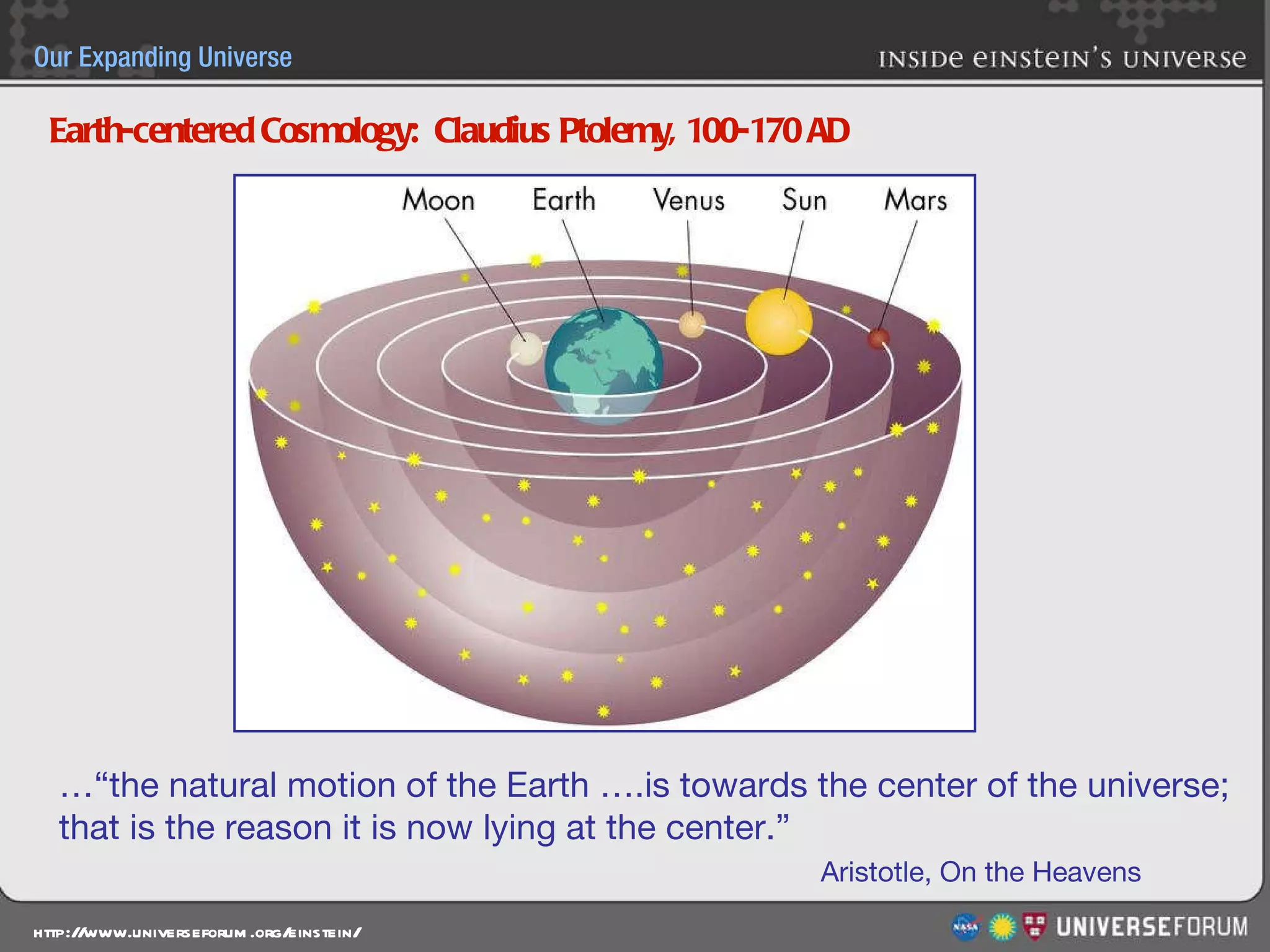
