This study investigates the impact of tilt angle, shading, and temperature on the performance of photovoltaic solar panels. Key findings include the optimal tilt angle for maximum power output being 60°, a greater negative effect of horizontal shading compared to vertical shading, and increased temperature leading to lower electrical conversion efficiency. The methodology involved extensive experimental setups and the use of various measurement tools to assess the power output and efficiency under different conditions.









![20
Discussion with Error Analysis
All measurements obtained by the EKO MP-170 PV Module & Array Tester are accurate
to the order of 10-6. Because these errors are so small compared to the measurements, they can be
neglected. Error propagation for Pmpp Ratio, Power (Figures [12, 13]) yield similar results, and
can be neglected as well.
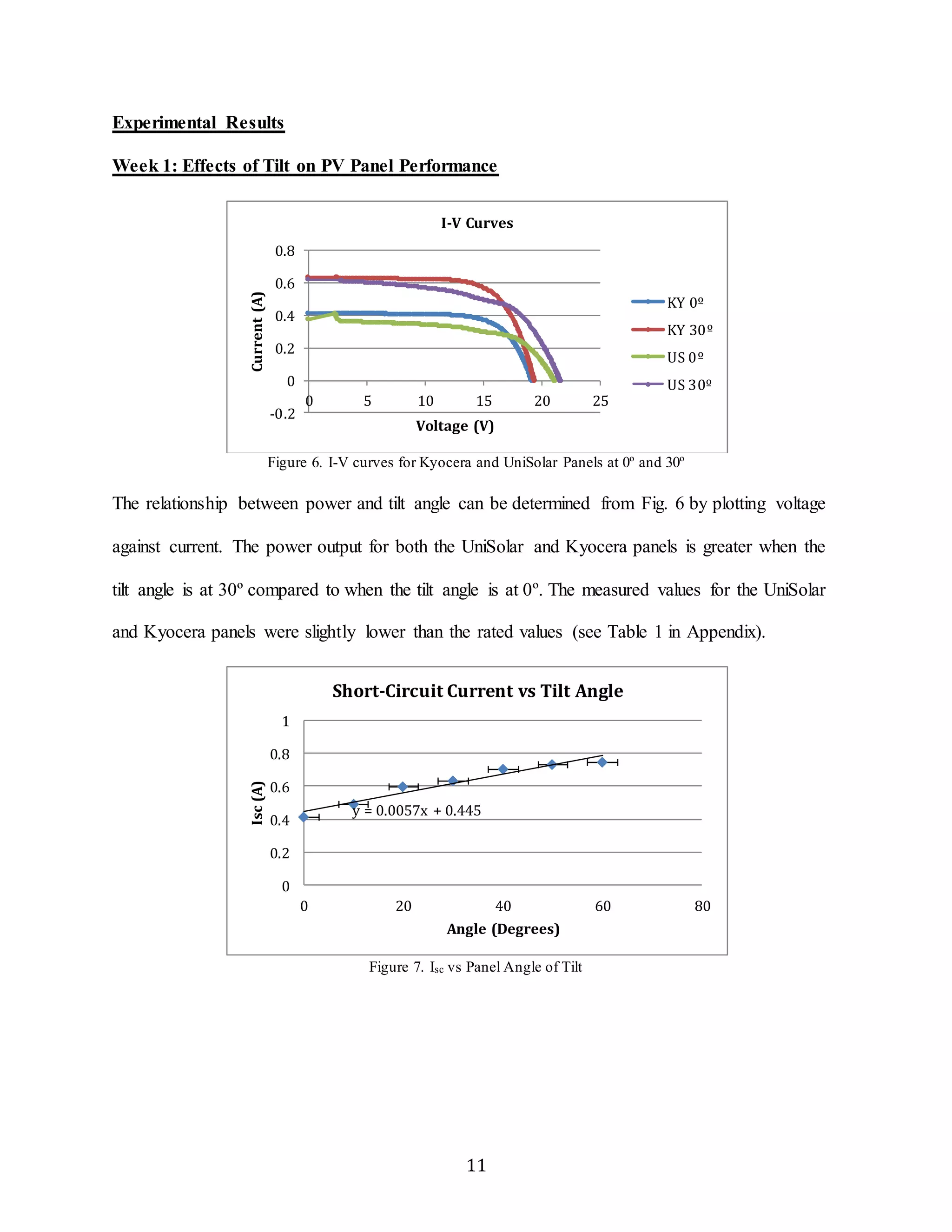
Week 1:
The figures and the recorded data show that both types of solar panel slightly vary from
the rated (stc) specifications. The rated values were slightly higher than the measured values at
every angle. This could be due to the location where the data was recorded and it could be
caused by the effect of shading on the solar panels. Further, the rated values represent extremely
high efficiency, whereas the measured values do not necessarily represent the maximally
optimizing all factors (such as temperature and irradiance). Voltage should theoretically increase
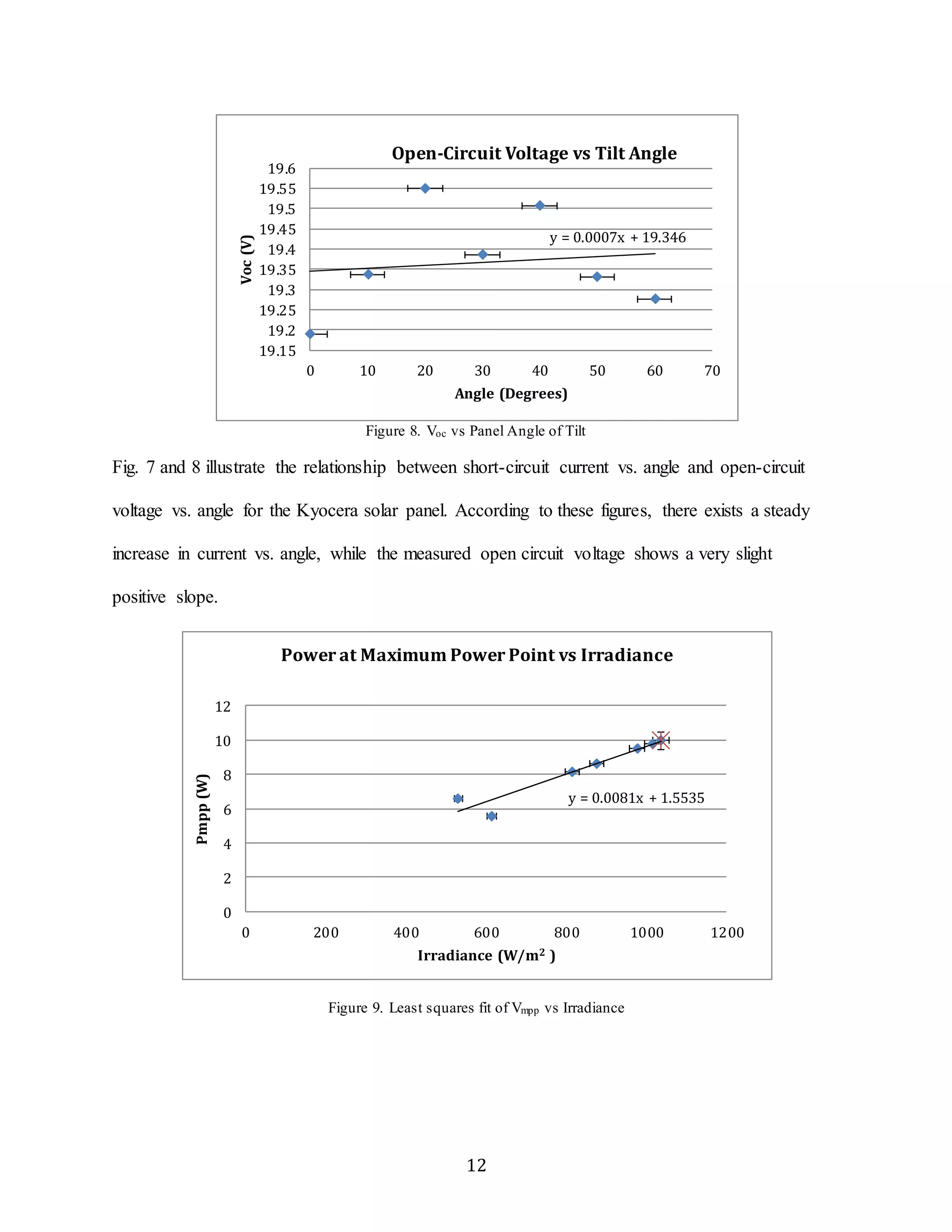
with solar irradiance because more voltage would be generated when there is more irradiance.
