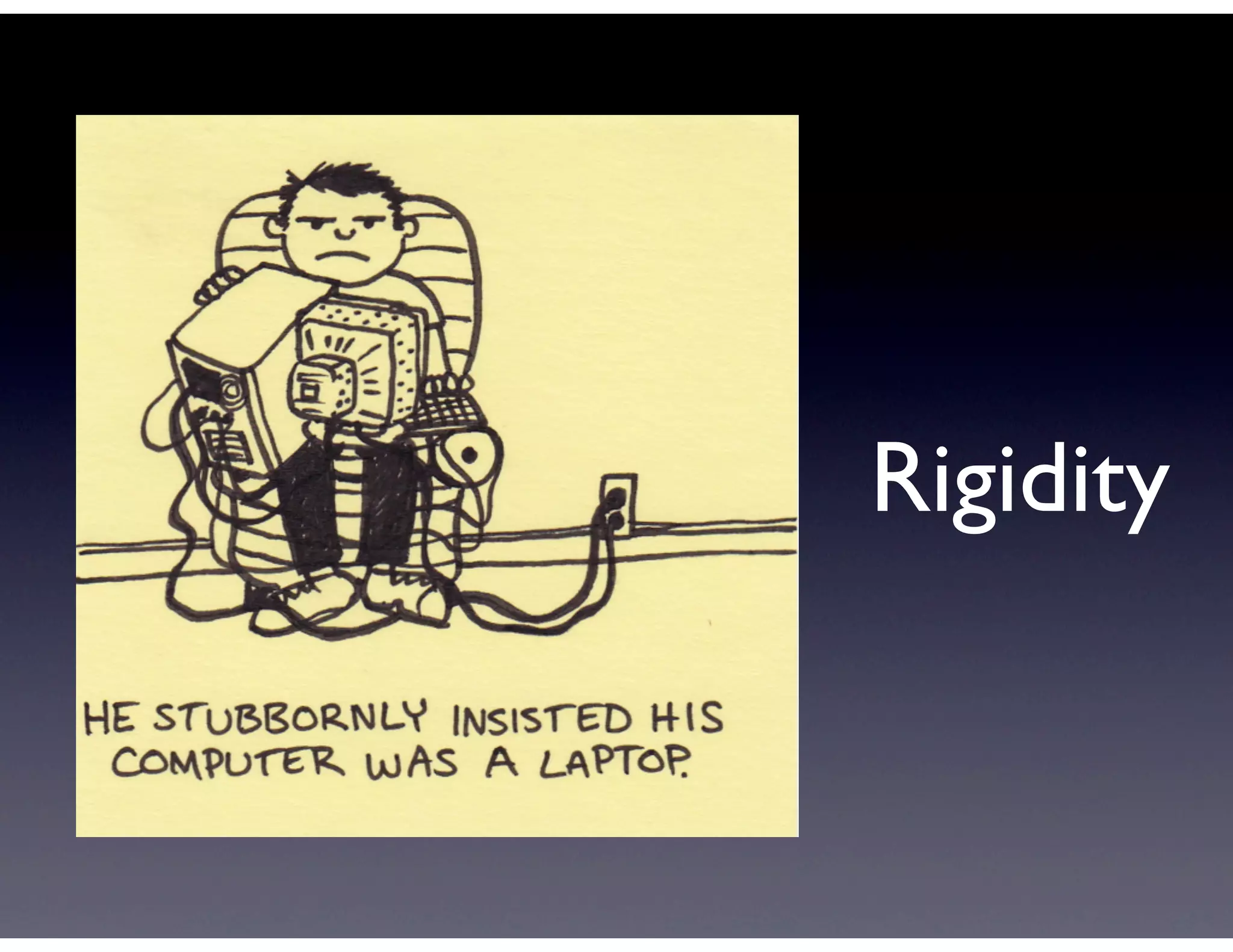
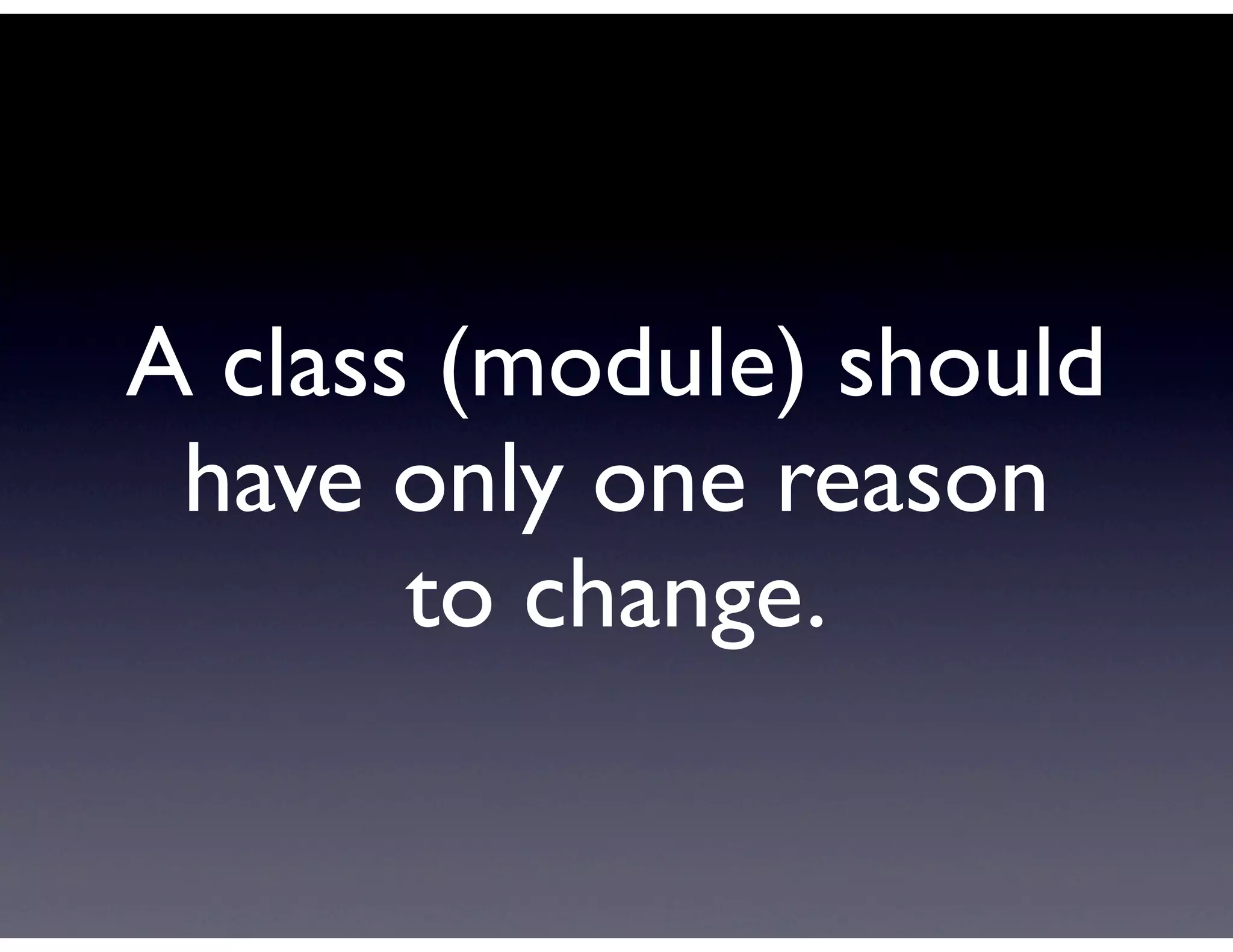
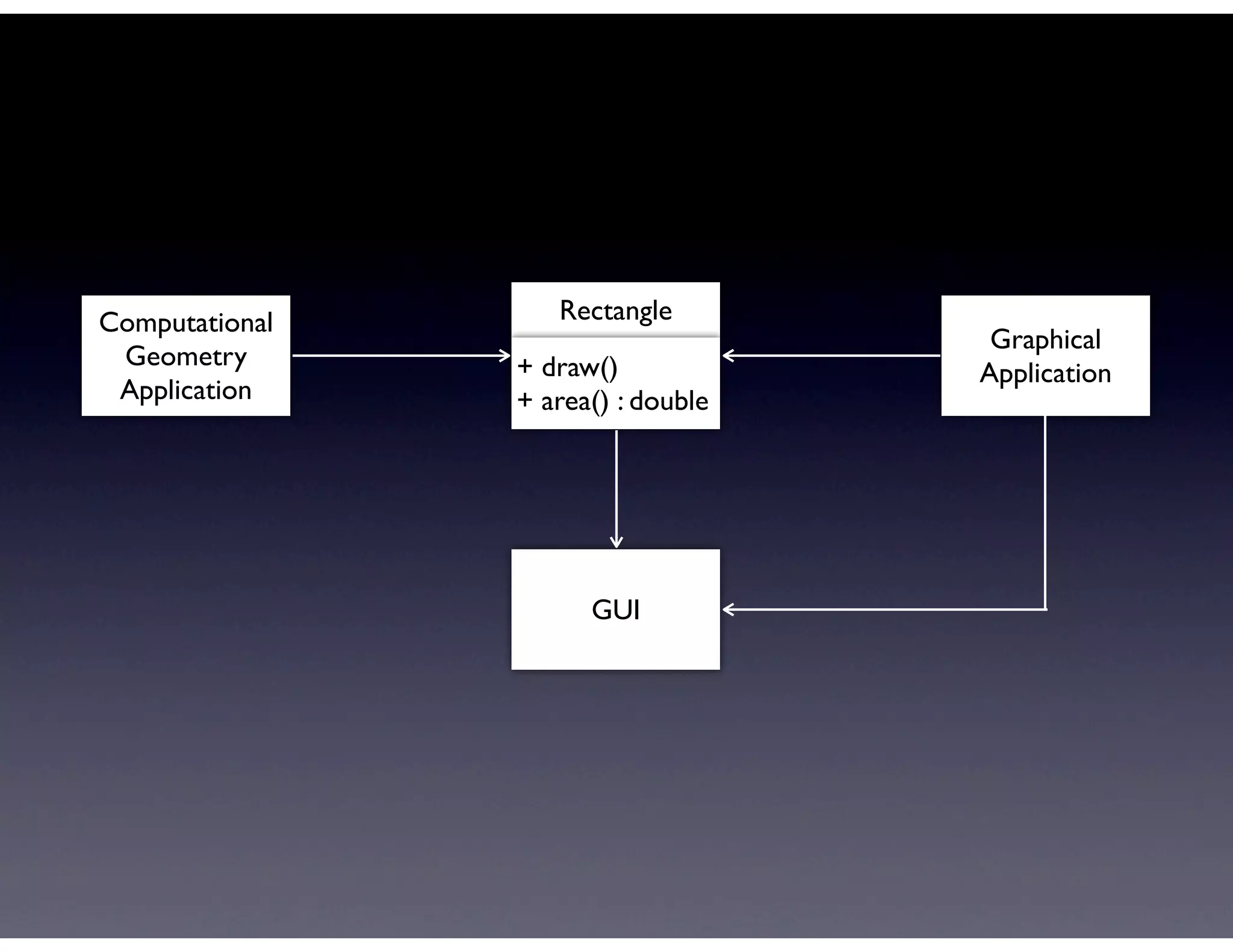
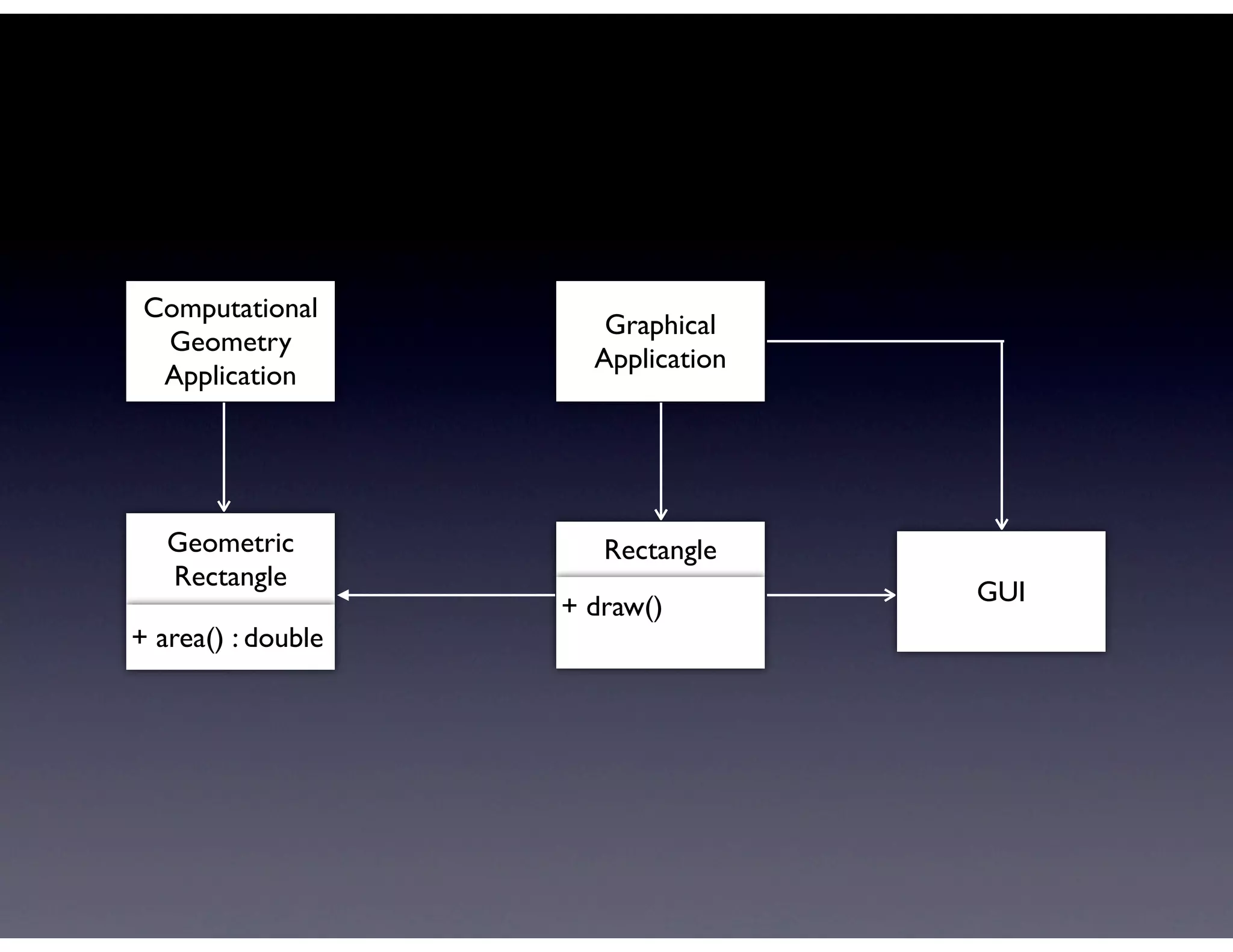