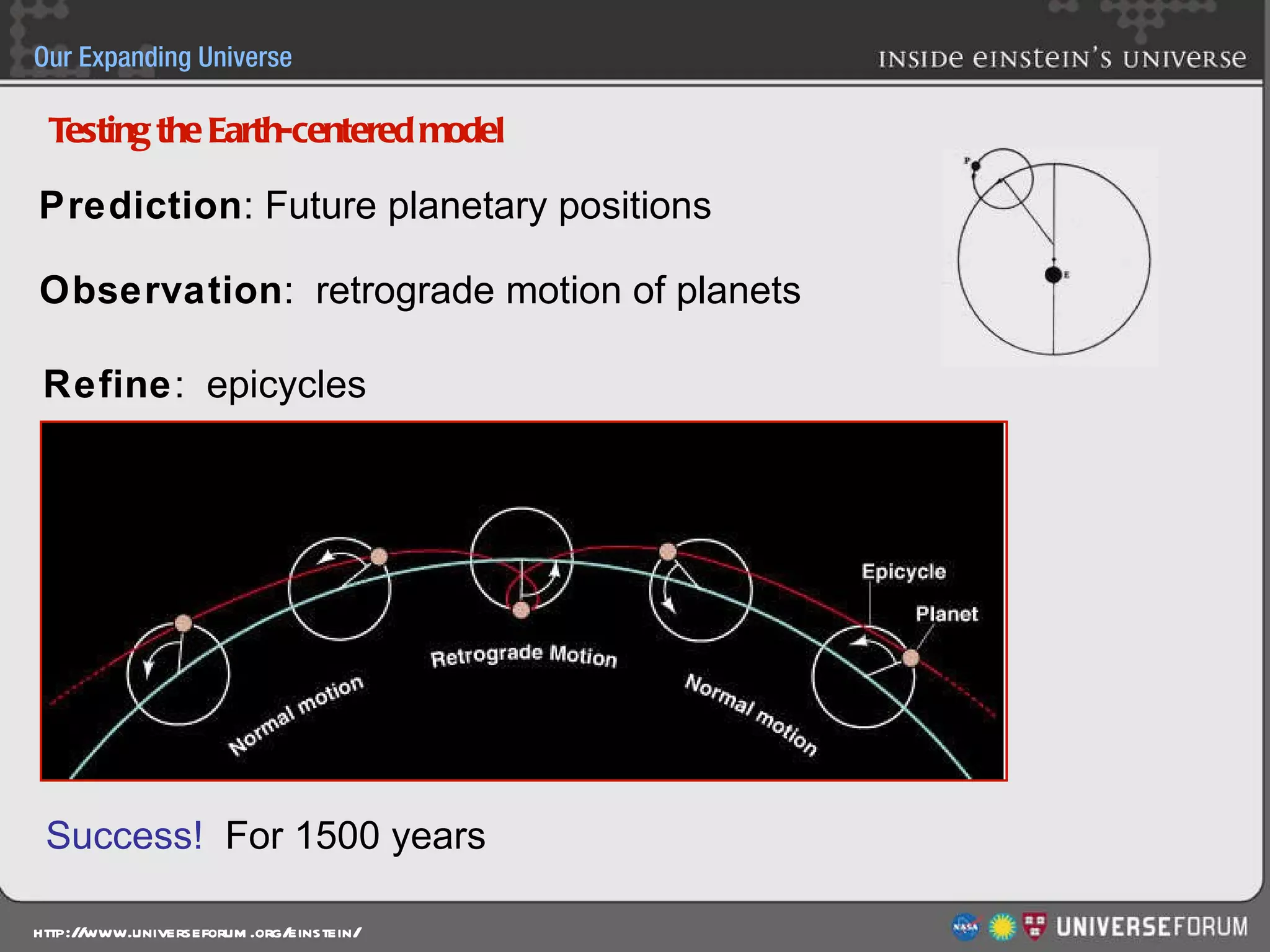
