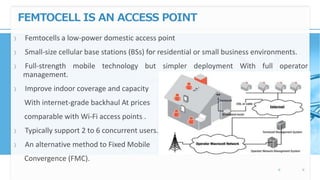
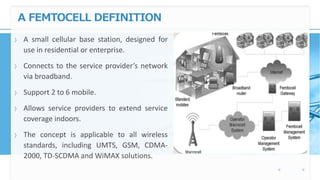
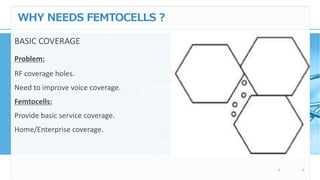
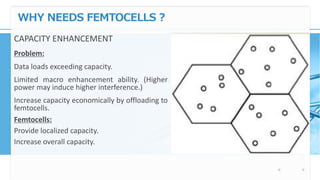
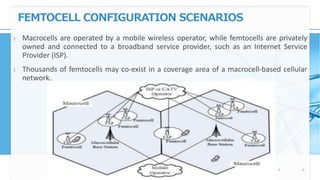
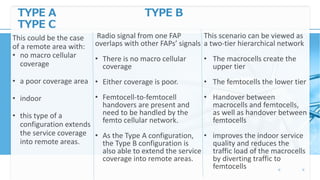
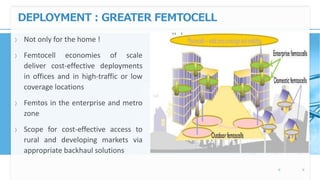
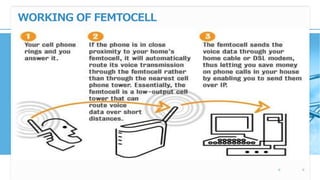
Femtocell technology provides improved indoor mobile phone coverage and capacity. A femtocell is a small cellular base station that connects standard mobile devices to a mobile operator's network using a residential broadband connection. Femtocells enhance signal quality and coverage for mobile users inside homes and offices by establishing a mini cellular network connected to the macro network of the mobile operator. They offer benefits like improved coverage, increased network capacity, and a better user experience for calls made indoors.




![FEMTOCELL : FEMTOFORUM
〉 Femtocells are low-power wireless access points
that operate in licensed spectrum to connect
standard mobile devices to a mobile operator’s
network using residential DSL or cable broadband
connections. [Femto forum]
〉 By 2013, 204 million users on 60 million access
points worldwide. [ABI Research]
〉 Femtocell base station is also known as home
basestation, home access point, or home Node B.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/femtocell-ppt-161127155622/85/Femtocell-ppt-5-320.jpg)