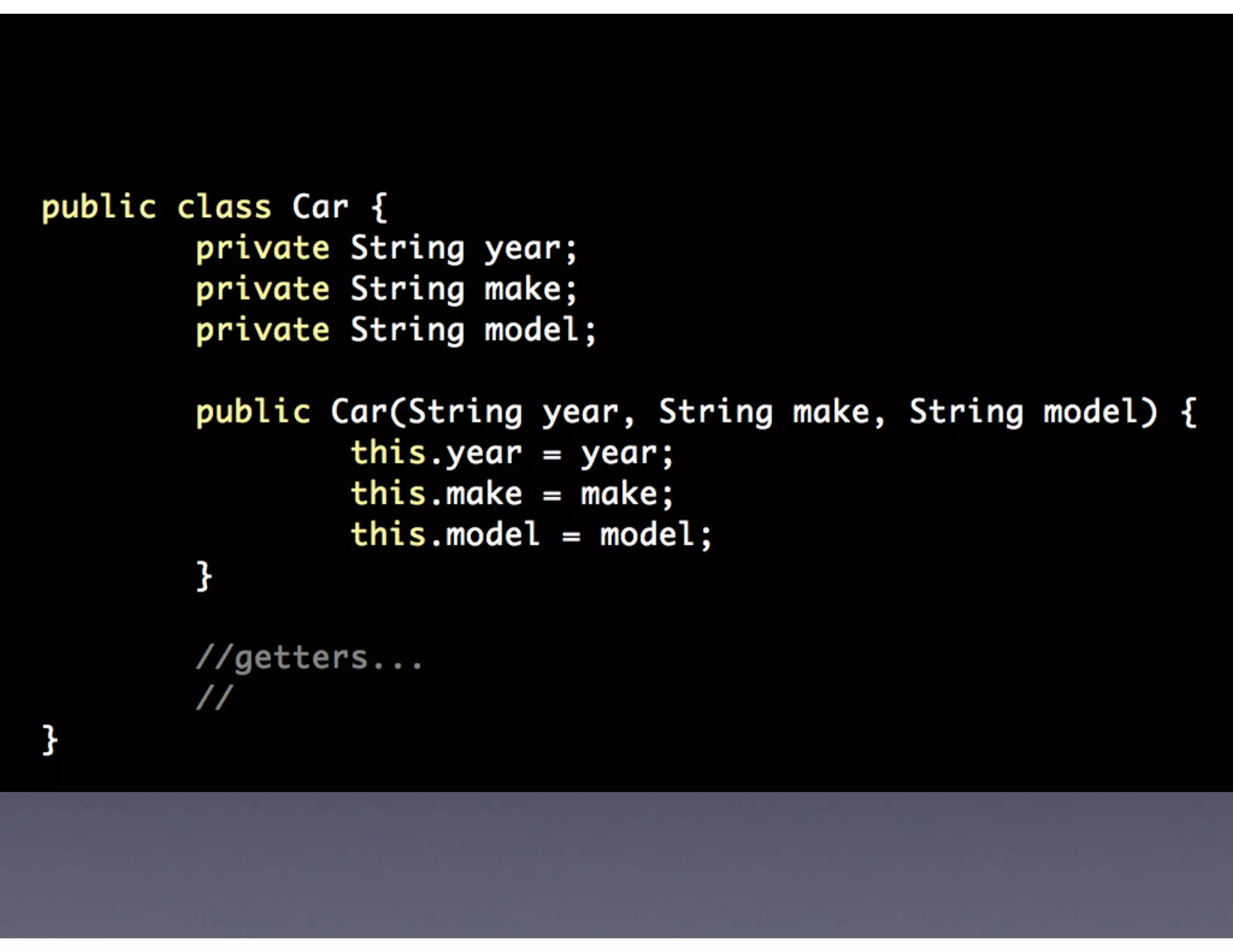
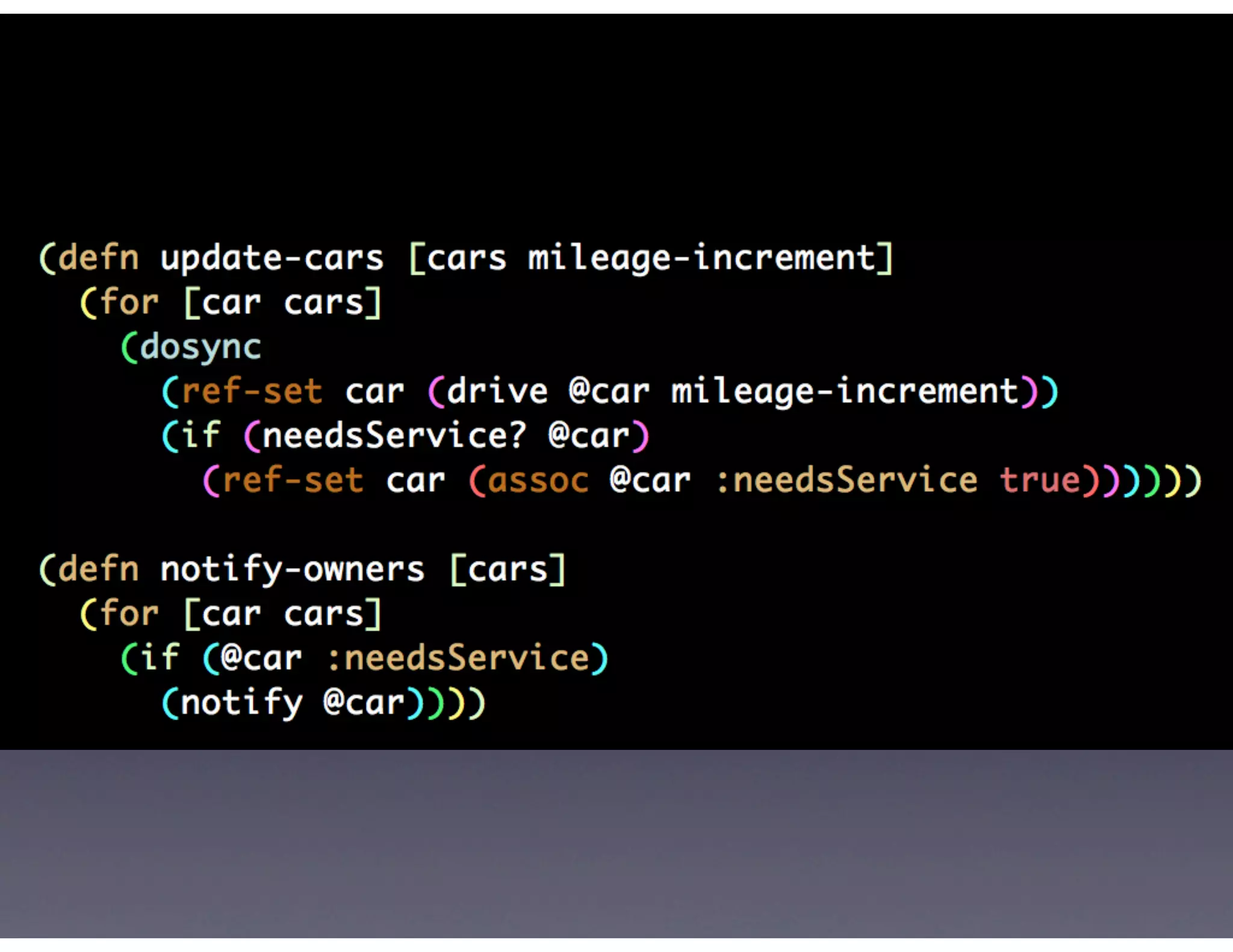
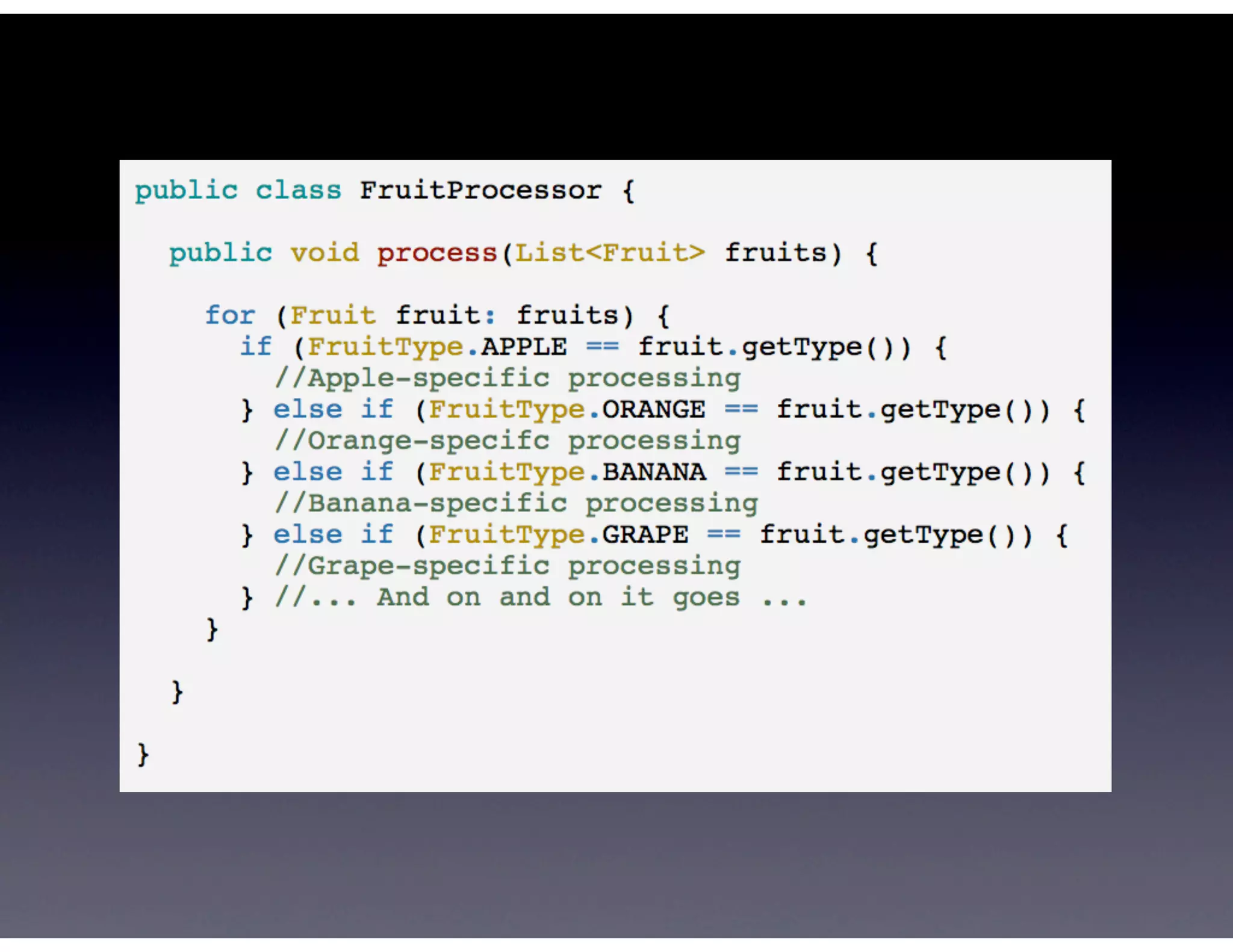
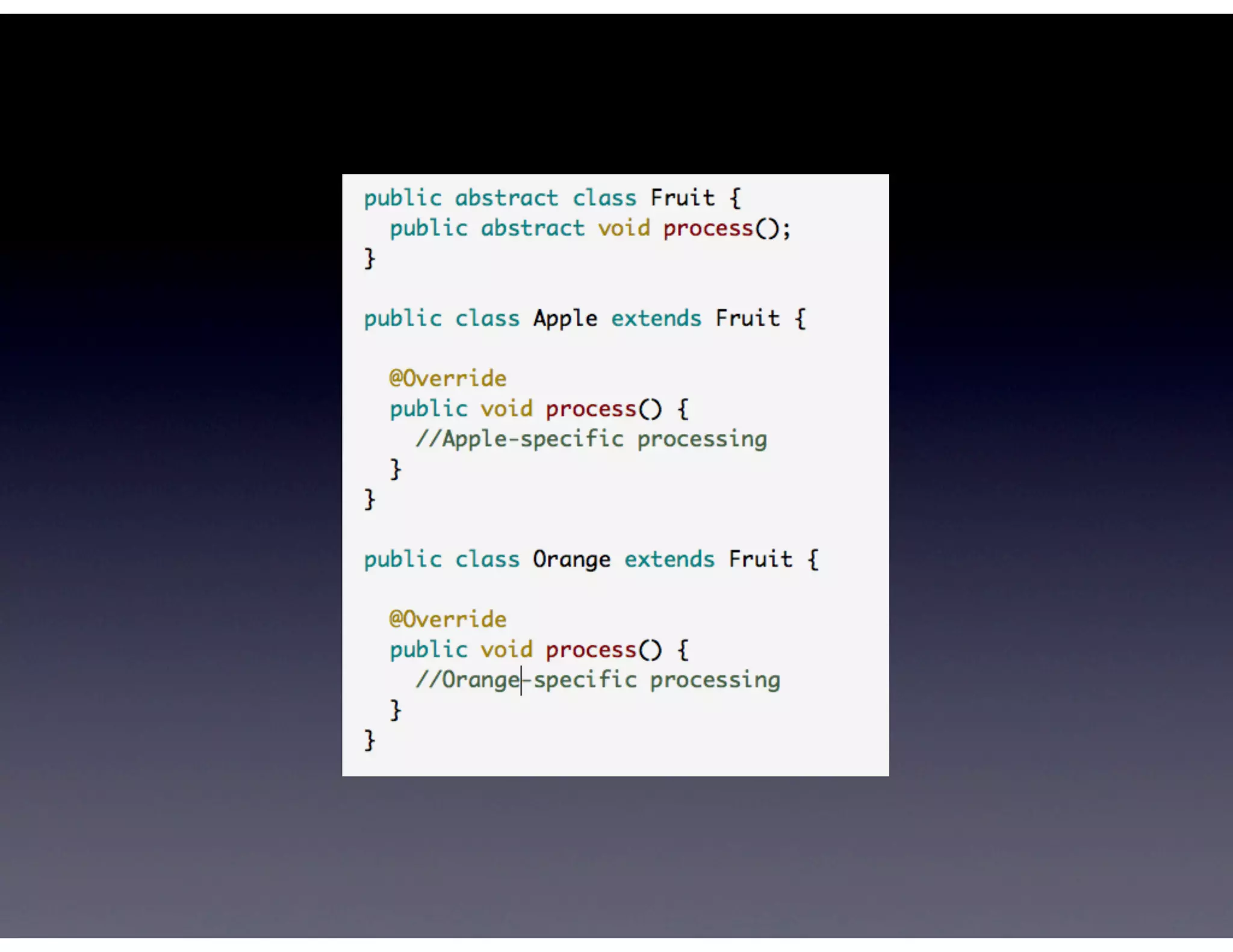
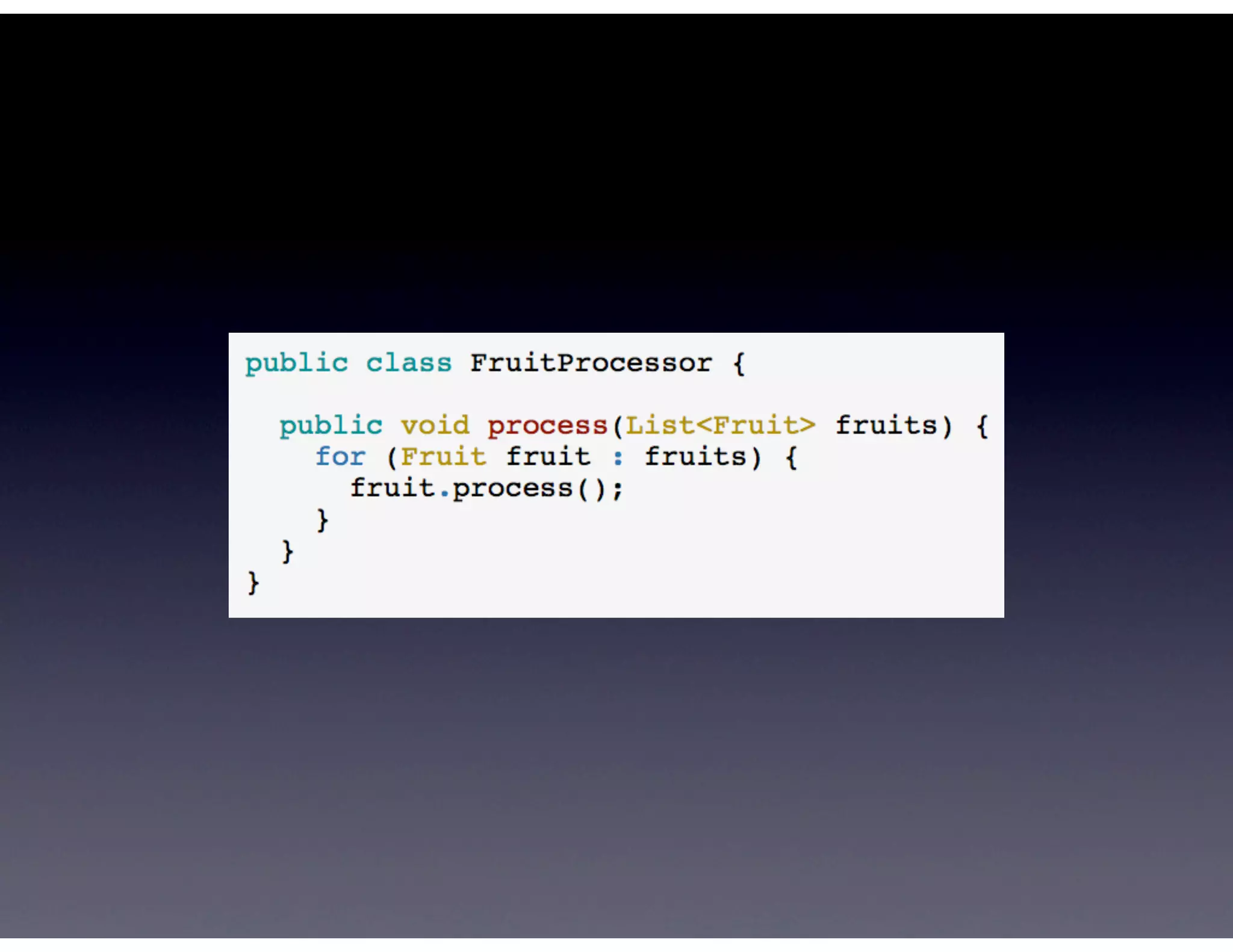