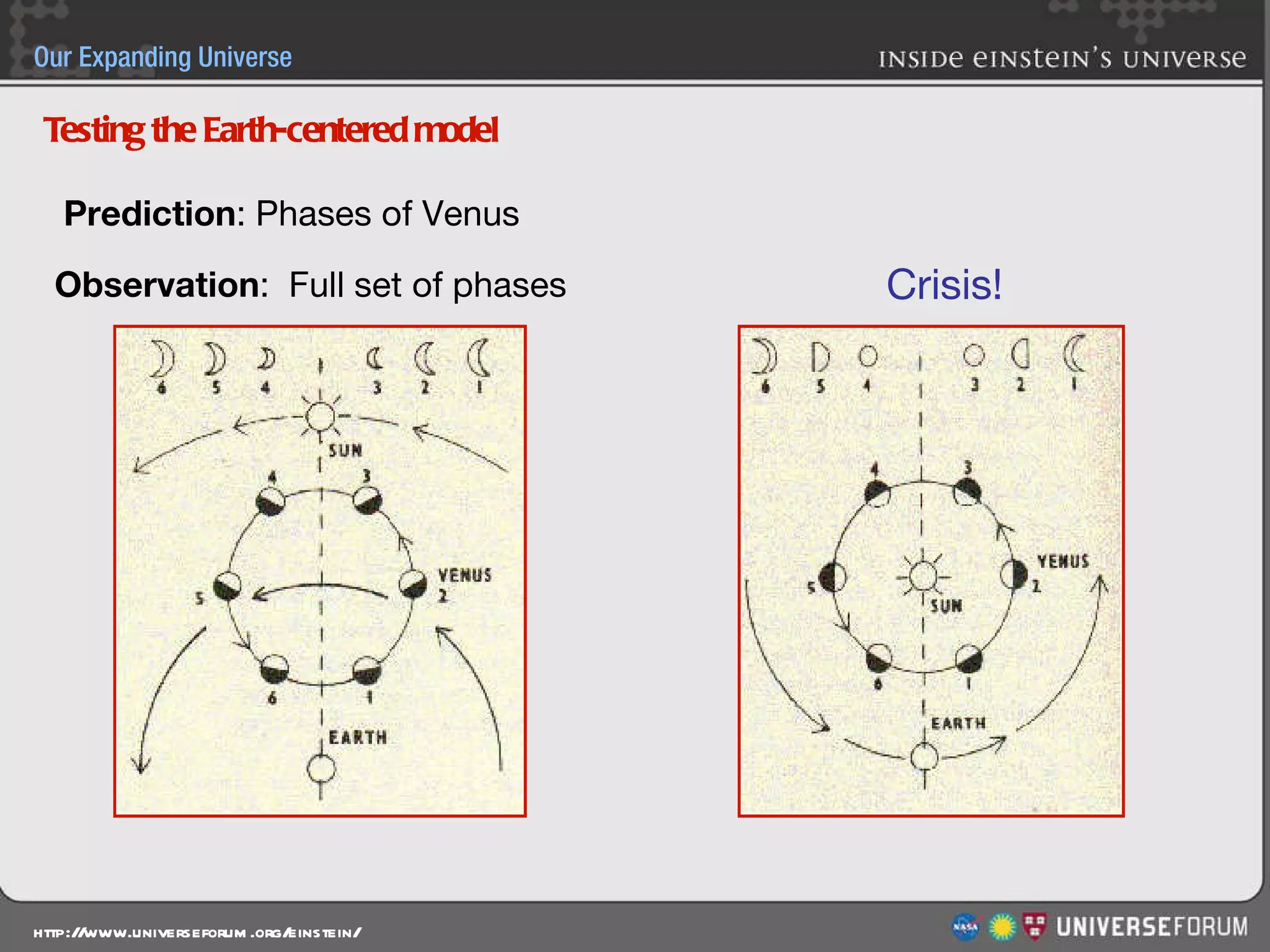
