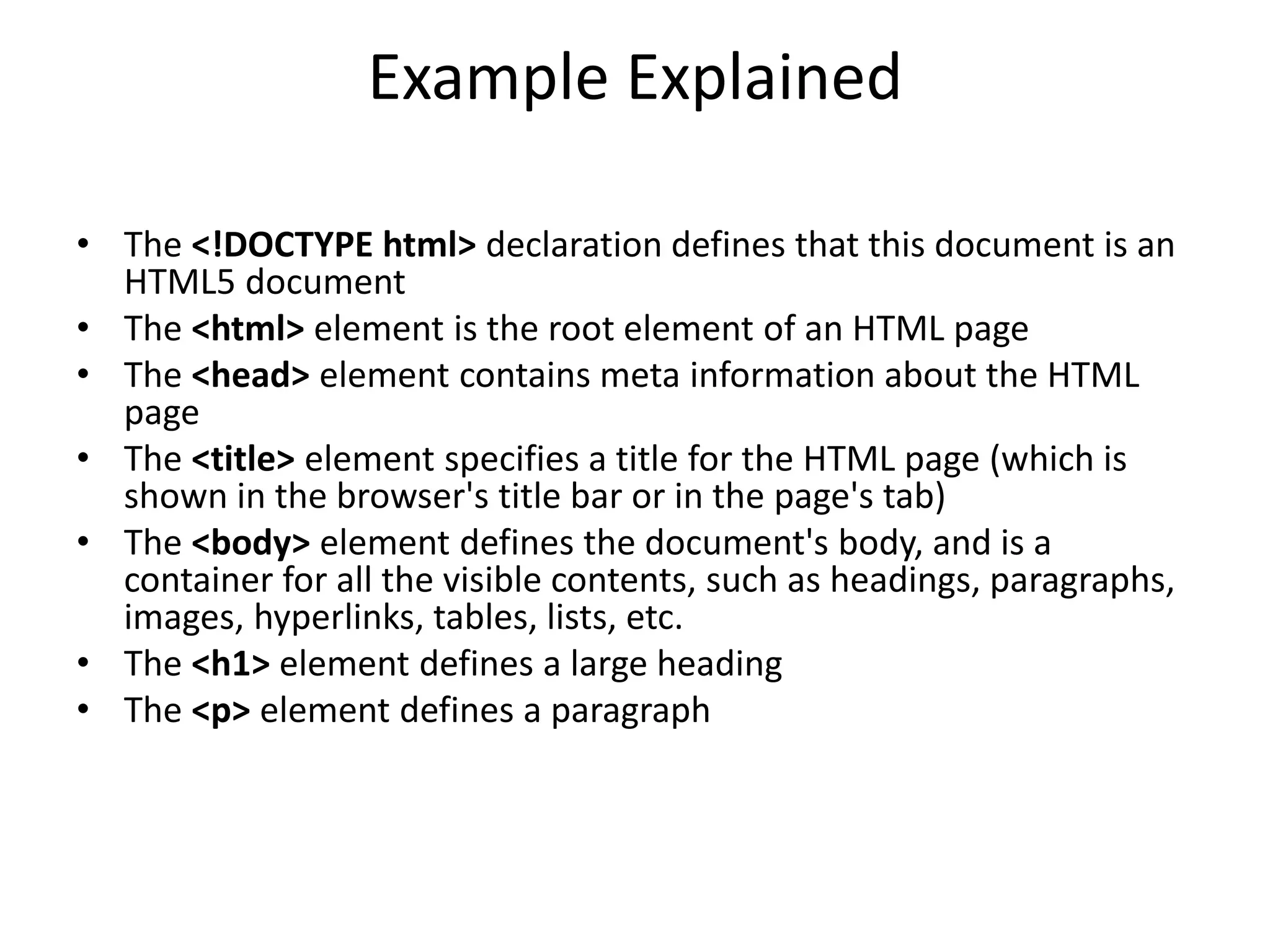
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is the standard markup language used to create web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page using elements like <html>, <head>, <body>, <h1>, <p>, <a>, <img>, which define headings, paragraphs, links, and images. HTML documents are made up of these elements and their attributes, forming a tree structure. The HTML source code of a web page can be viewed by clicking Ctrl+U or the right-click menu.