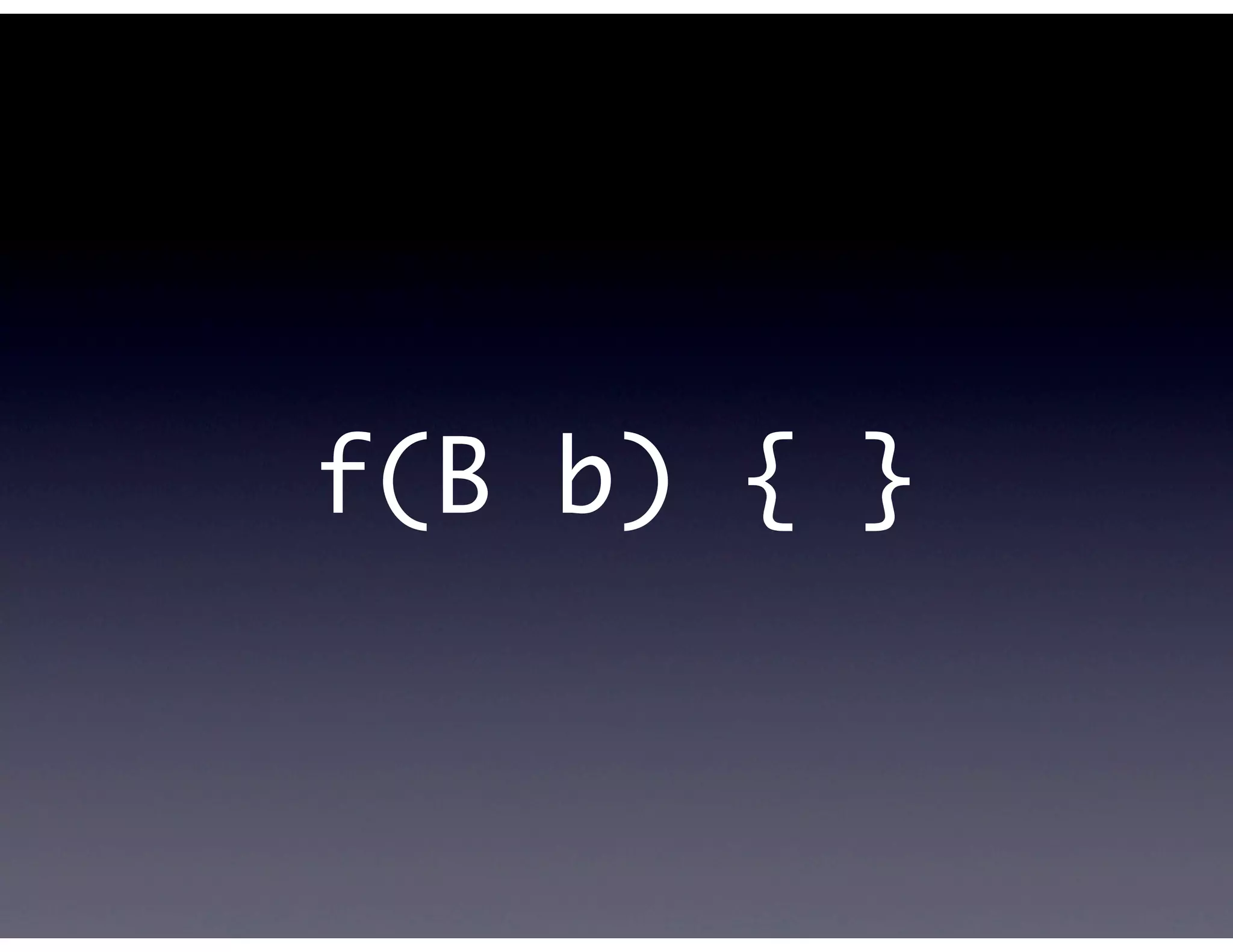
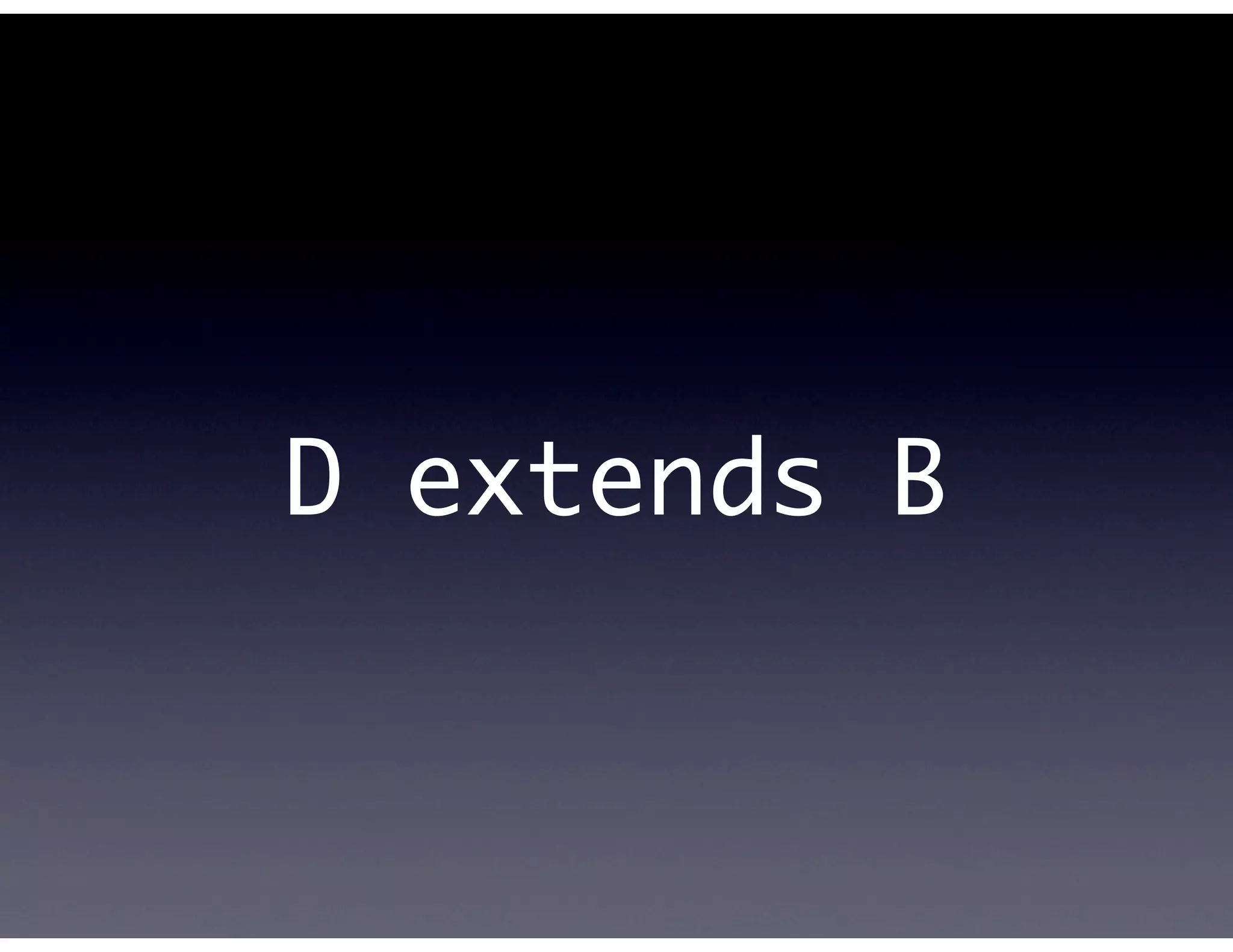
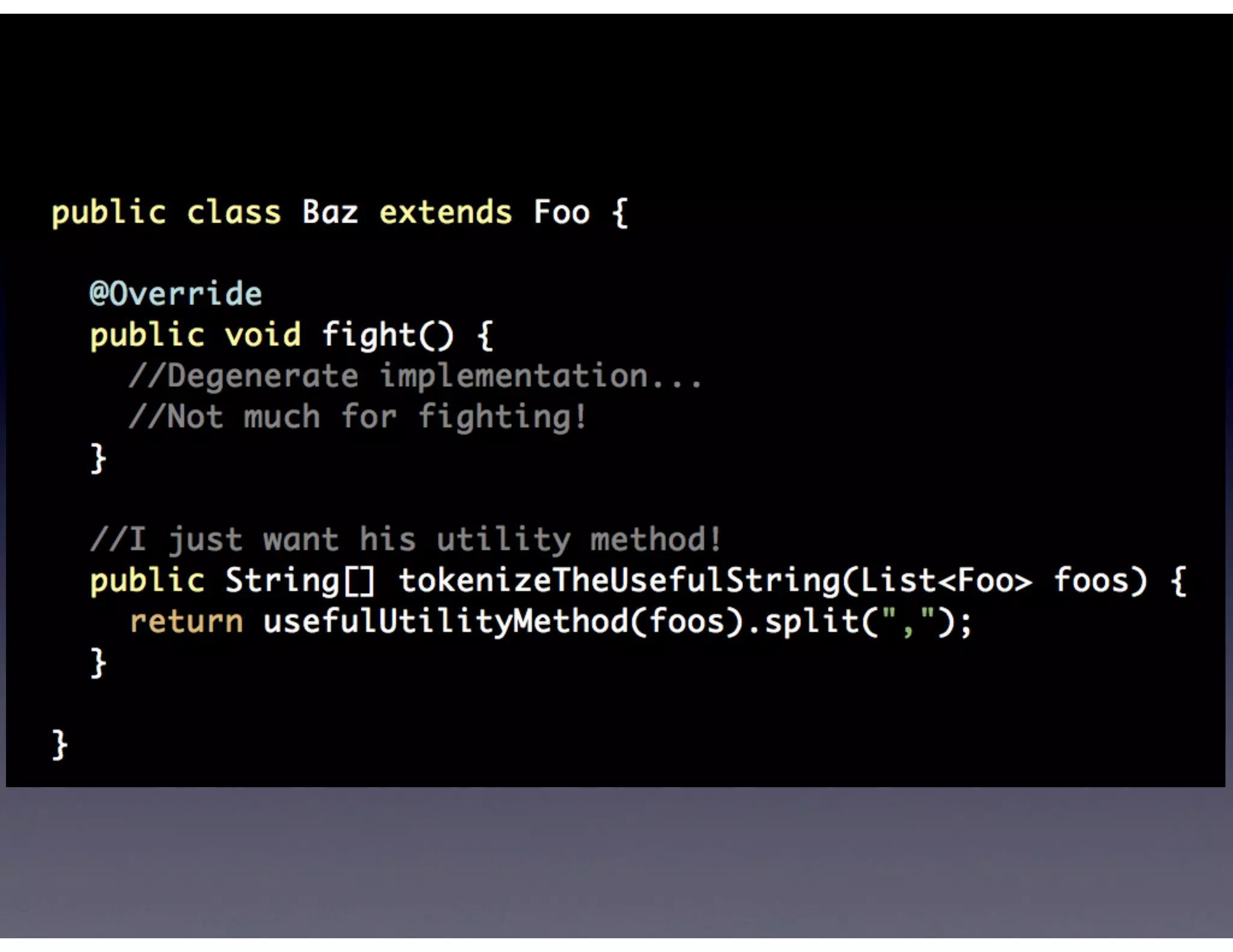
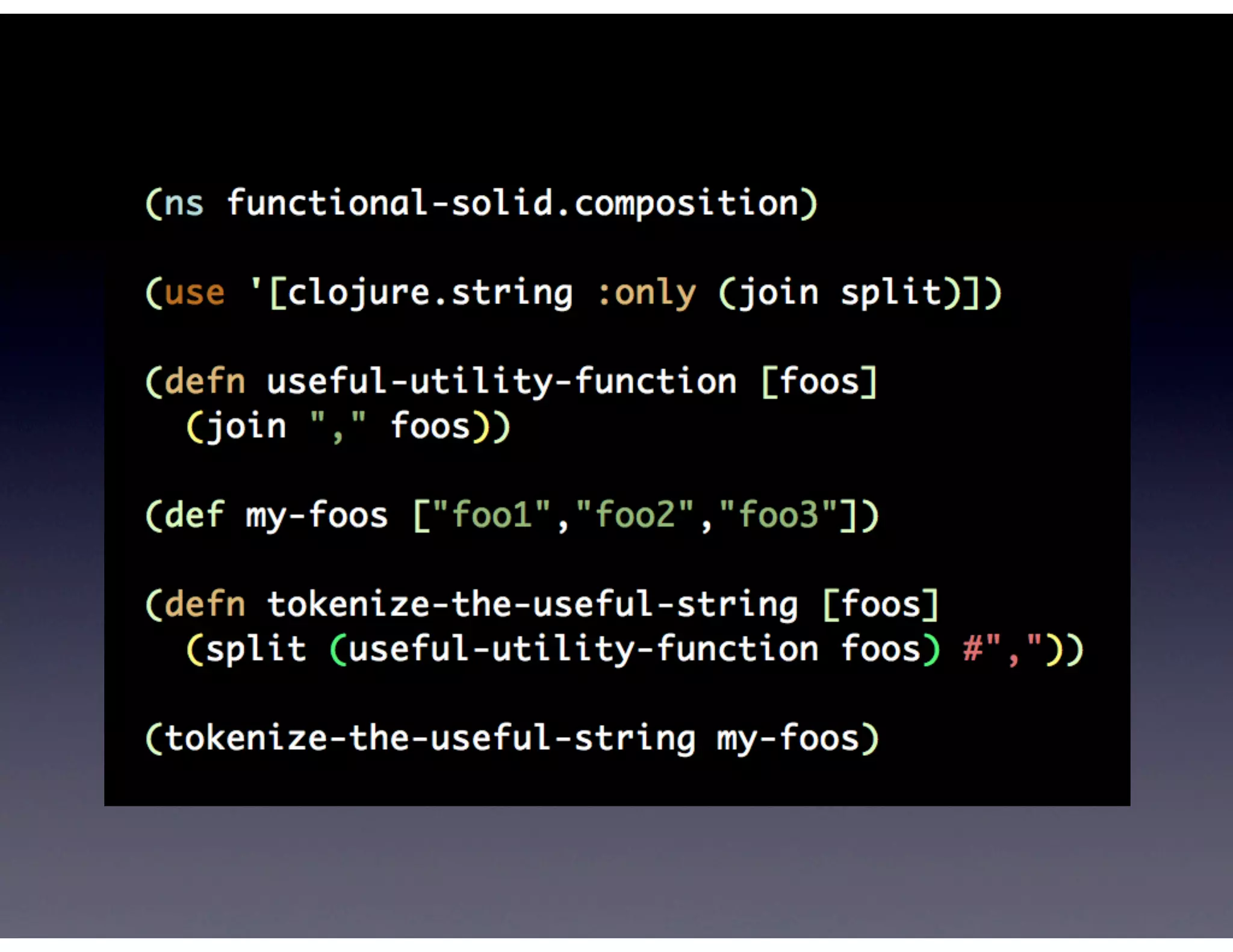
