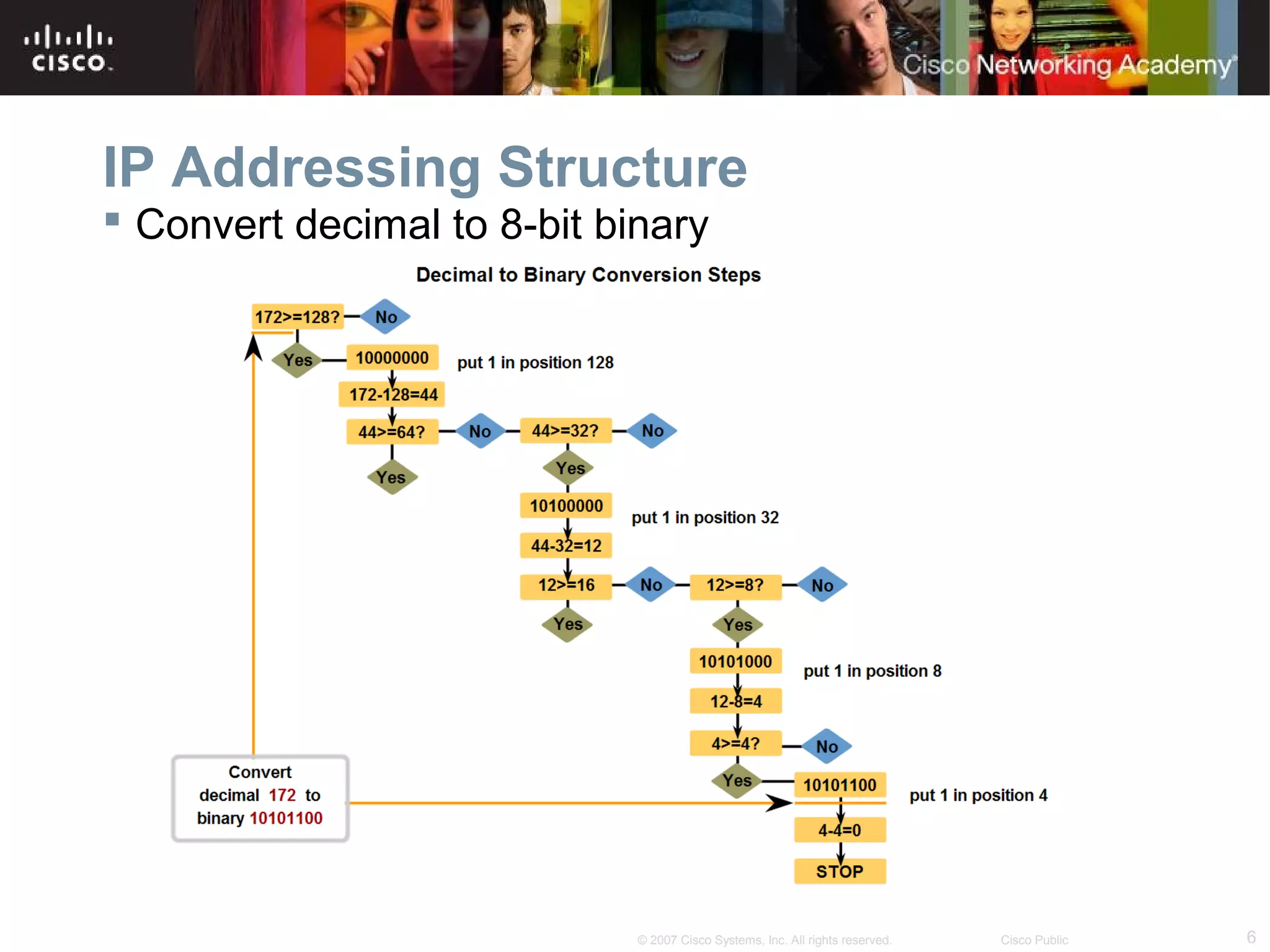
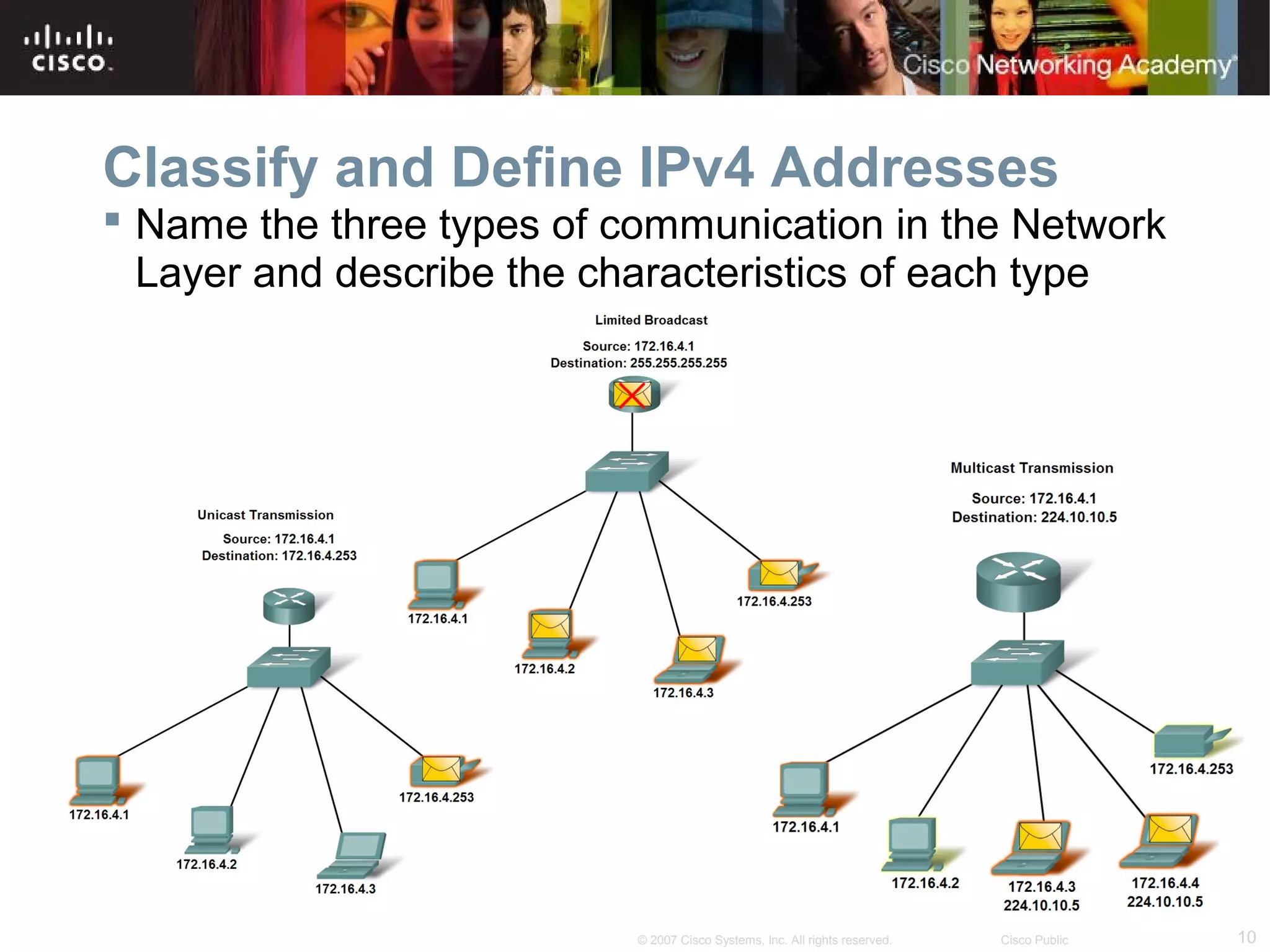
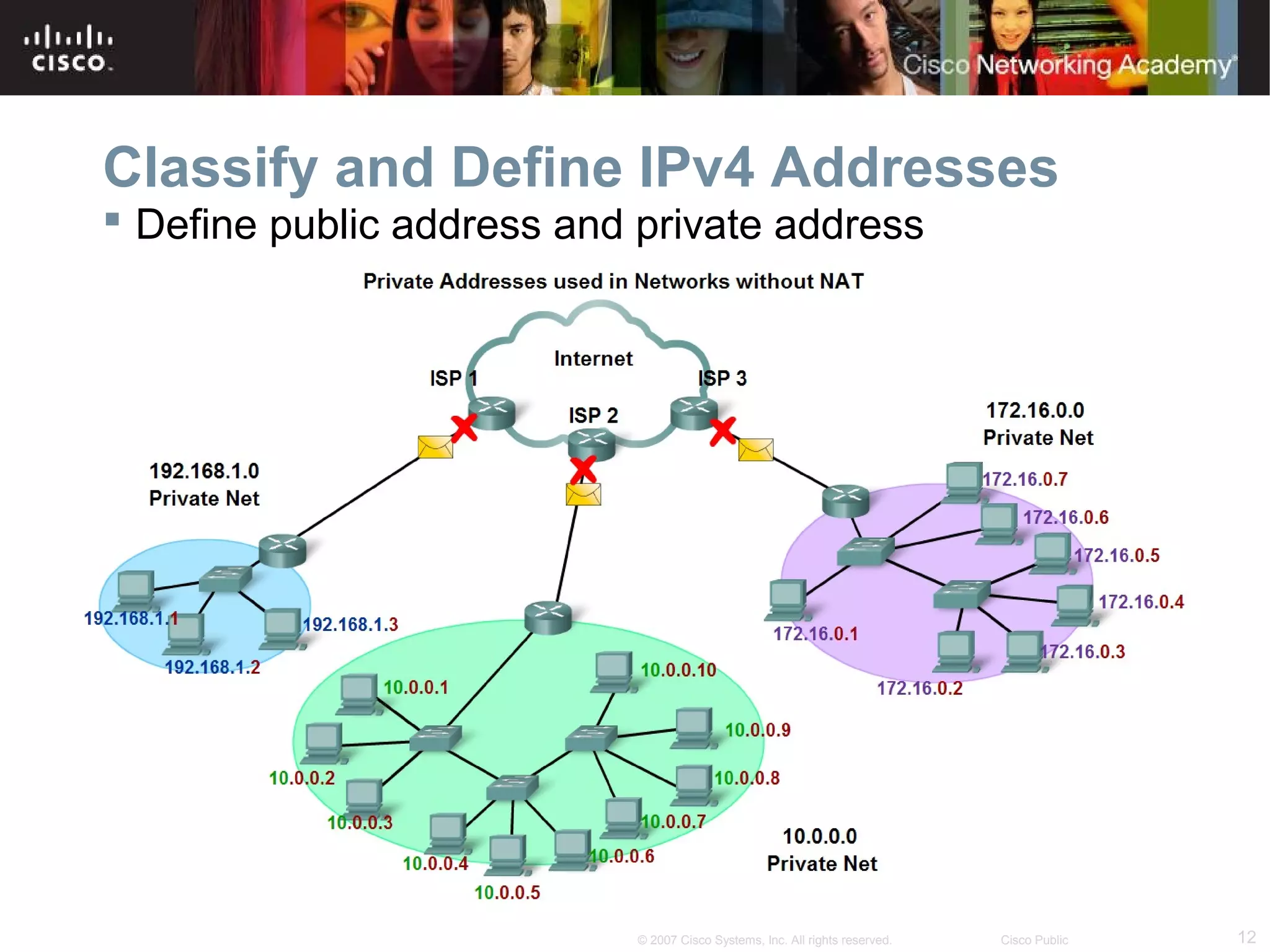
