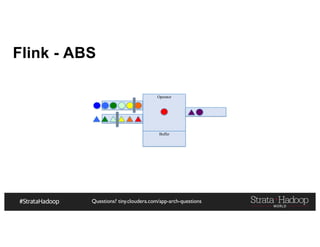
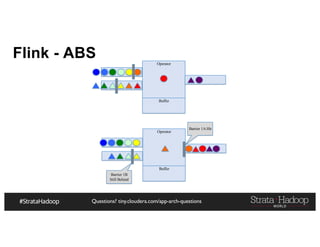
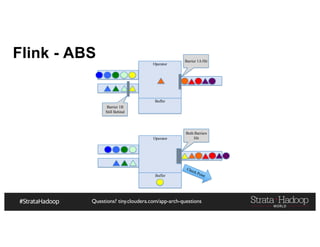
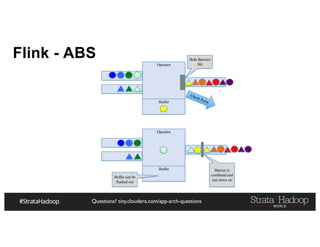
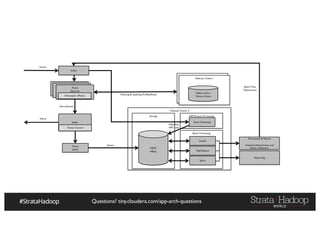
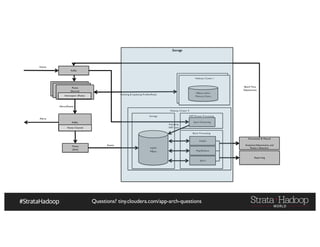
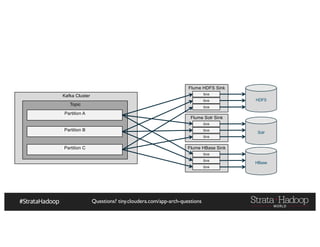
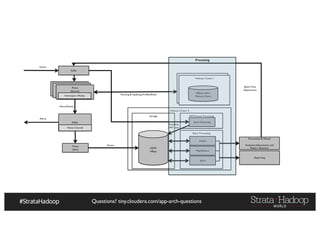
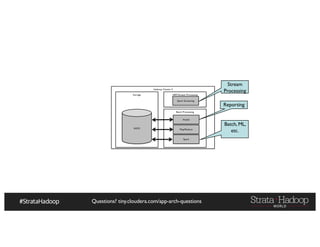
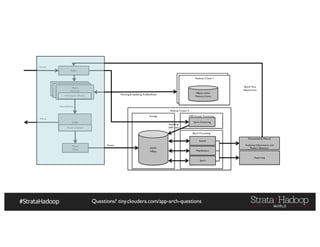
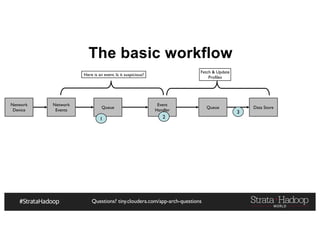
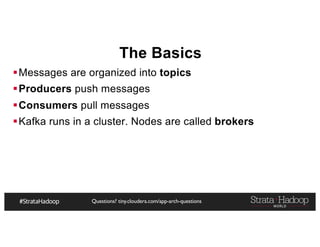
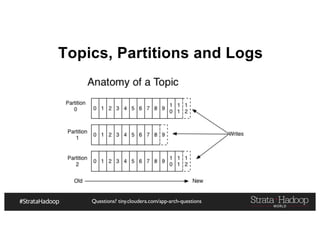
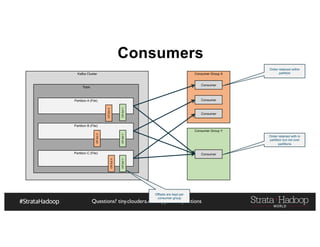
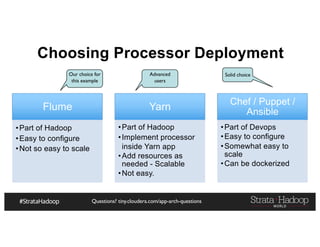
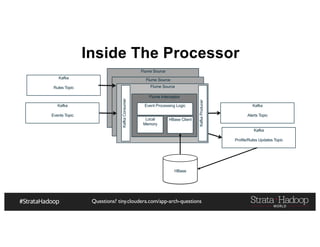
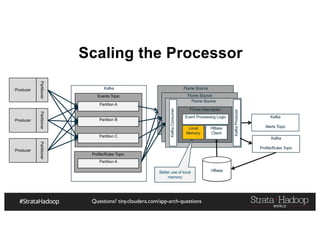
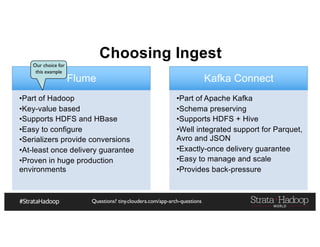
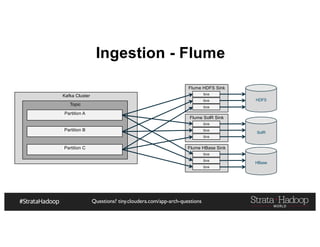
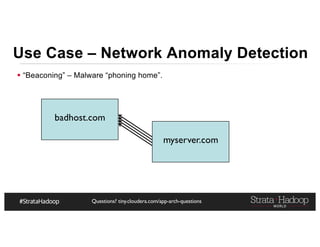
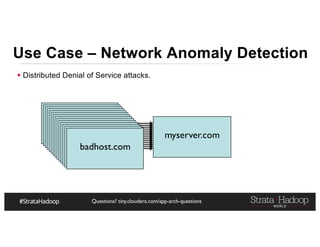
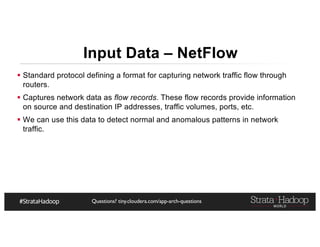
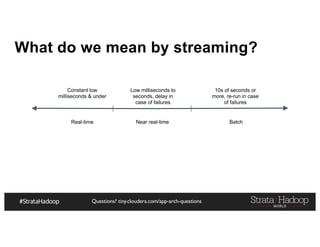
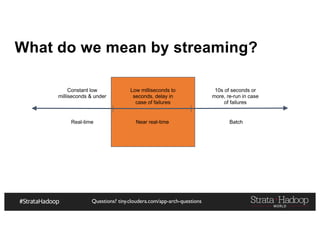