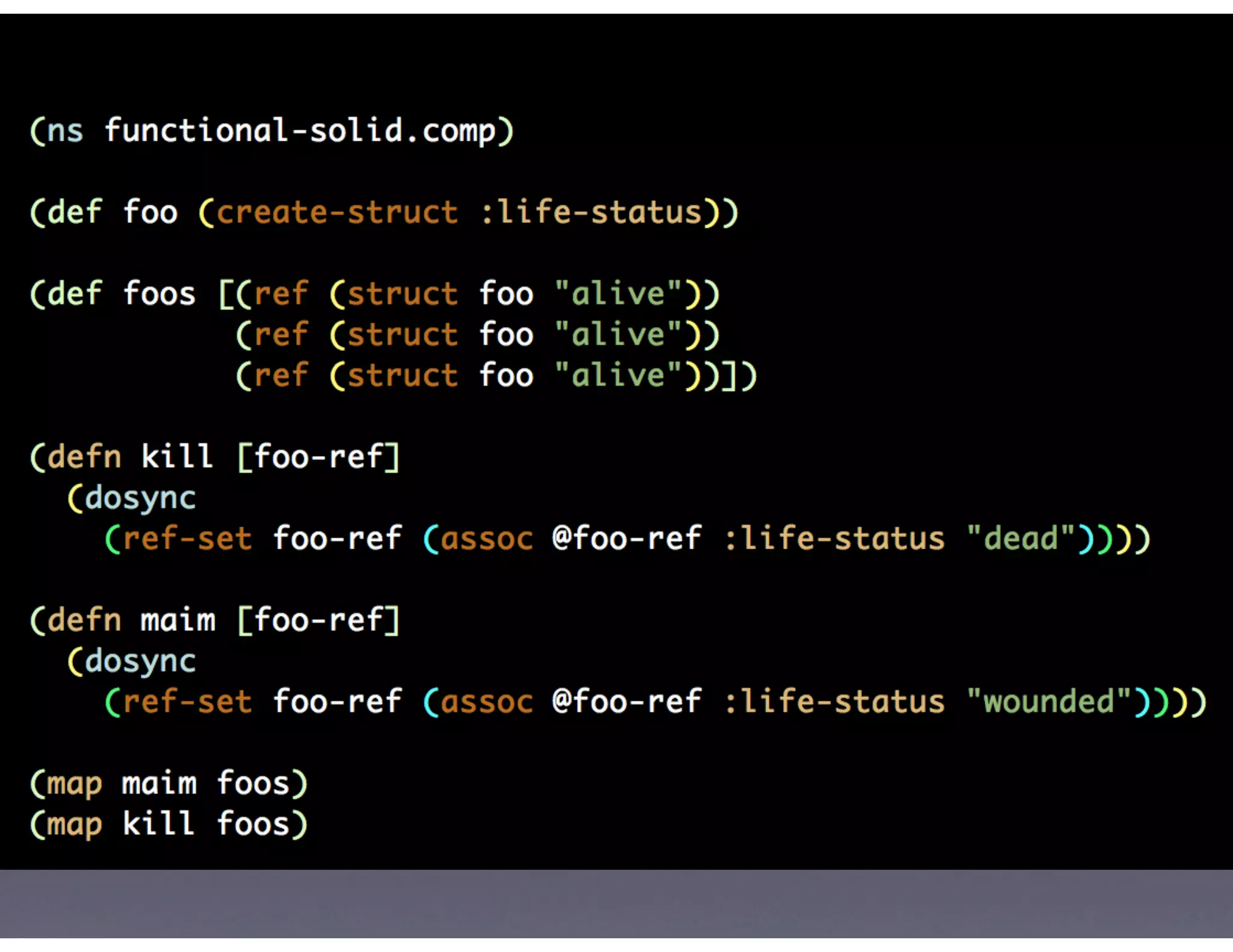
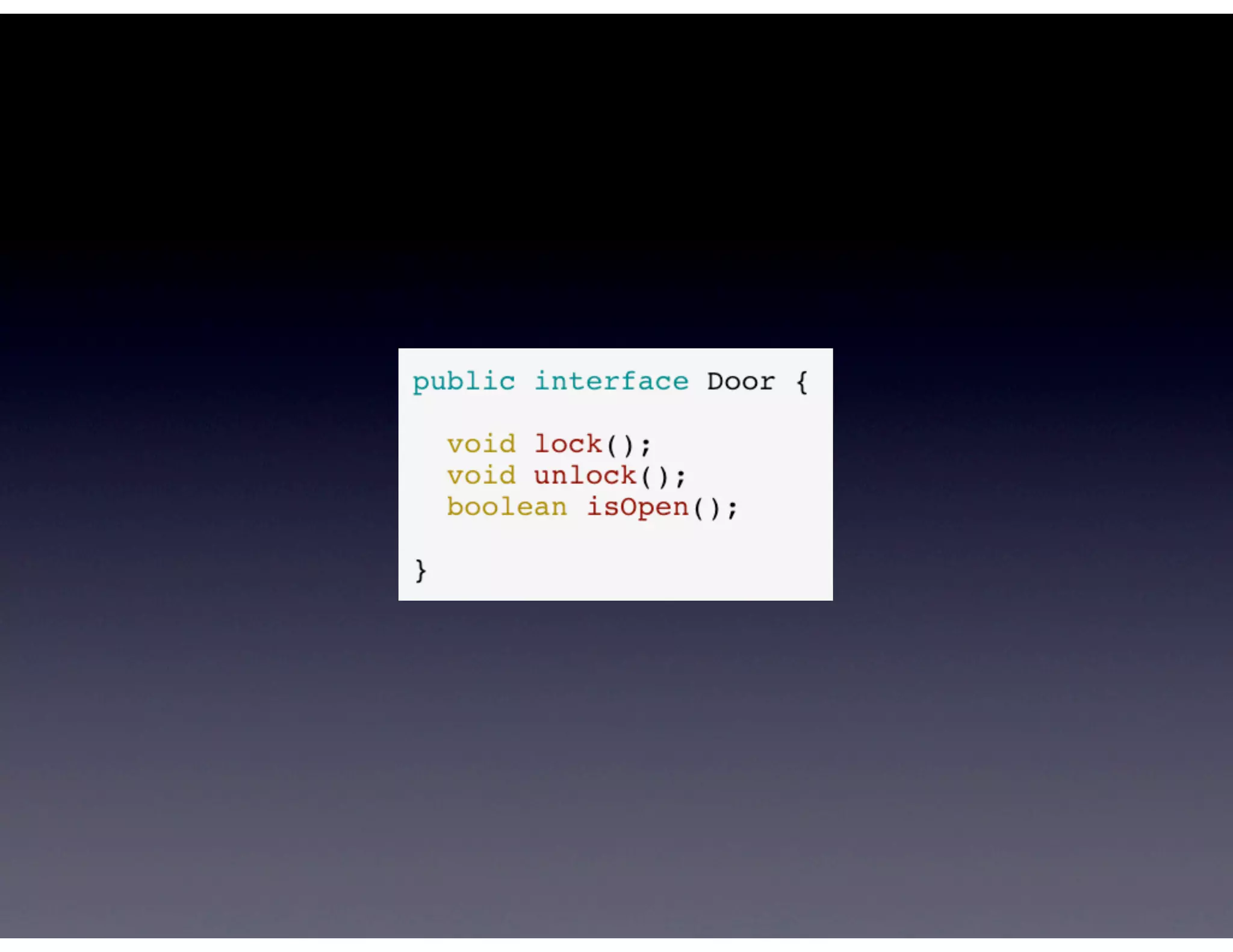
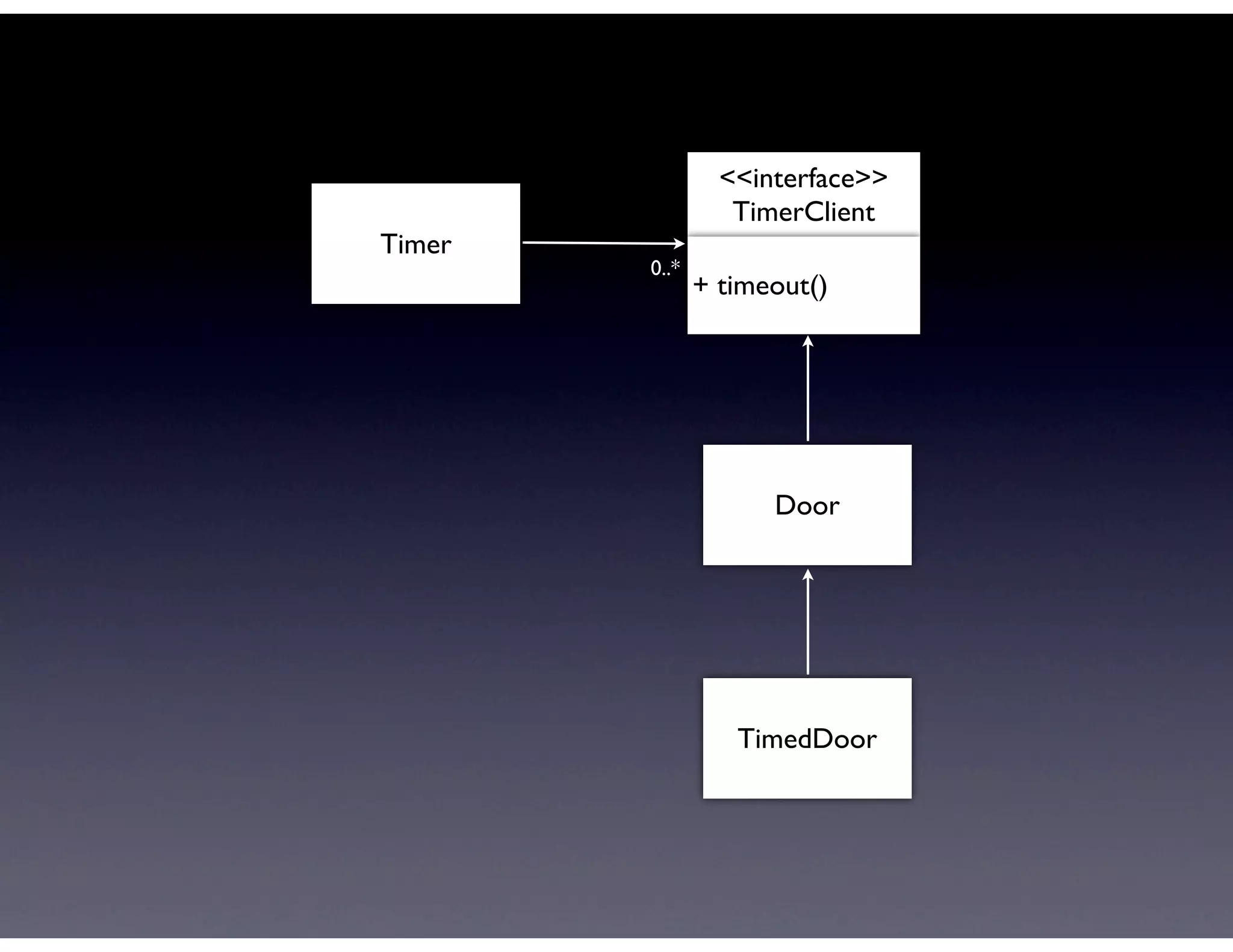
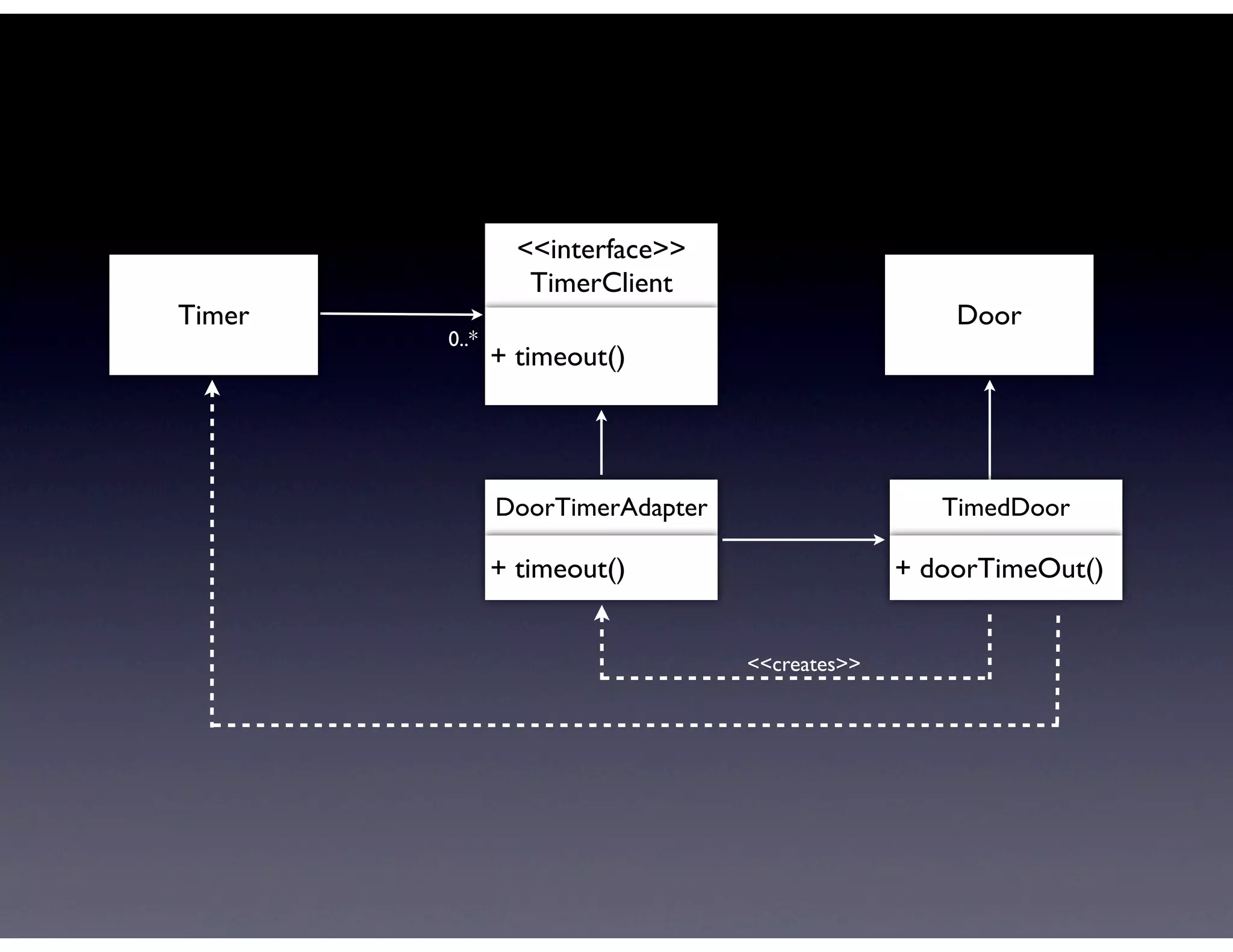
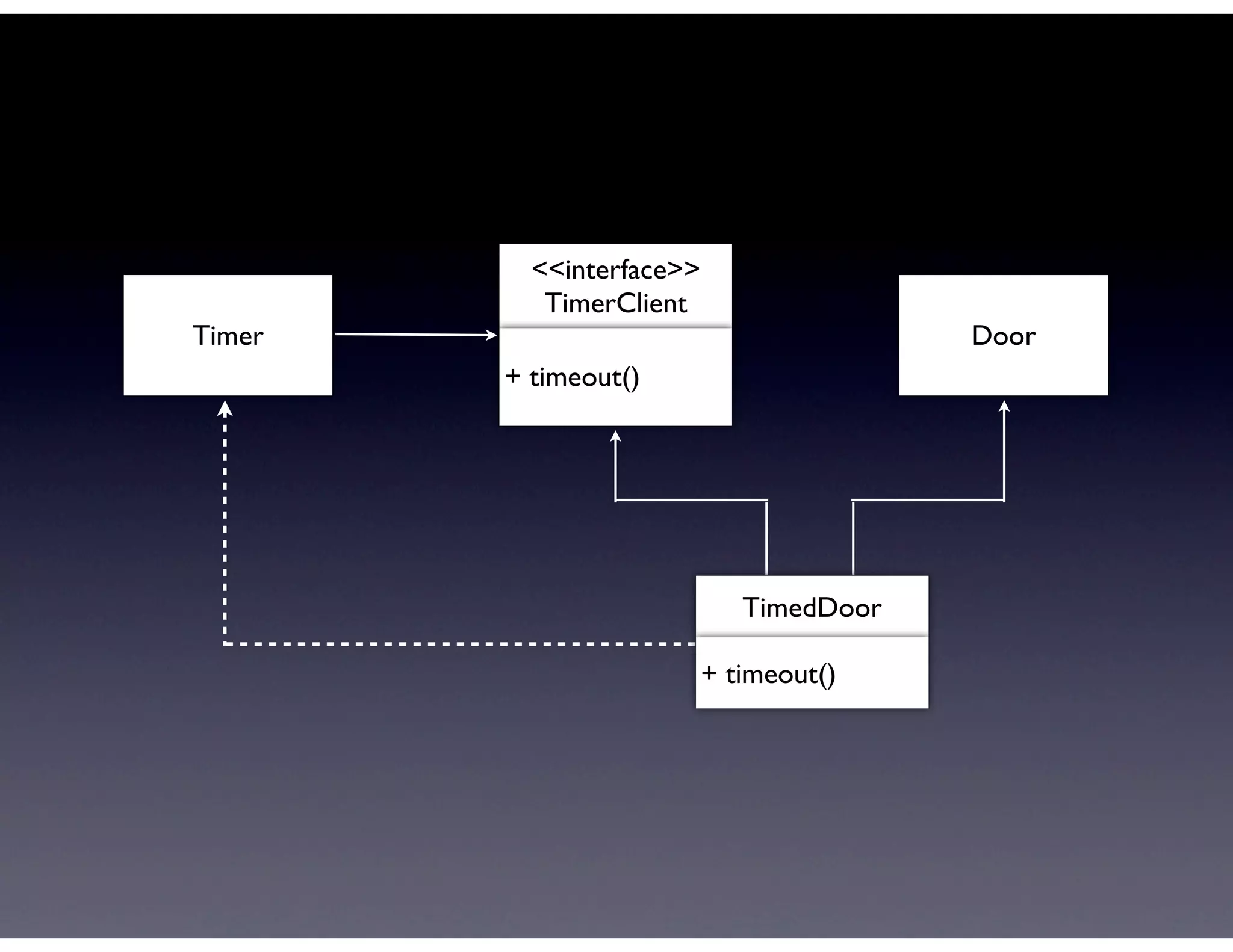