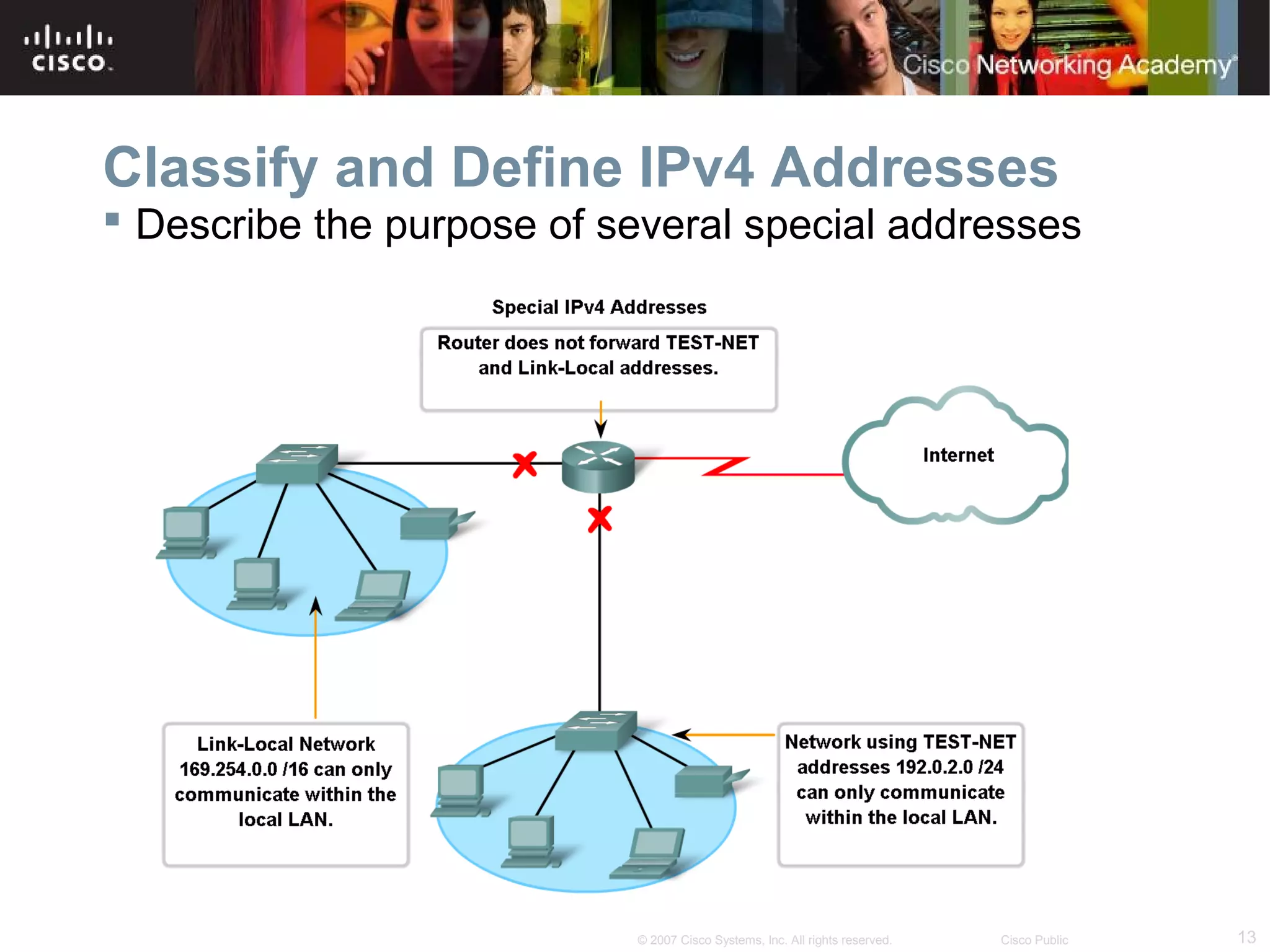
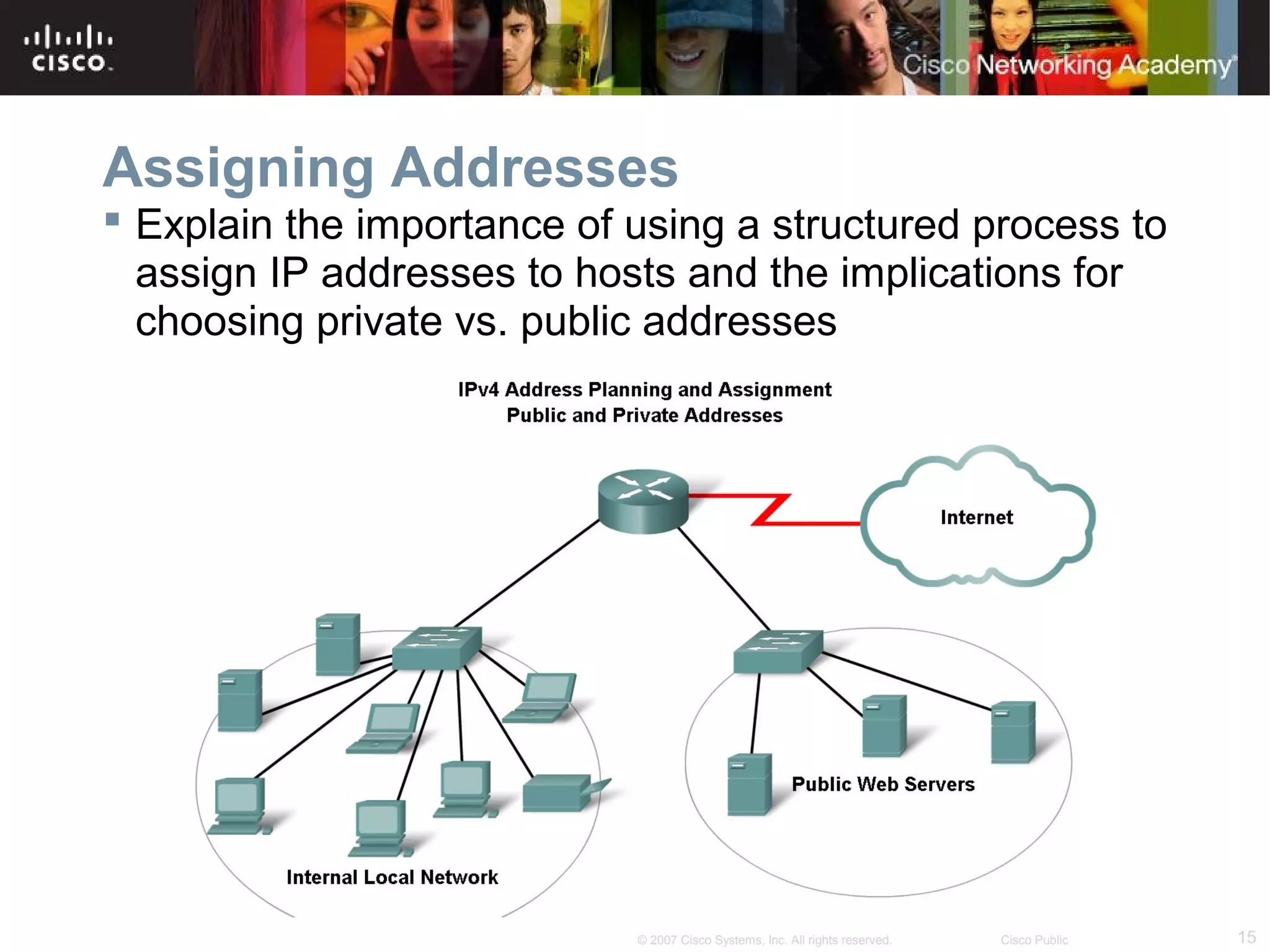
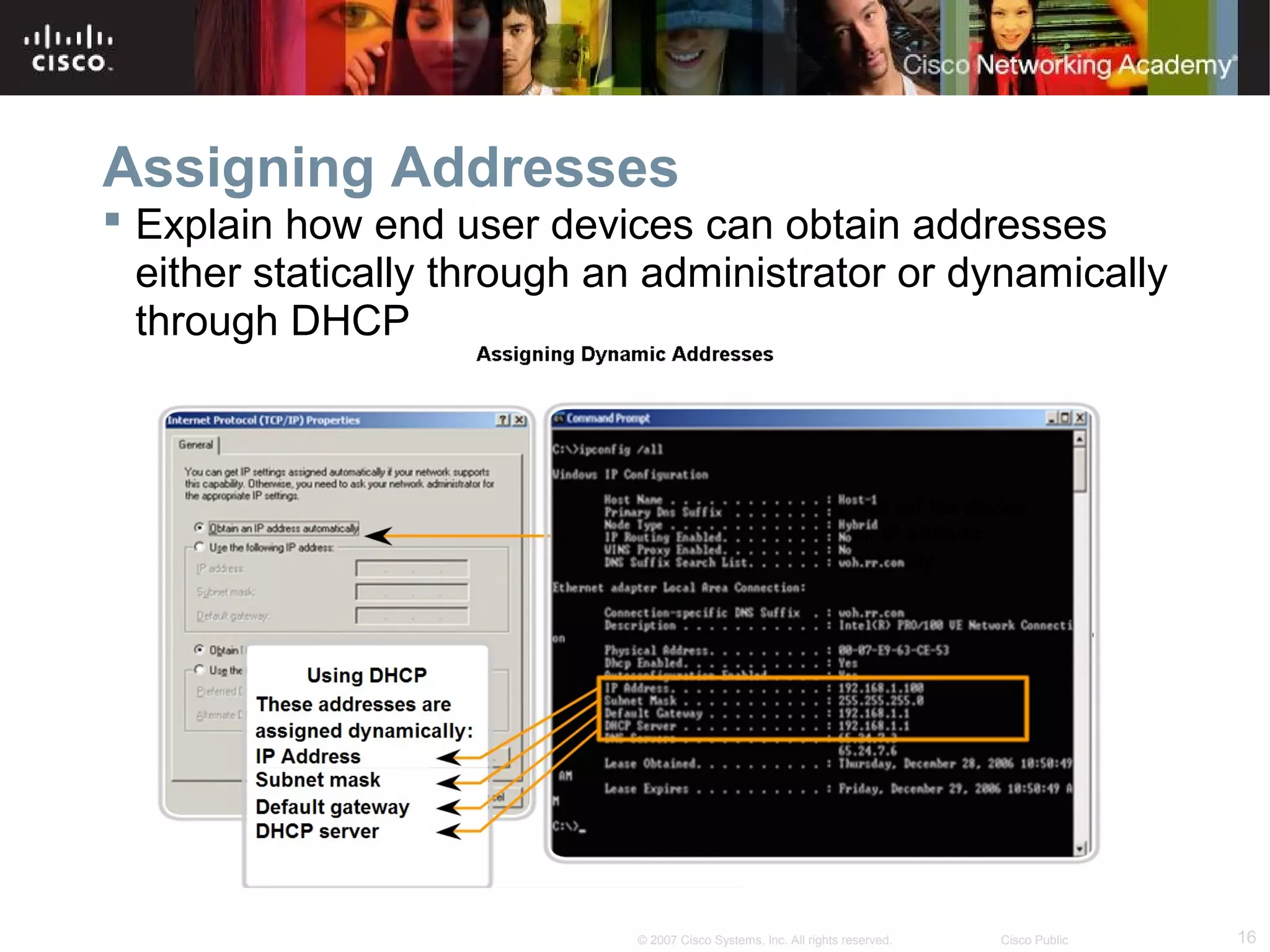
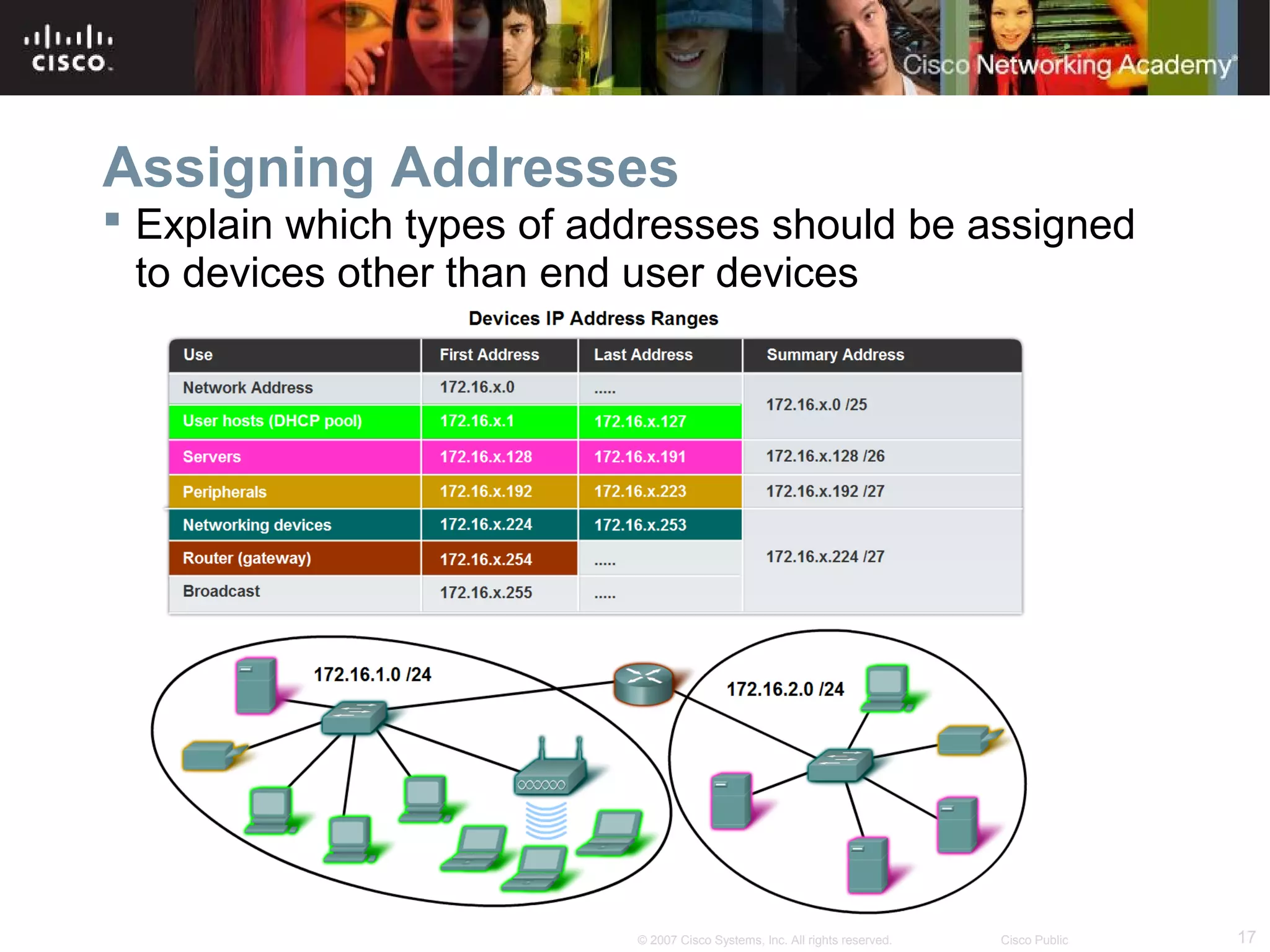