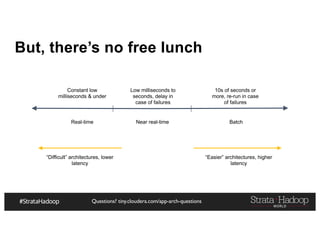
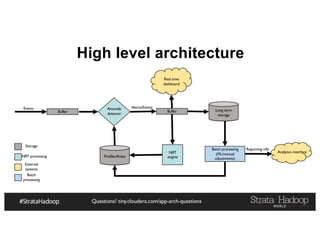
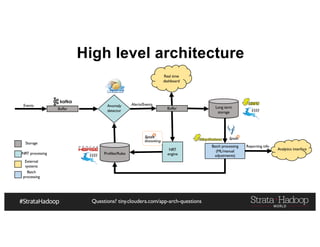
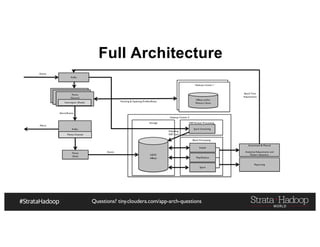
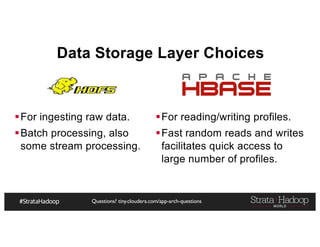
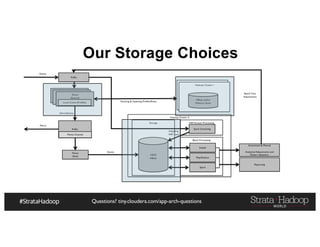
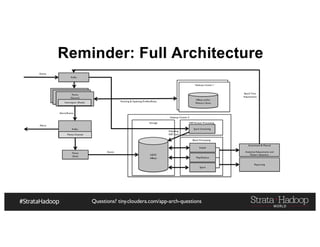
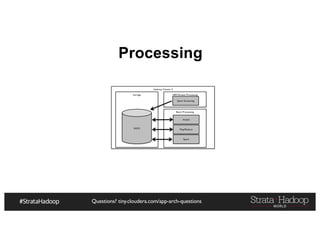
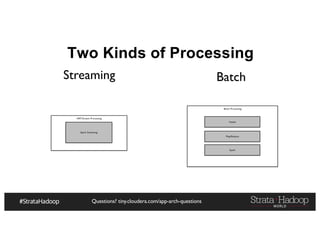
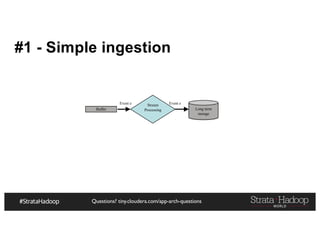
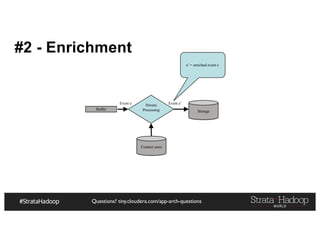
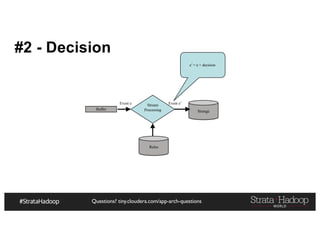
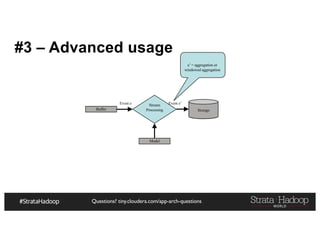
The document provides a detailed overview of Hadoop application architectures focused on fraud detection and anomaly detection in network traffic. It discusses various use cases, architectural challenges, storage considerations, and processing frameworks for real-time and batch data handling. The document also compares different streaming technologies, such as Spark Streaming and Flink, highlighting their features and benefits.



























