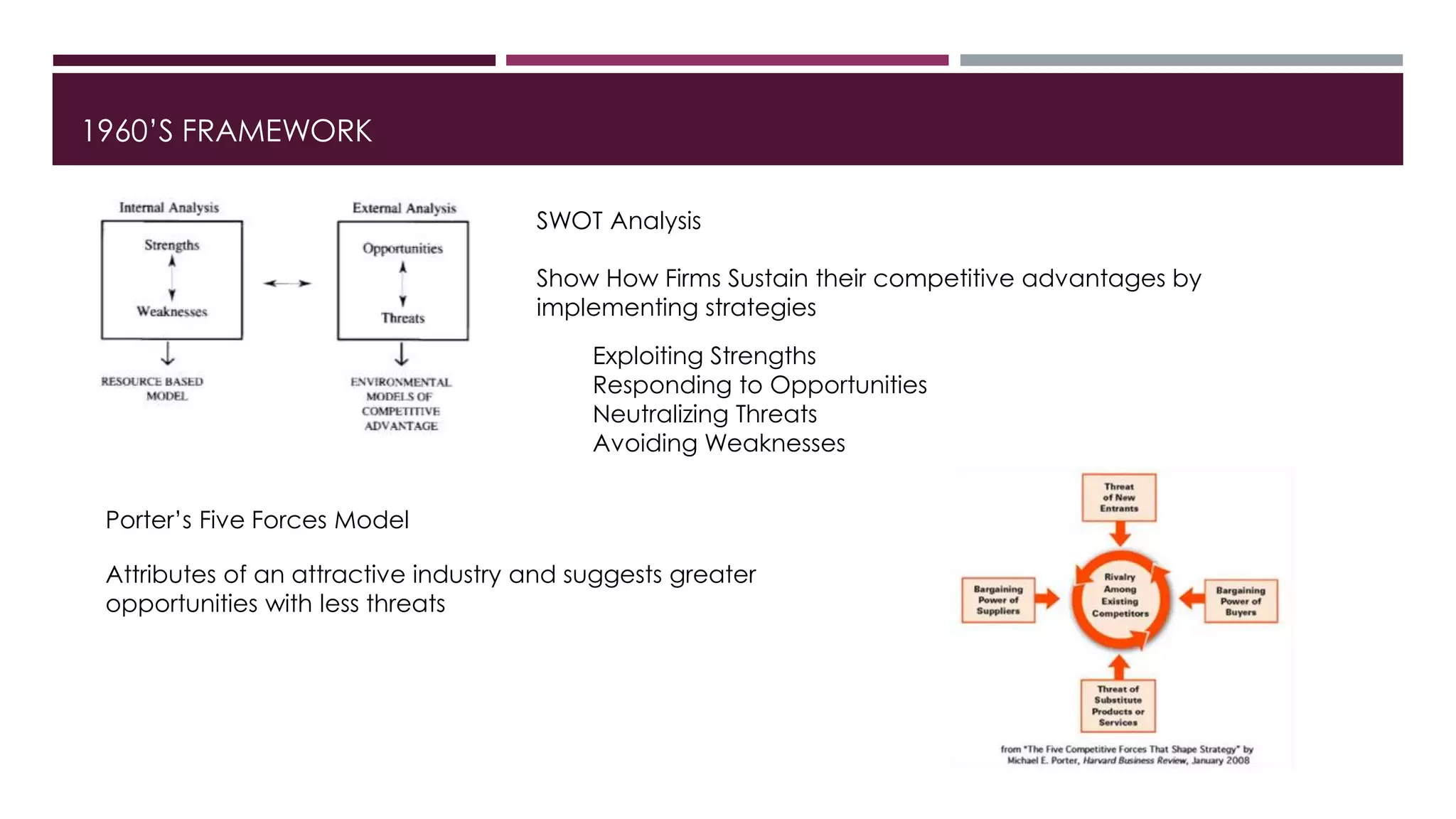
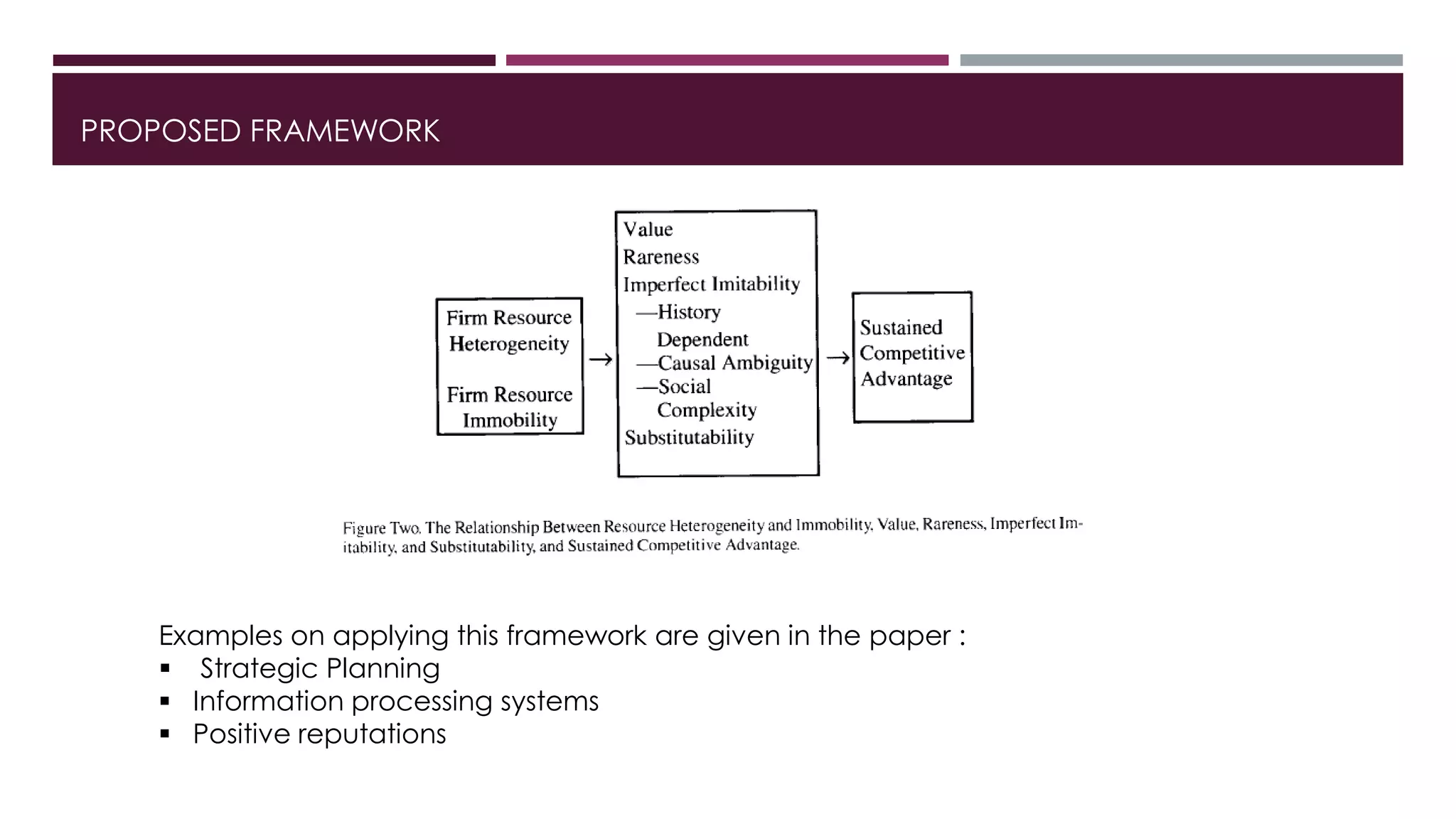
The document discusses a framework for analyzing firm resources as a source of sustained competitive advantage, emphasizing the importance of resource heterogeneity and immobility. It categorizes firm resources into physical, human, and organizational capital, and explores their roles in implementing value-creating strategies that are difficult for competitors to imitate. The paper also raises questions about the implications of resource characteristics on achieving sustained competitive advantage and their impact on social welfare.