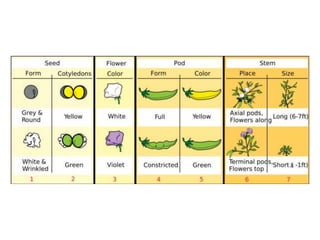
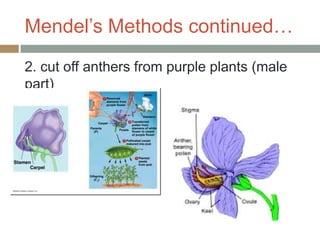
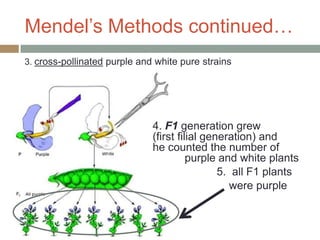
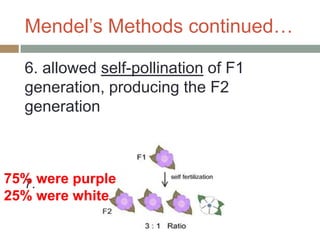
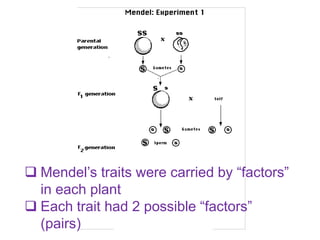
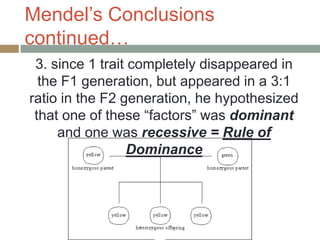
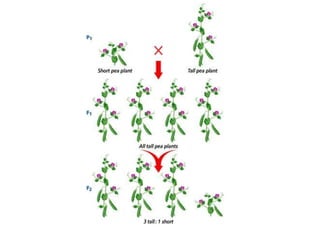
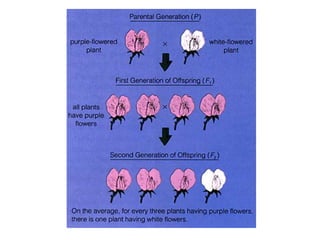
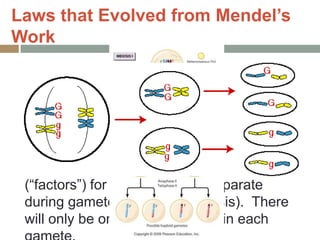
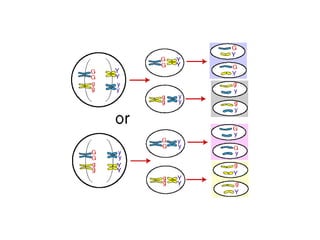
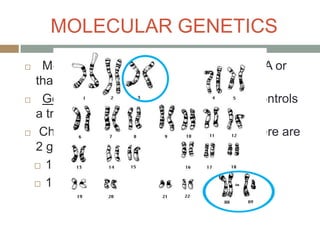
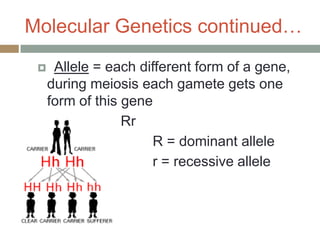
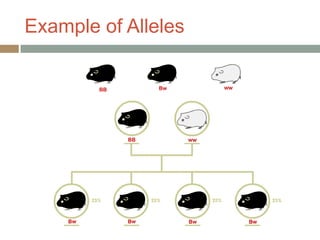
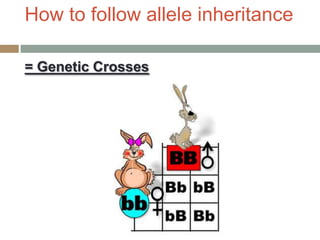
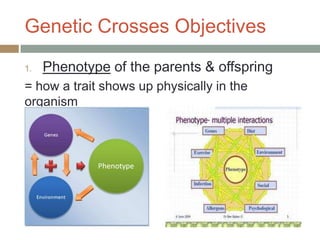
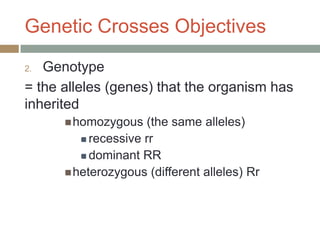
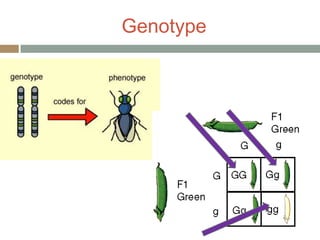
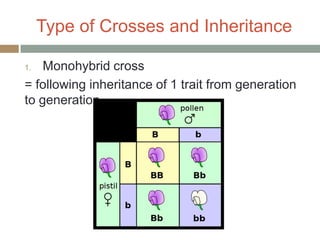
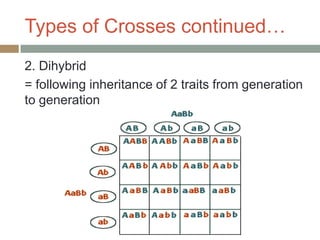
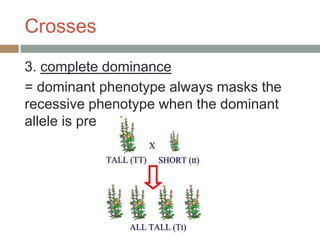