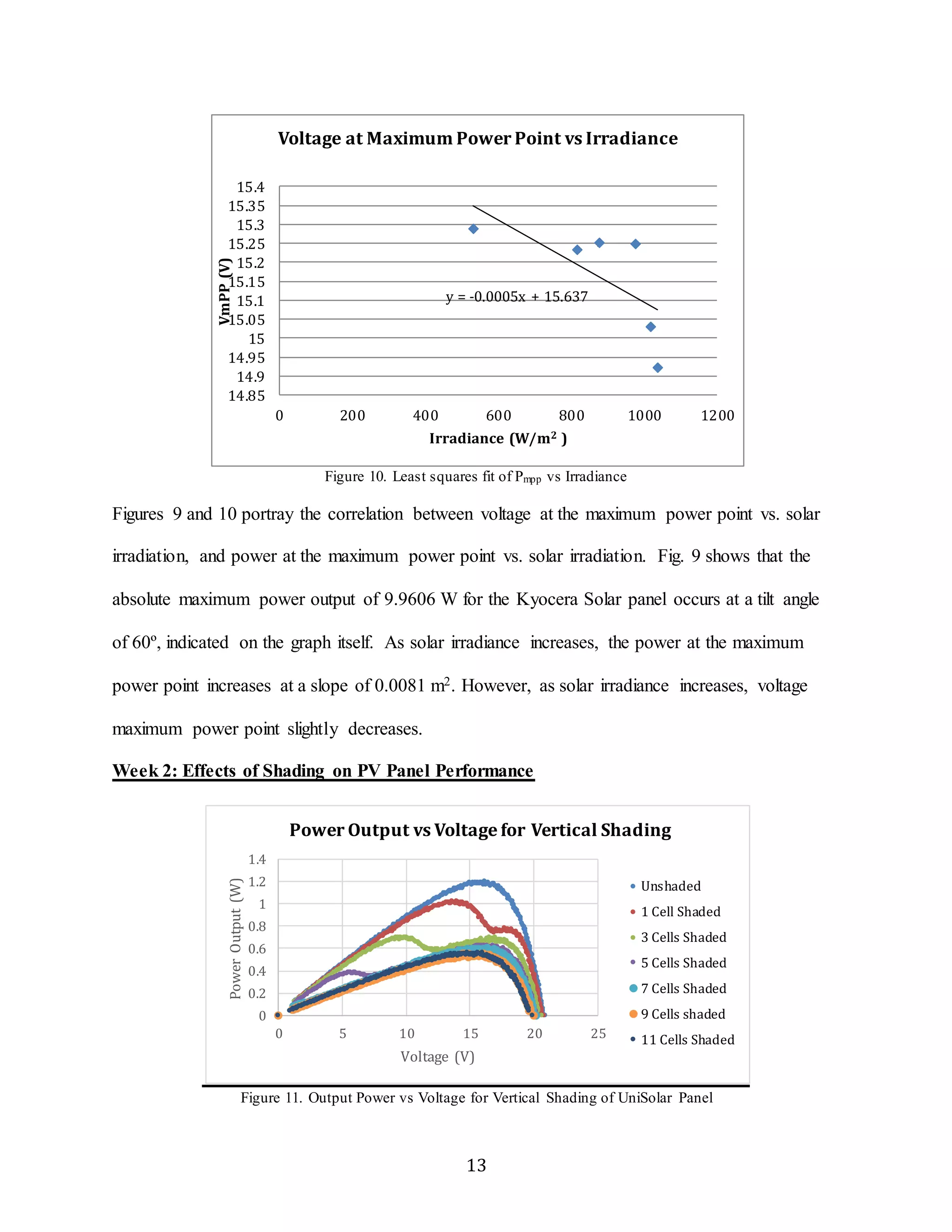
However, Fig. 10 shows a negative relation between voltage and solar irradiance. This could be
explained by other factors affecting the actual voltage that was generated. The voltage decreases
at in extremely slight negative fashion, indicating that a small factor, such as a slight temperature
shift, could have switched the voltage from barely positive to barely negative.
According to the Power at maximum power point vs. Irradiance curves, the maximum
panel power output occurs at an angle of 60 degrees, where irradiance is at the greatest. This
potentially can be attributed to the time of day the data was collected. Because it was late
afternoon, the sun had shifted from the highest point and came in at a lower angle, thus changing
the angle at which the highest irradiance would be observed. The maximum power point occurs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentalstudyoftheeffectsoftiltshadingandtemperatureonphotovoltaicpanelperformance-guptatsurutal-141122082047-conversion-gate02/75/Experimental-study-of-the-effects-of-tilt-shading-and-temperature-on-photovoltaic-panel-performance-gupta-tsuruta-lin-moynihan-20-2048.jpg)
![on the I-V curve where the curves transitions to a decreasing slope due to power being related to
21
voltage and current by P = IV.