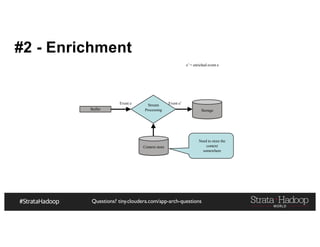

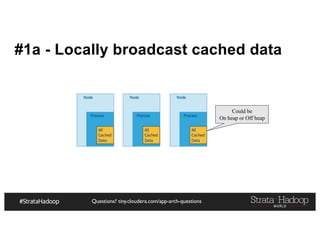
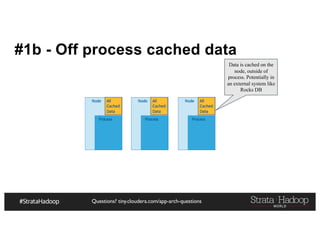
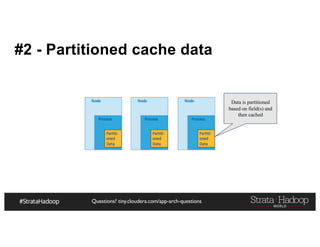
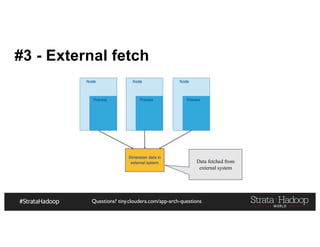
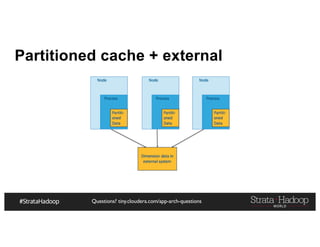


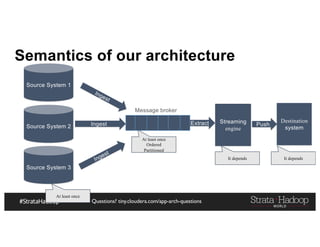

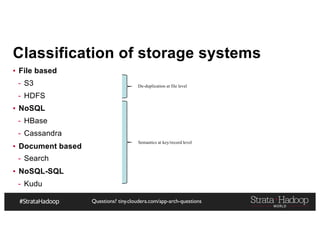


![Questions? tiny.cloudera.com/app-arch-questions
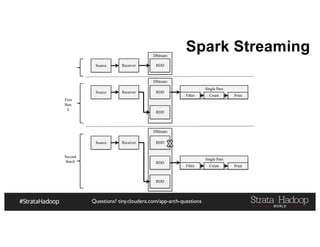
Spark Streaming Example
1. val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]”)
2. val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
3. val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
4. val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
5. val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
6. val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
7. wordCounts.print()
8. SSC.start()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haafraudlunchv1-161101005315/85/Fraud-Detection-with-Hadoop-67-320.jpg)
![Questions? tiny.cloudera.com/app-arch-questions
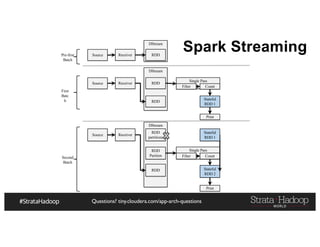
Spark Streaming Example
1. val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]”)
2. val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
3. val lines = sc.textFile(path, 2)
4. val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
5. val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
6. val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
7. wordCounts.print()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haafraudlunchv1-161101005315/85/Fraud-Detection-with-Hadoop-68-320.jpg)