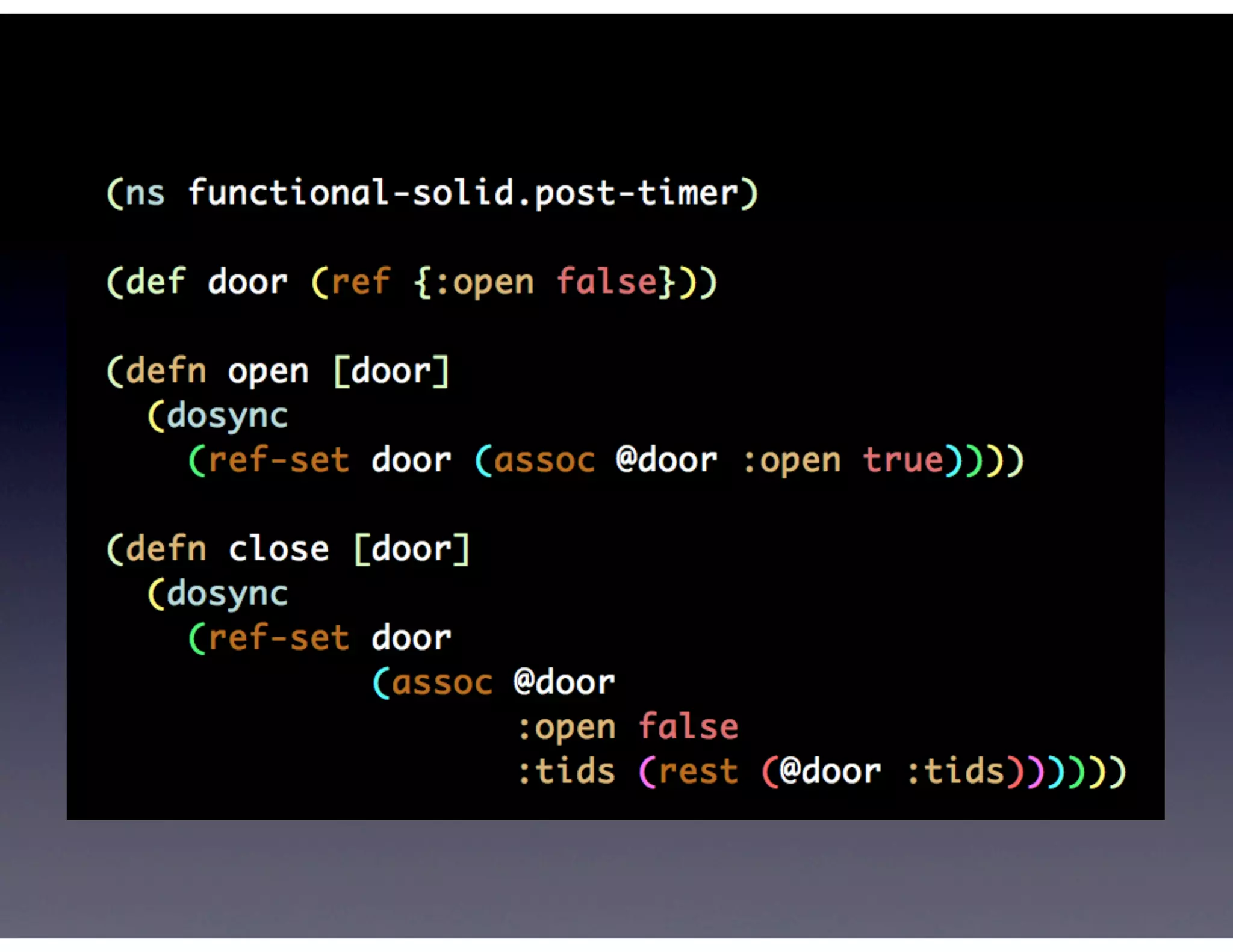
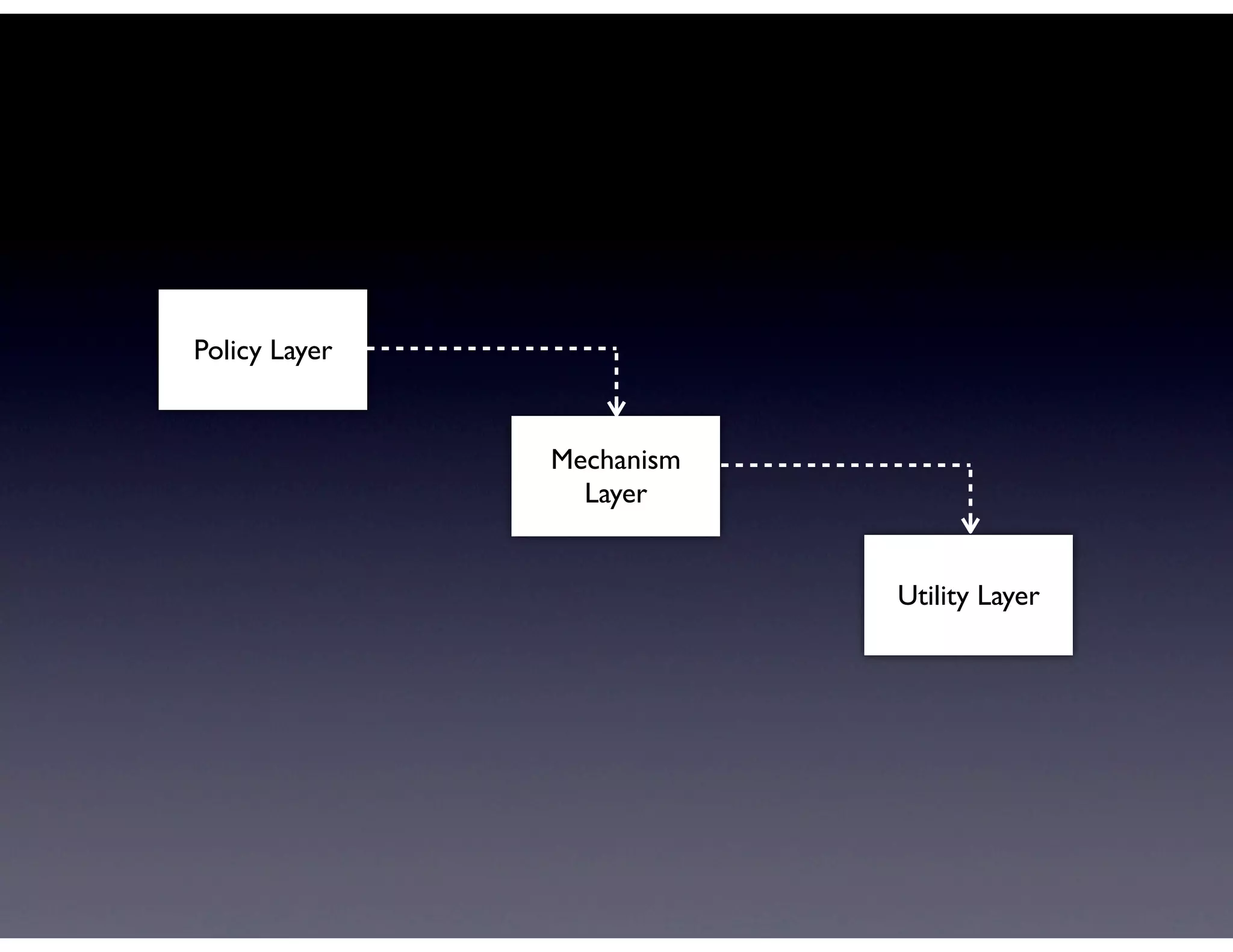
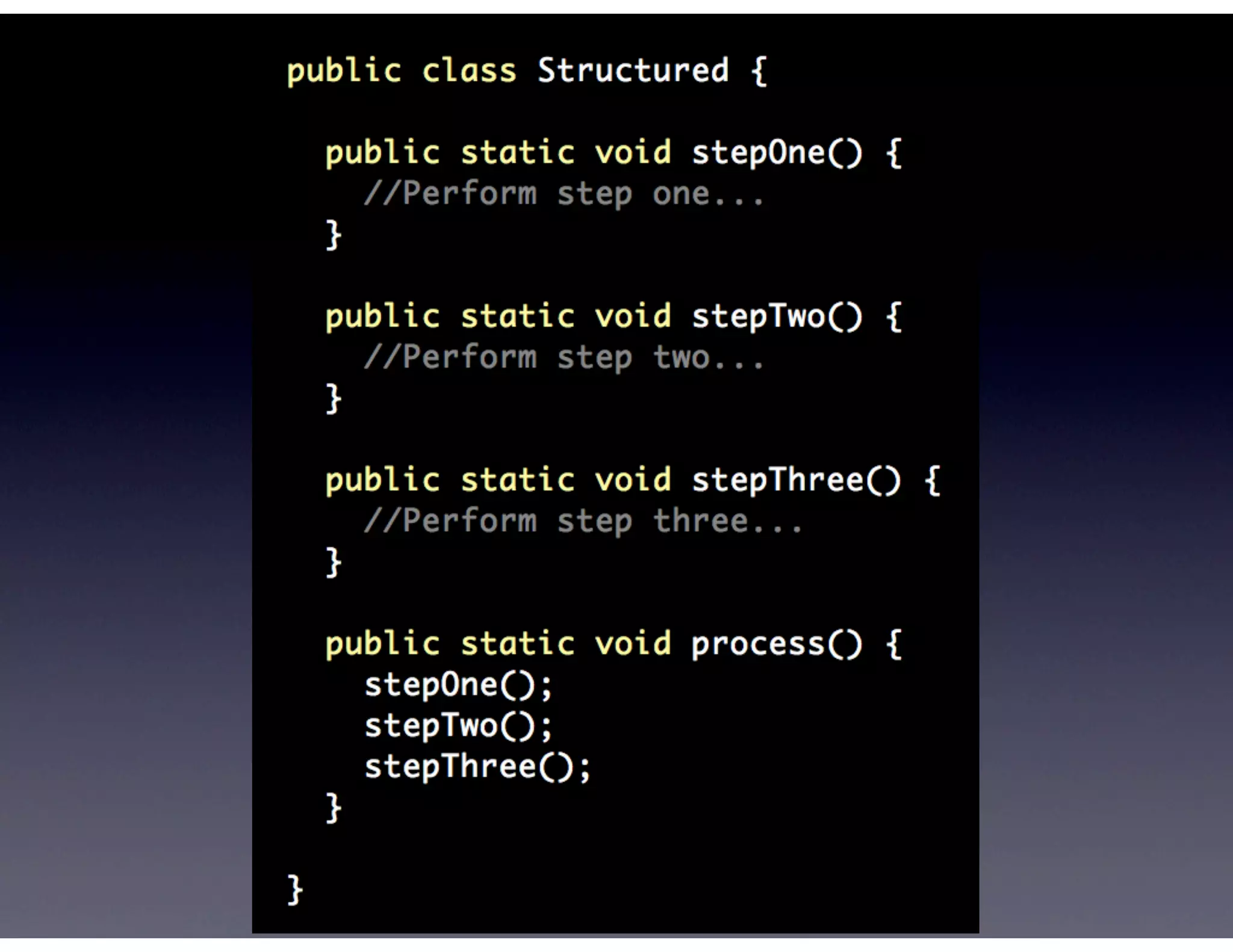
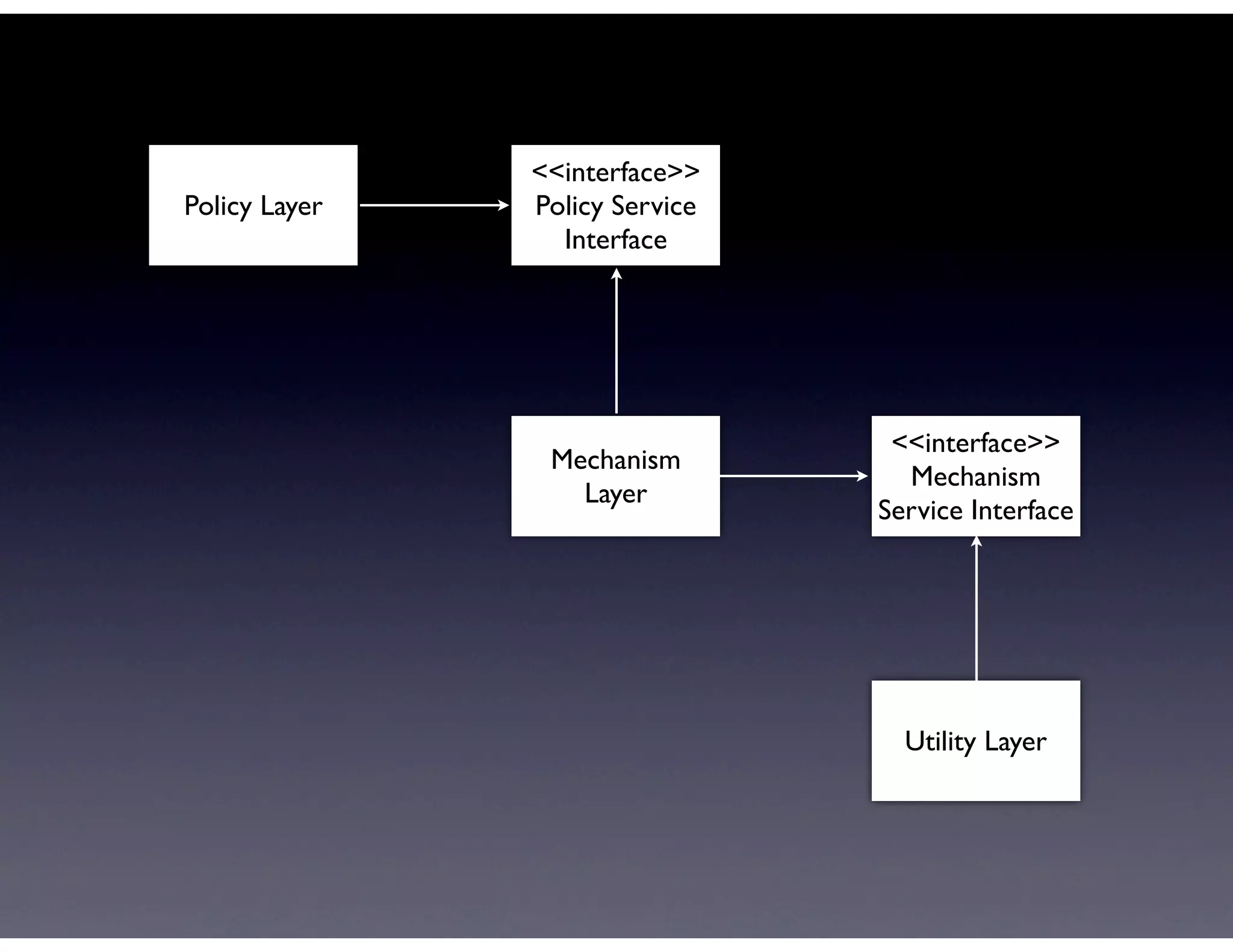