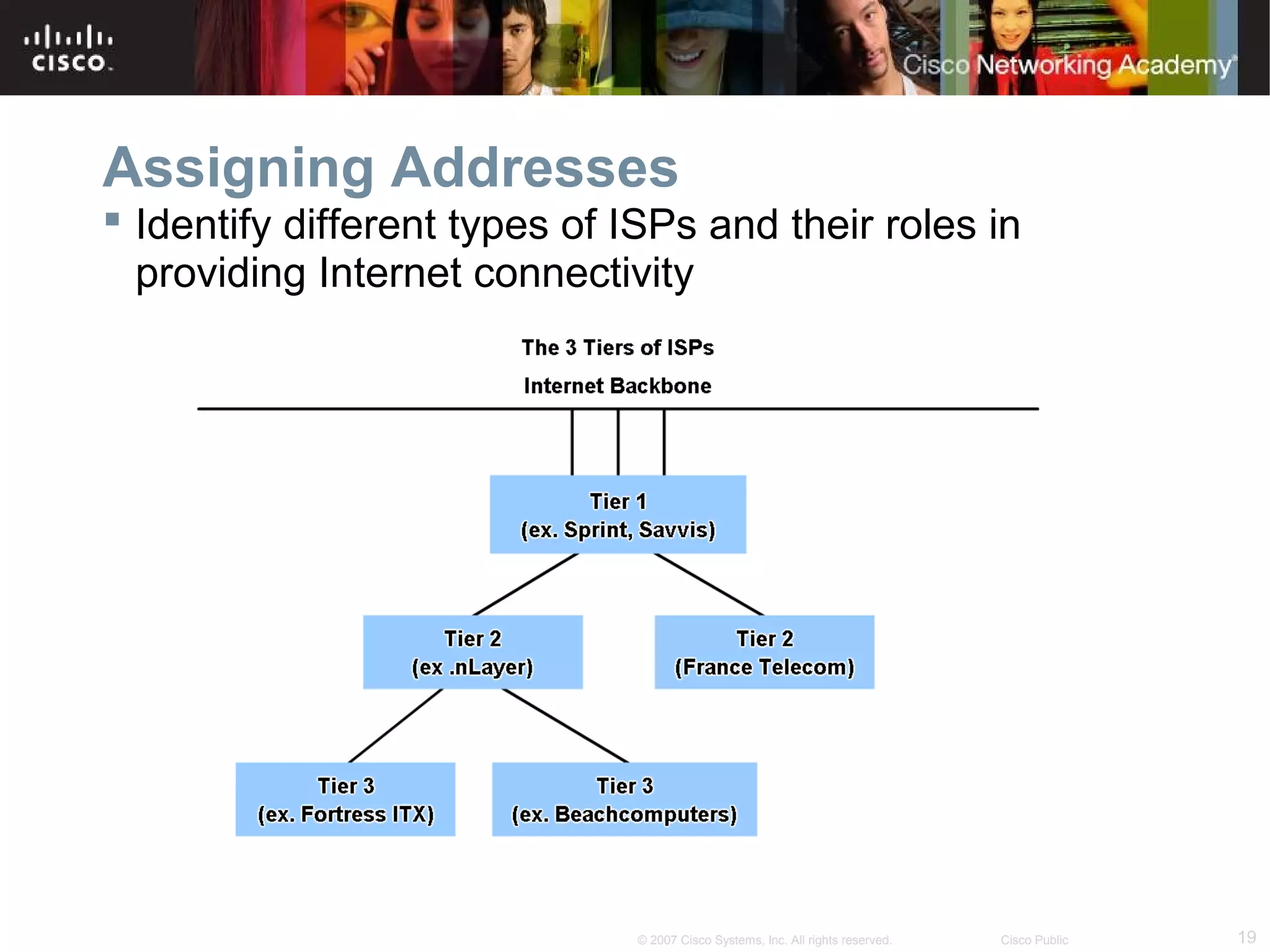
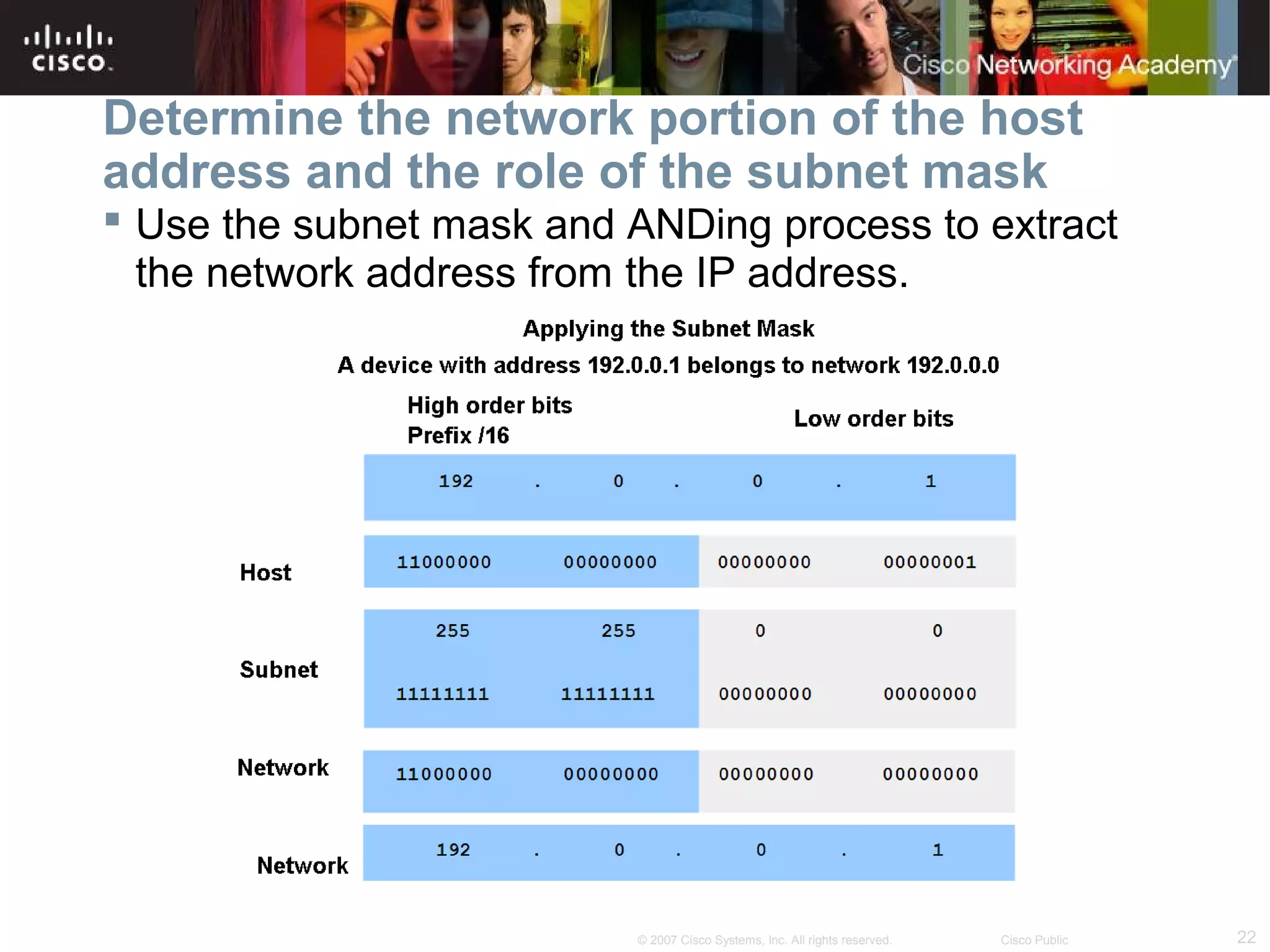
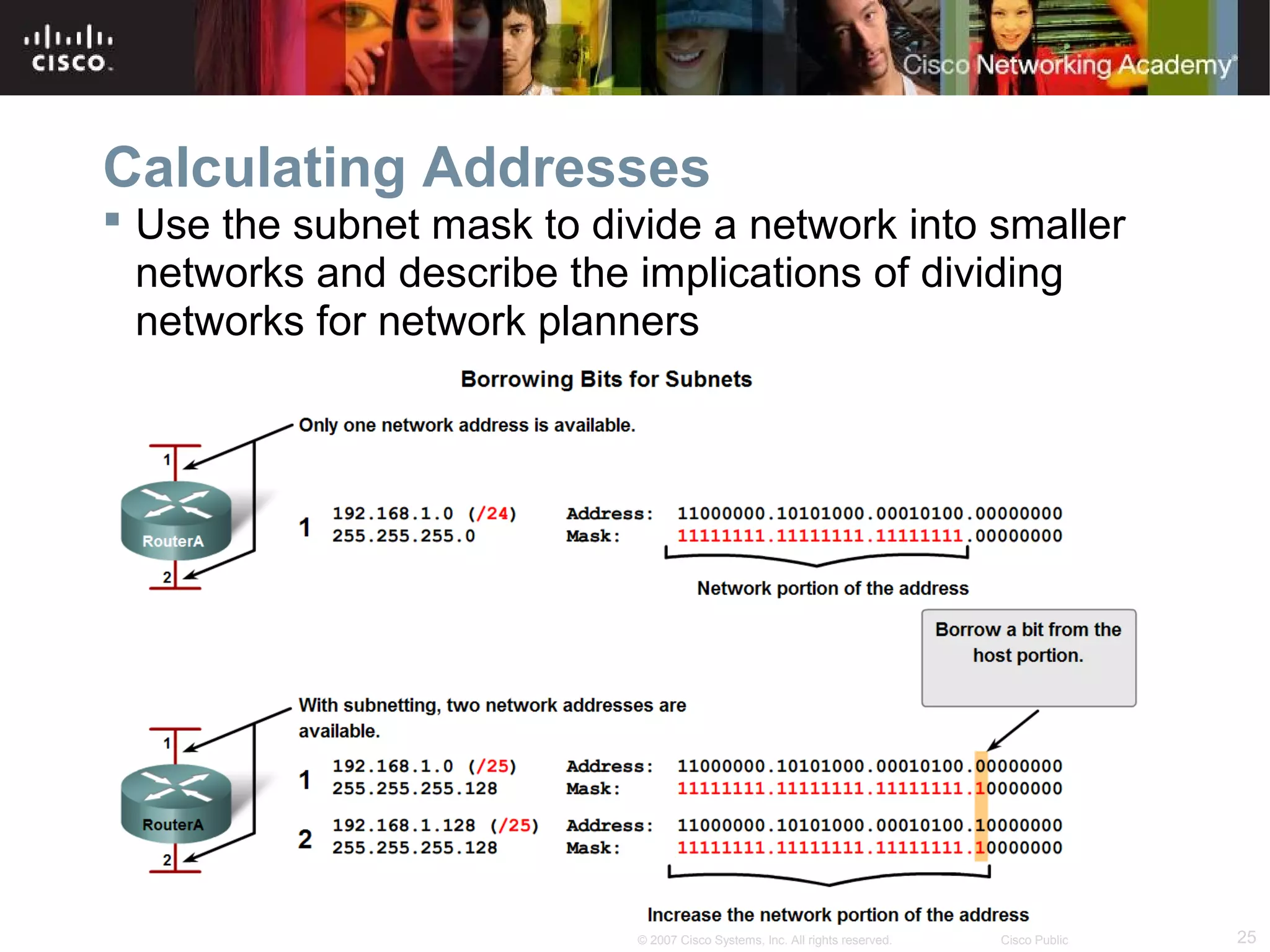