While taking measurements at different angles, we needed to manually measure the angle
as well as hold the PV panel at the desired angle by hand. Due to these imprecise experimental
techniques the errors associated with PV panel angle are large, +/- 3 degrees. Another type of
error was having negative slope for Vmpp vs. Irradiance is due to application-related errors where
we might have accidentally changed the orientation of the sensors or not accounted for other
factors in the environment. The built in intrinsic errors within the M-170 sensor unit in the
measurement of voltage, current, power, and irradiance are negligible.
Week 2:
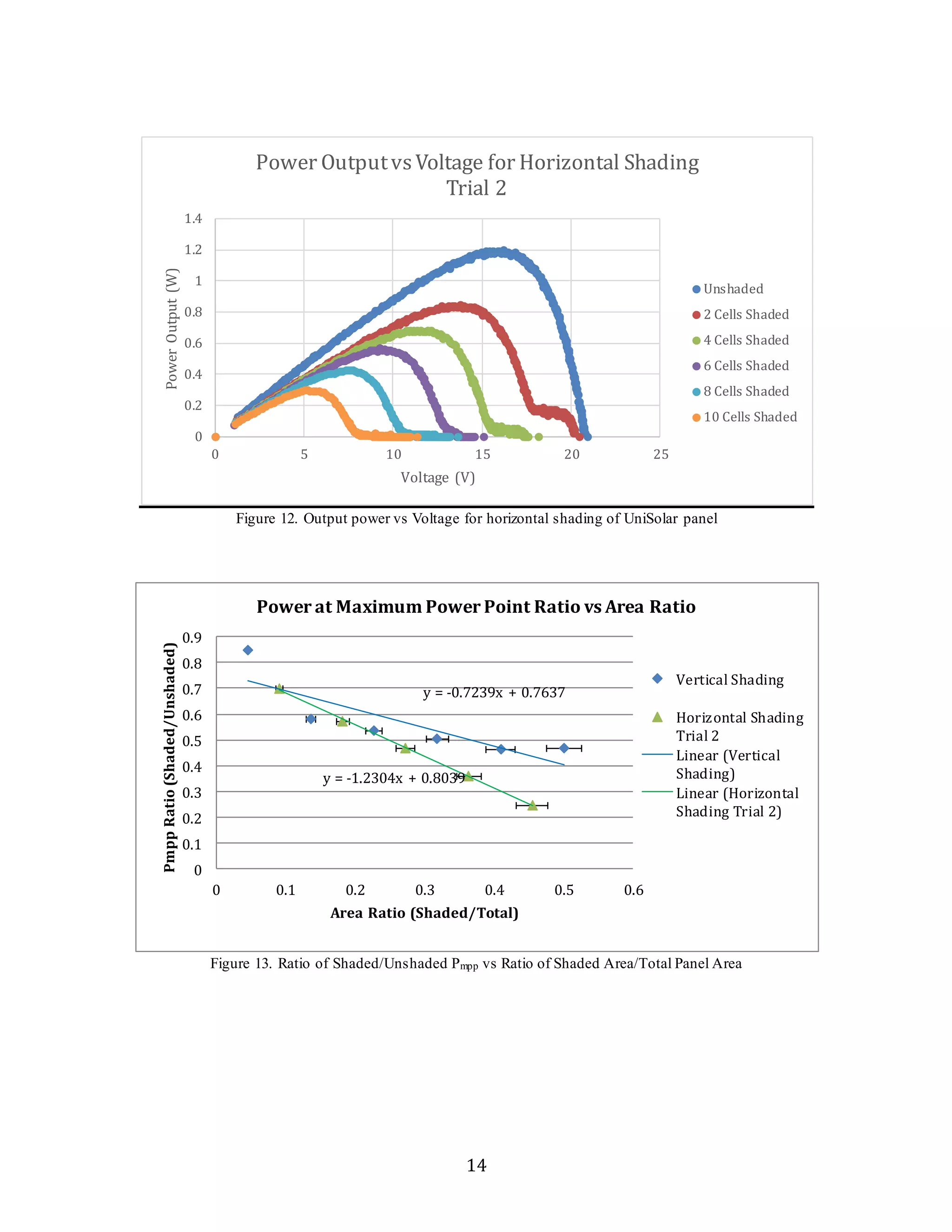
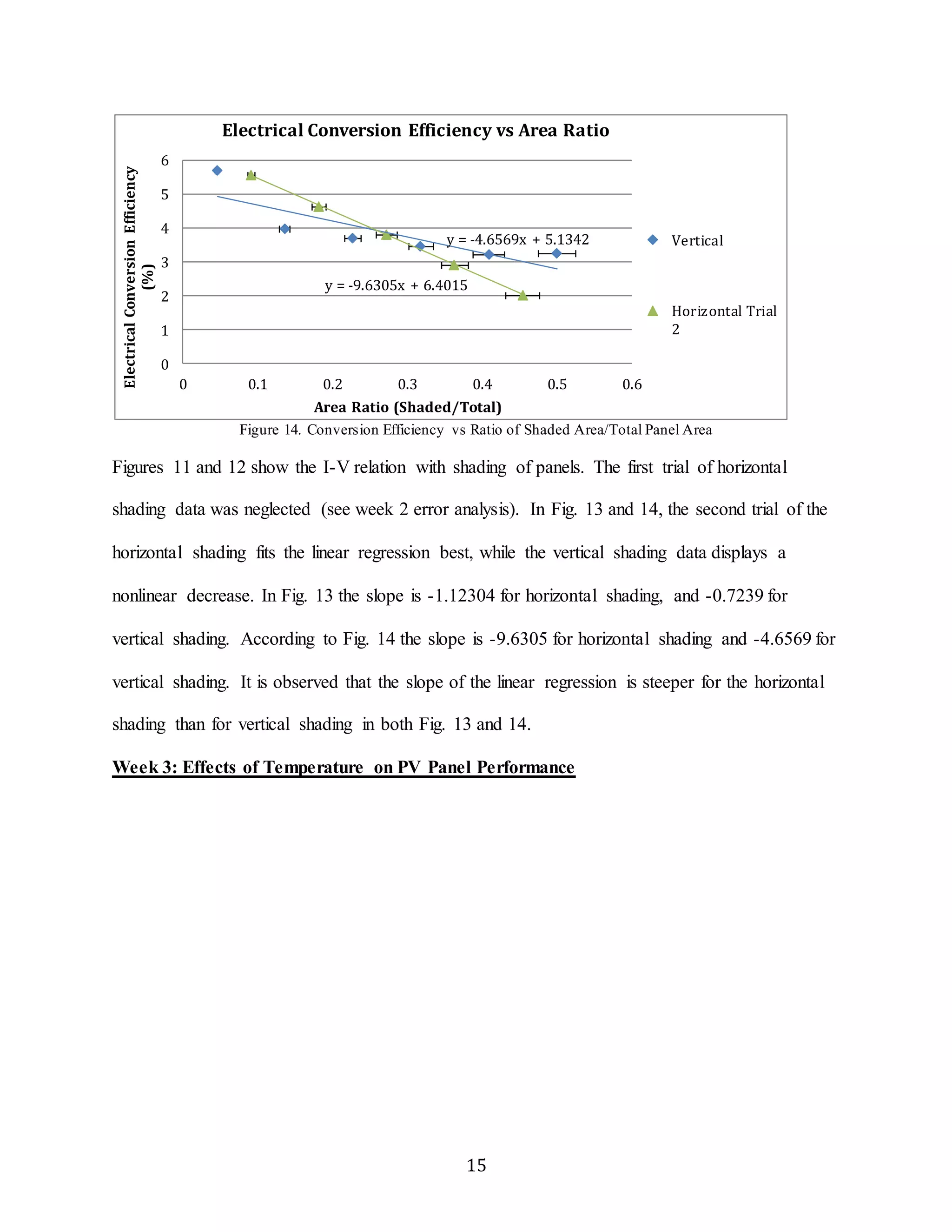