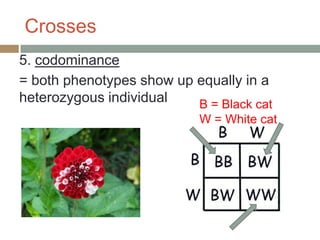
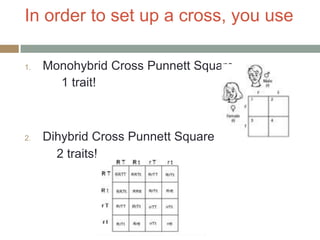
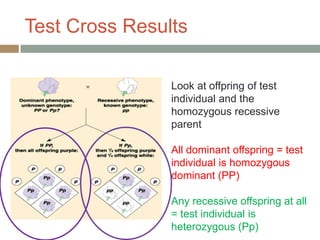
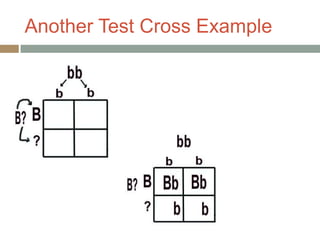
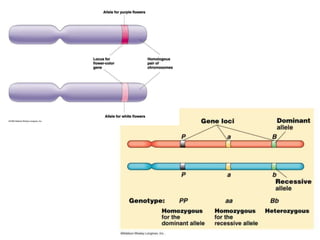
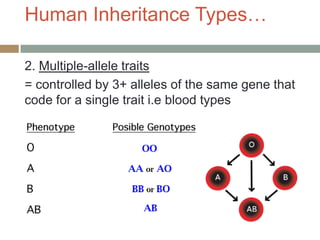
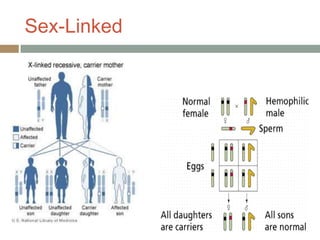
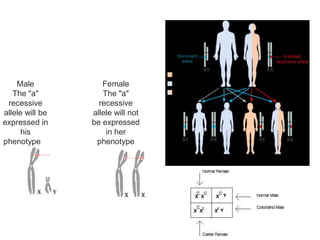
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants in the 1850s and 1860s to study inheritance of traits. He observed that traits were inherited in predictable patterns, with dominant traits masking recessive traits in the offspring of crosses. His work established the fundamental laws of genetics, including segregation of alleles, independent assortment of traits, and dominance. Mendel's work laid the foundation for the field of molecular genetics and our modern understanding of genes and inheritance.