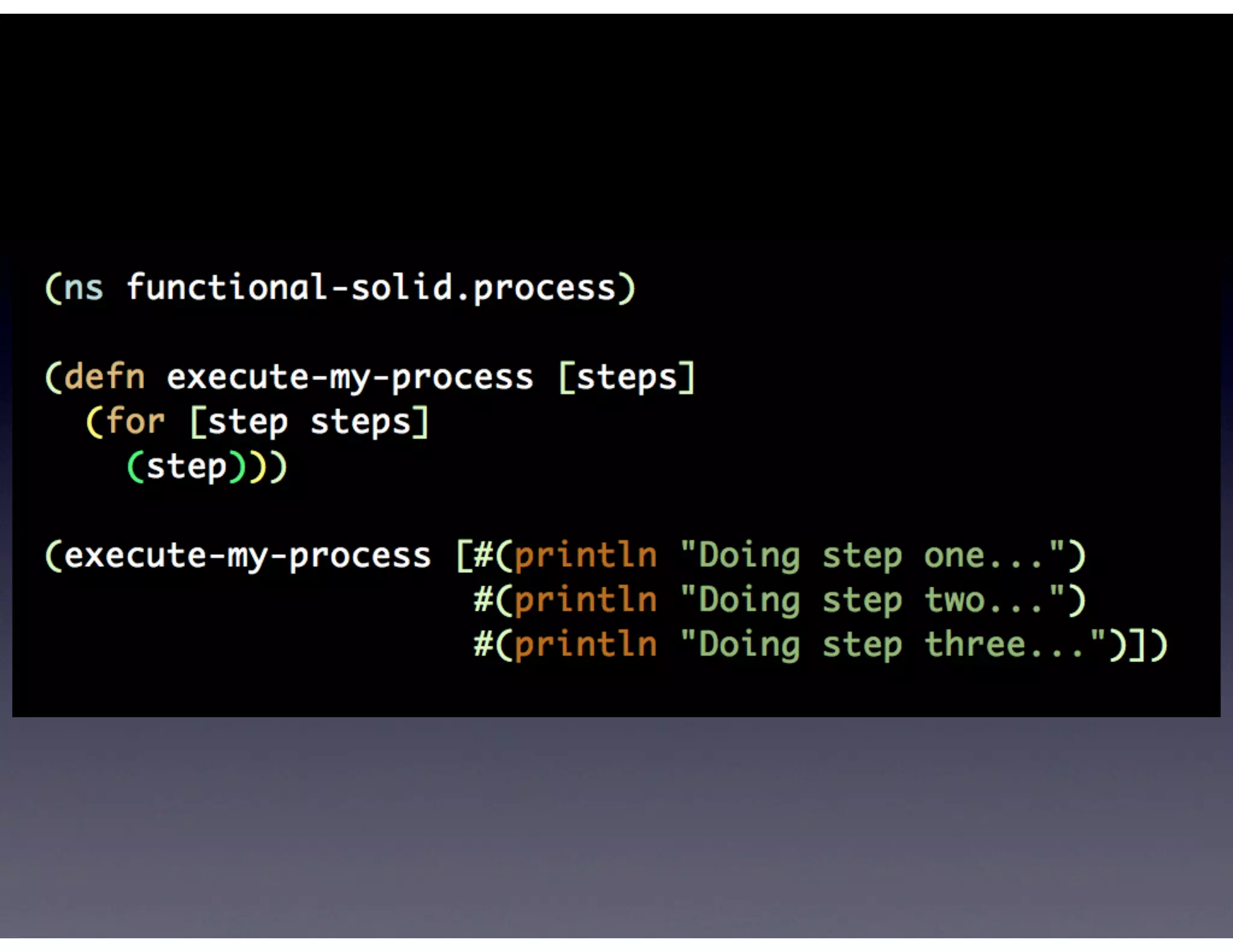
This document provides biographical information about the speaker Matt Stine and outlines the topics he will cover in his presentation. Stine will discuss how software designs tend to degrade over time due to various factors, and how following the SOLID principles of object-oriented design can help address this problem and make designs more functional in nature. He will also cover trends in how software systems evolve, different programming paradigms, and the ongoing quest for software design "best practices."