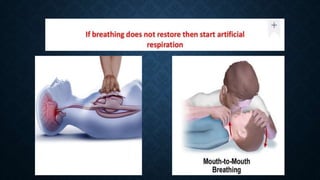
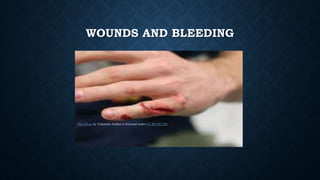
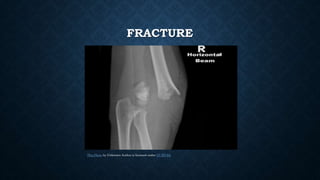
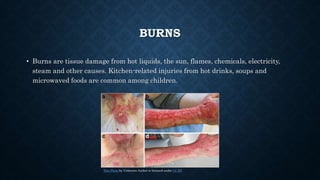
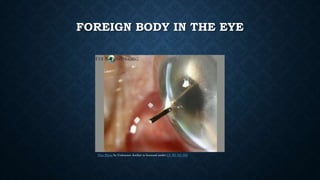
First aid is providing immediate care to someone who is injured or ill. The key priorities of first aid are maintaining an open airway, ensuring breathing and circulation. Common conditions requiring first aid include asphyxia, drowning, shock, wounds, burns, injuries, foreign objects, and poisoning. For each condition, the summary outlines signs and symptoms and provides recommendations for initial management and care until emergency medical services arrive.