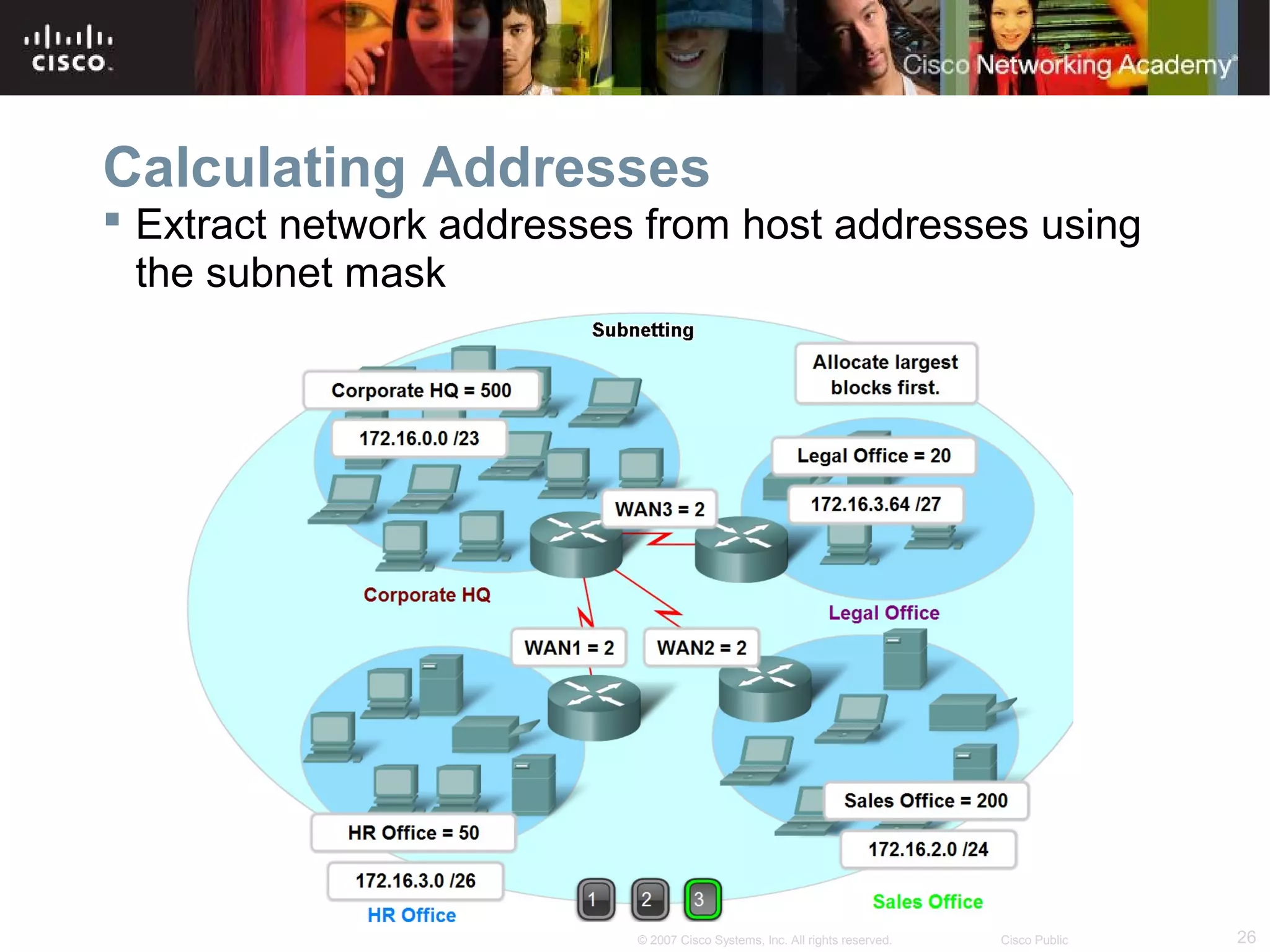
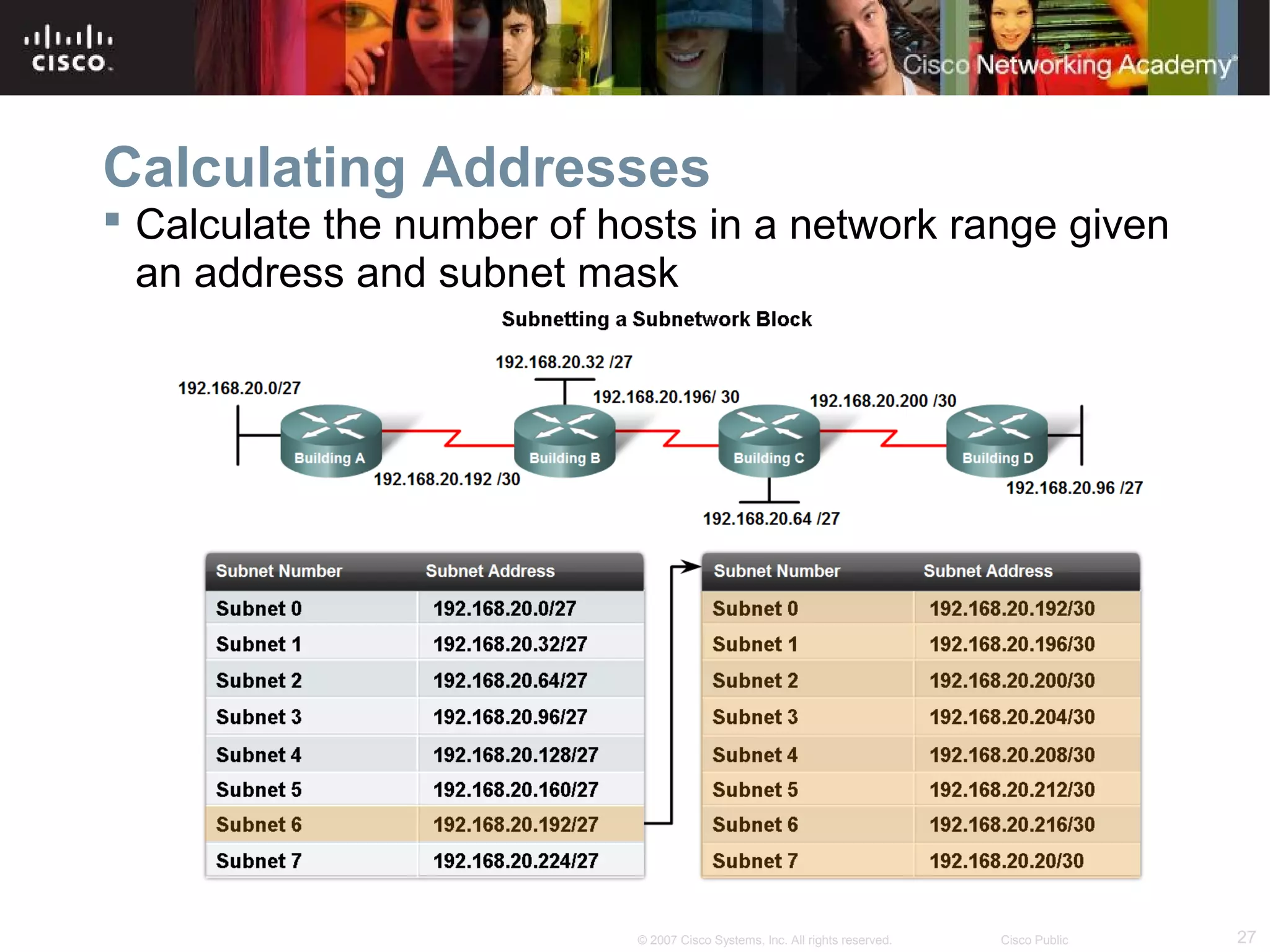
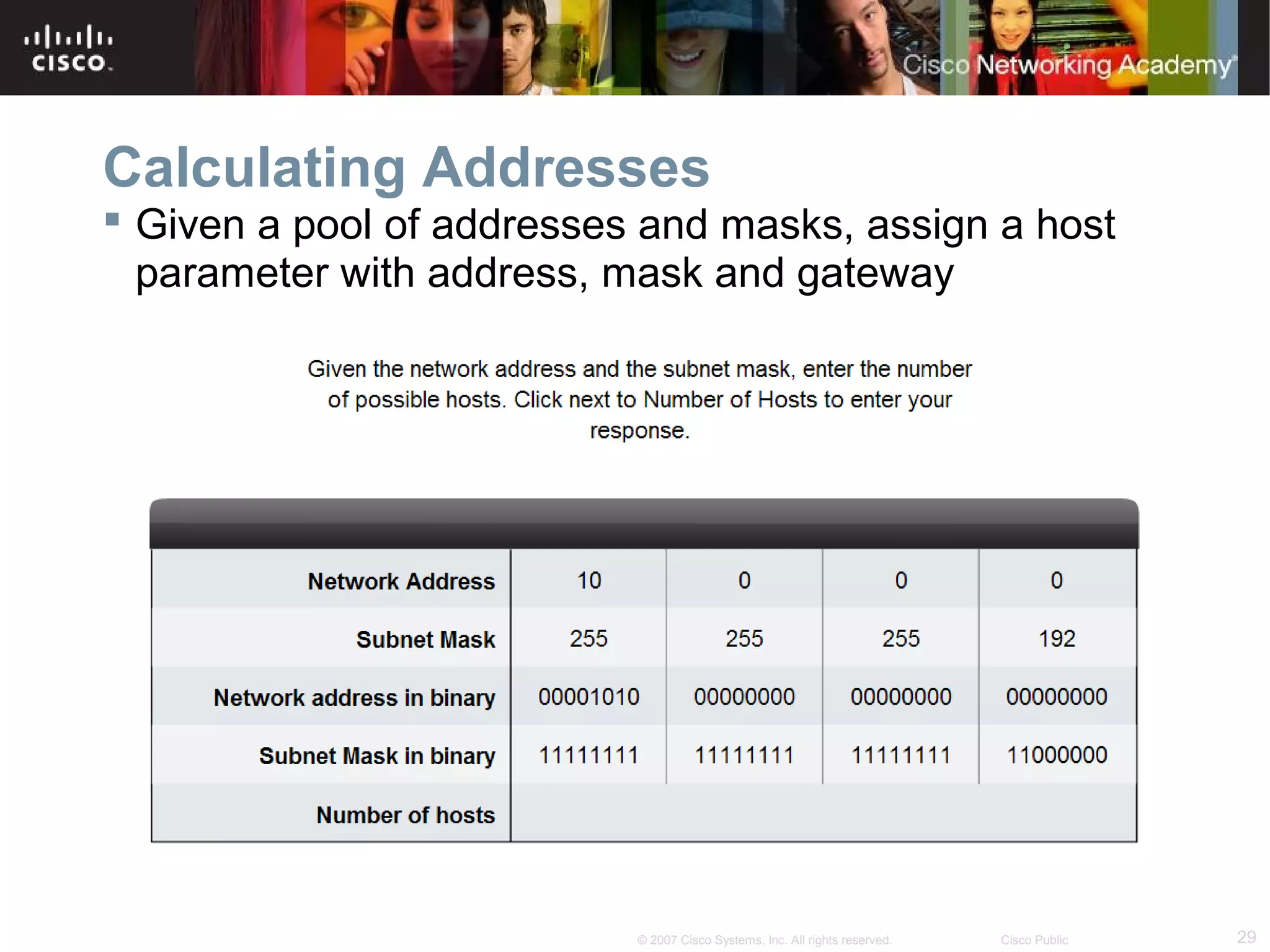
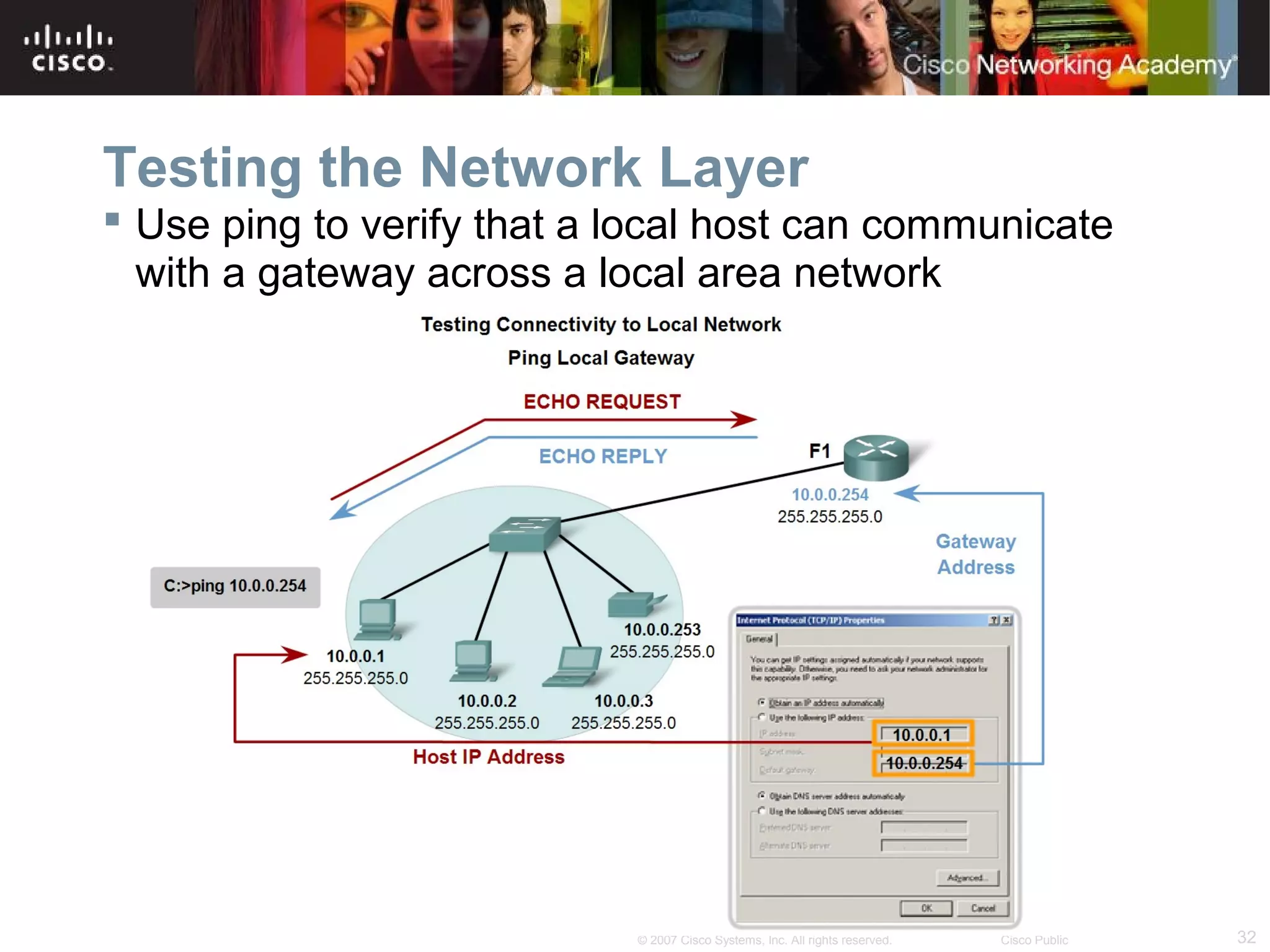