The results imply that PV systems are designed so as to maximize the power output even
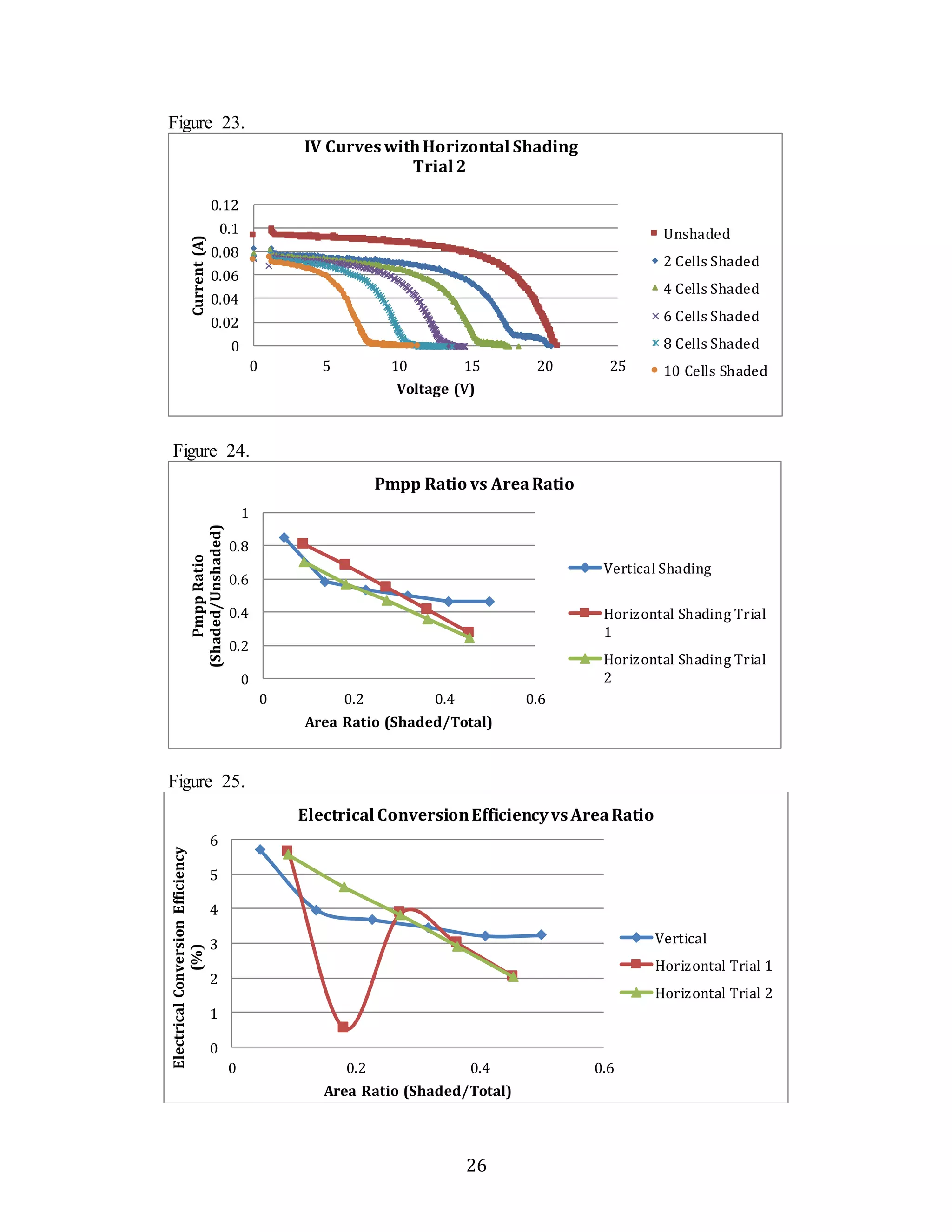
when shaded. The more rapid decrease in both power at maximum power point and electrical
conversion efficiency for horizontal shading compared to vertical shading (Figures [13, 14]) can
possibly be attributed to the way the individual cells of the PV panel are connected. While
vertically shading, only one cell in each horizontal module (group of two horizontal PV cells)
falls was shaded. That cell falls to a power output of zero, but the power output of the entire
module does not fall to zero. However, while horizontally shading, the entire module is covered,
