterizing mutation-associated genes including in cancer (mutational/oncogenomics). Applications of genomics include databases, sequence comparisons, gene expression analysis, studying drug actions, and identifying disease genes.

