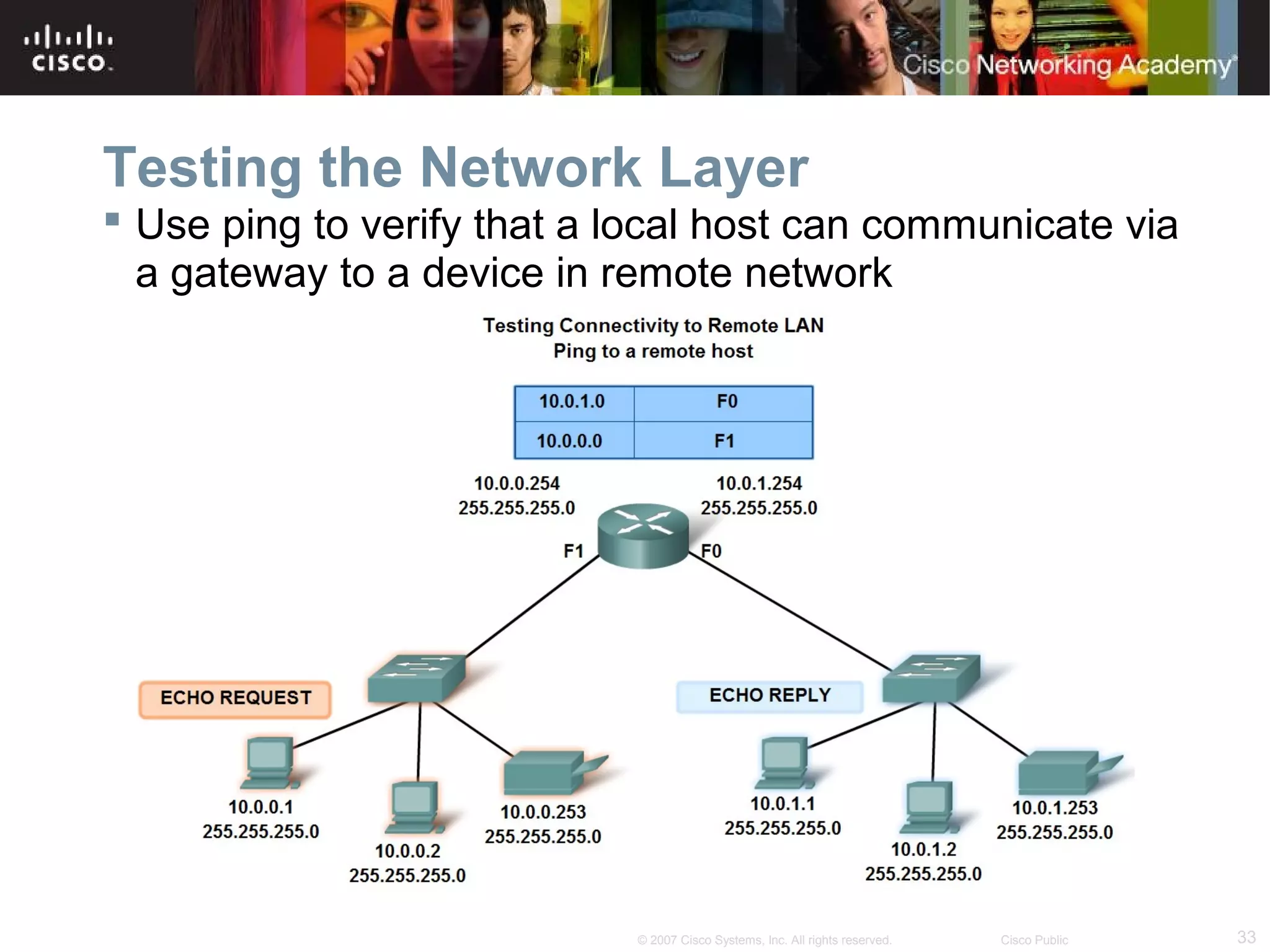
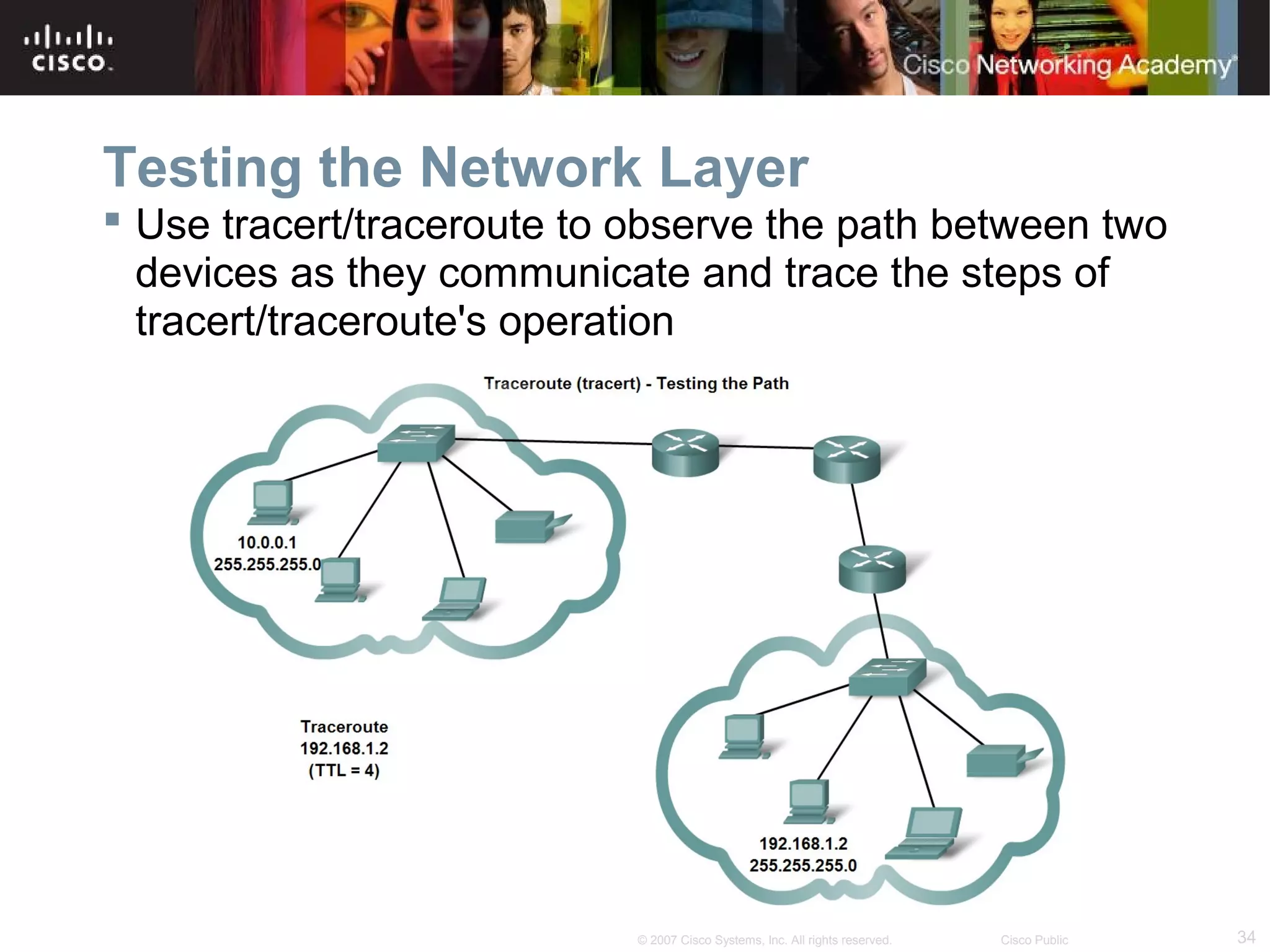
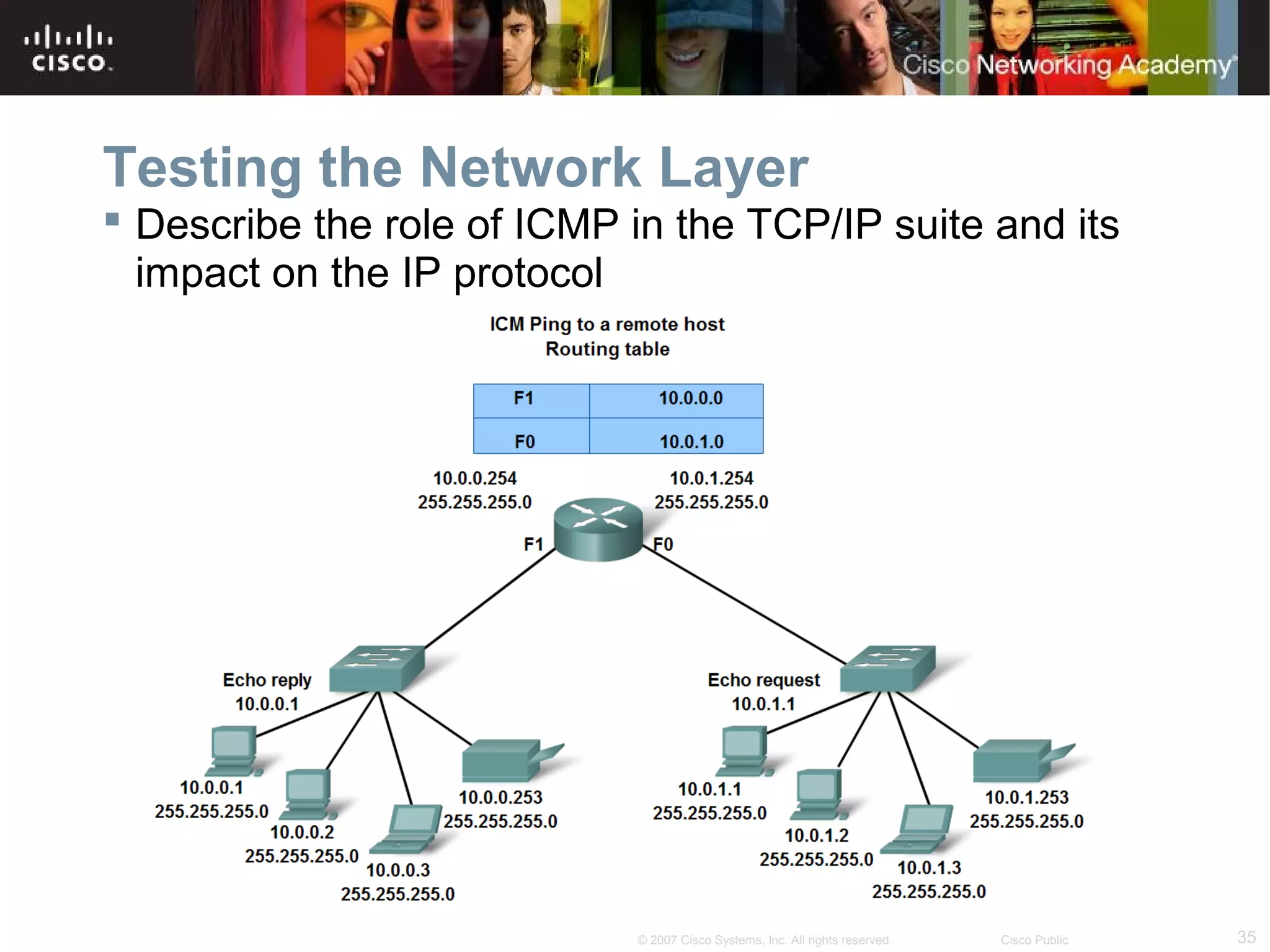
The document outlines objectives for teaching IPv4 networking fundamentals, including explaining IP address structures, classifying address types, assigning addresses, determining network portions from subnet masks, calculating network values, and testing connectivity. It provides exercises for converting binary and decimal numbers, identifying network components, configuring addressing schemes, and using ping and traceroute utilities.