and thus the entire power output of the full module falls to zero.4 In order to accommodate for
potential power losses due to shading, the PV system would have to be designed to minimize
coverage of full horizontal modules. To accomplish this, the rows of the PV panel could be wired
in series, while the columns could be wired in parallel. According to Ohm’s Law, the connection
in series would maximize output voltage, but would create power-draining loads when individual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentalstudyoftheeffectsoftiltshadingandtemperatureonphotovoltaicpanelperformance-guptatsurutal-141122082047-conversion-gate02/75/Experimental-study-of-the-effects-of-tilt-shading-and-temperature-on-photovoltaic-panel-performance-gupta-tsuruta-lin-moynihan-21-2048.jpg)



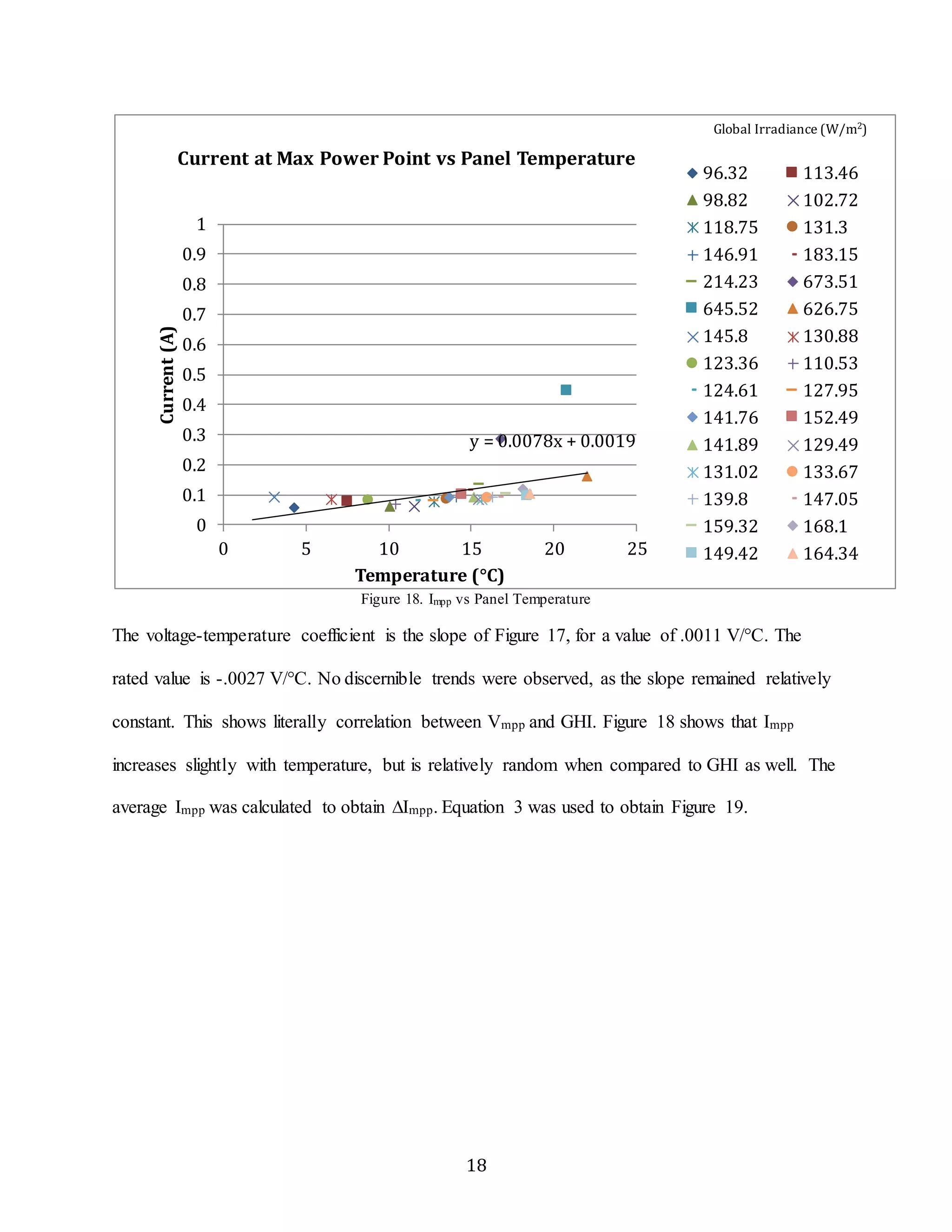
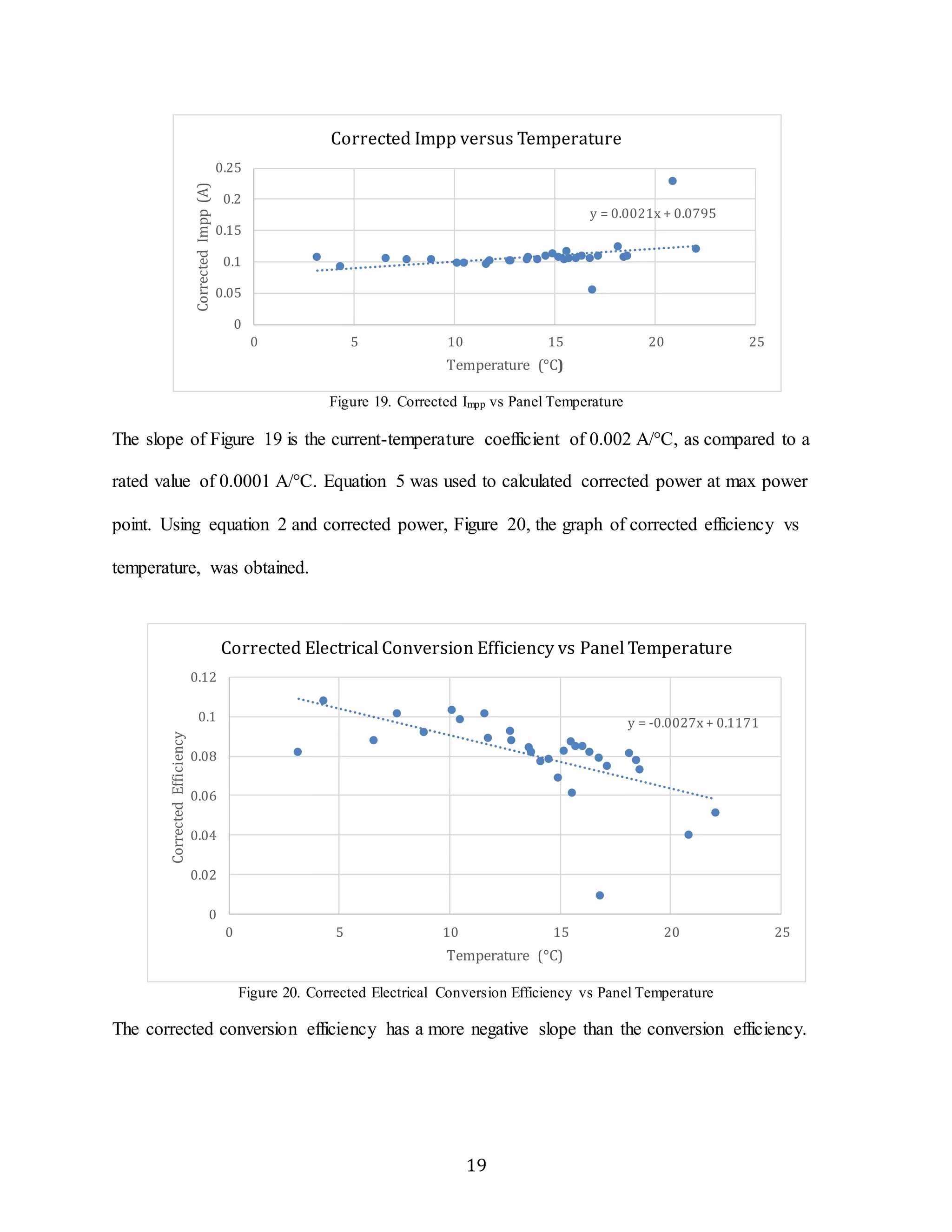
![Current at Max Power Point vs Panel Temp
y = 0.016x - 0.0821
0 5 10 15 20 25
Temperature (°C)
27
Figure 26.
Table 1.
KY PV
Panel
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-0.1
Current (A)
Solar
Irradiance
(Er)[W/m^2]
y = 0.0014x + 0.0708
Trial 1
Trial 2
Trial 1 Impp
Trial 2 Impp
PV Device
Temp.[degC] Isc[A] Voc[V] Pm[W] Ipm[A] Vpm[V]
Rated 1000 25 0.62 21.7 10 0.58 17.4
0 Degrees 614.415929 53.766987 0.413645 19.189079 5.589738 0.366618 15.246755
10
Degrees 530.923451 54.466408 0.488166 19.336191 6.589841 0.431026 15.288747
20
Degrees 814.993215 54.670582 0.59202 19.548725 8.123451 0.533357 15.230793
30
Degrees 875.20826 57.693634 0.633405 19.386742 8.58644 0.563004 15.251104
40
Degrees 977.099853 57.42136 0.7029 19.506508 9.532833 0.625251 15.246416
50
Degrees 1016.128024 60.871288 0.728513 19.330552 9.759039 0.649358 15.028747
60
Degrees 1036.060177 61.873493 0.744509 19.274462 9.960568 0.66762 14.919507](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentalstudyoftheeffectsoftiltshadingandtemperatureonphotovoltaicpanelperformance-guptatsurutal-141122082047-conversion-gate02/75/Experimental-study-of-the-effects-of-tilt-shading-and-temperature-on-photovoltaic-panel-performance-gupta-tsuruta-lin-moynihan-27-2048.jpg)