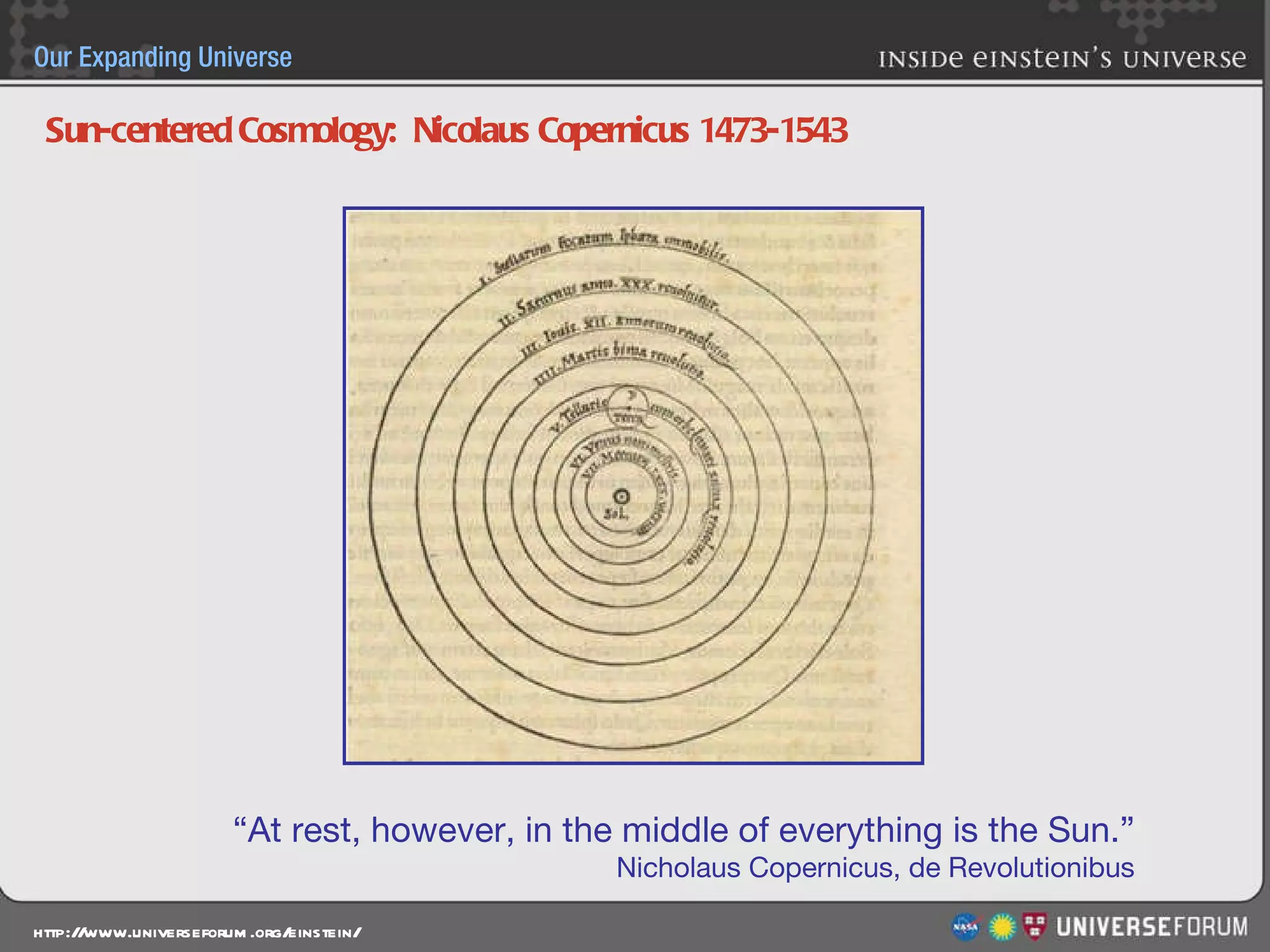
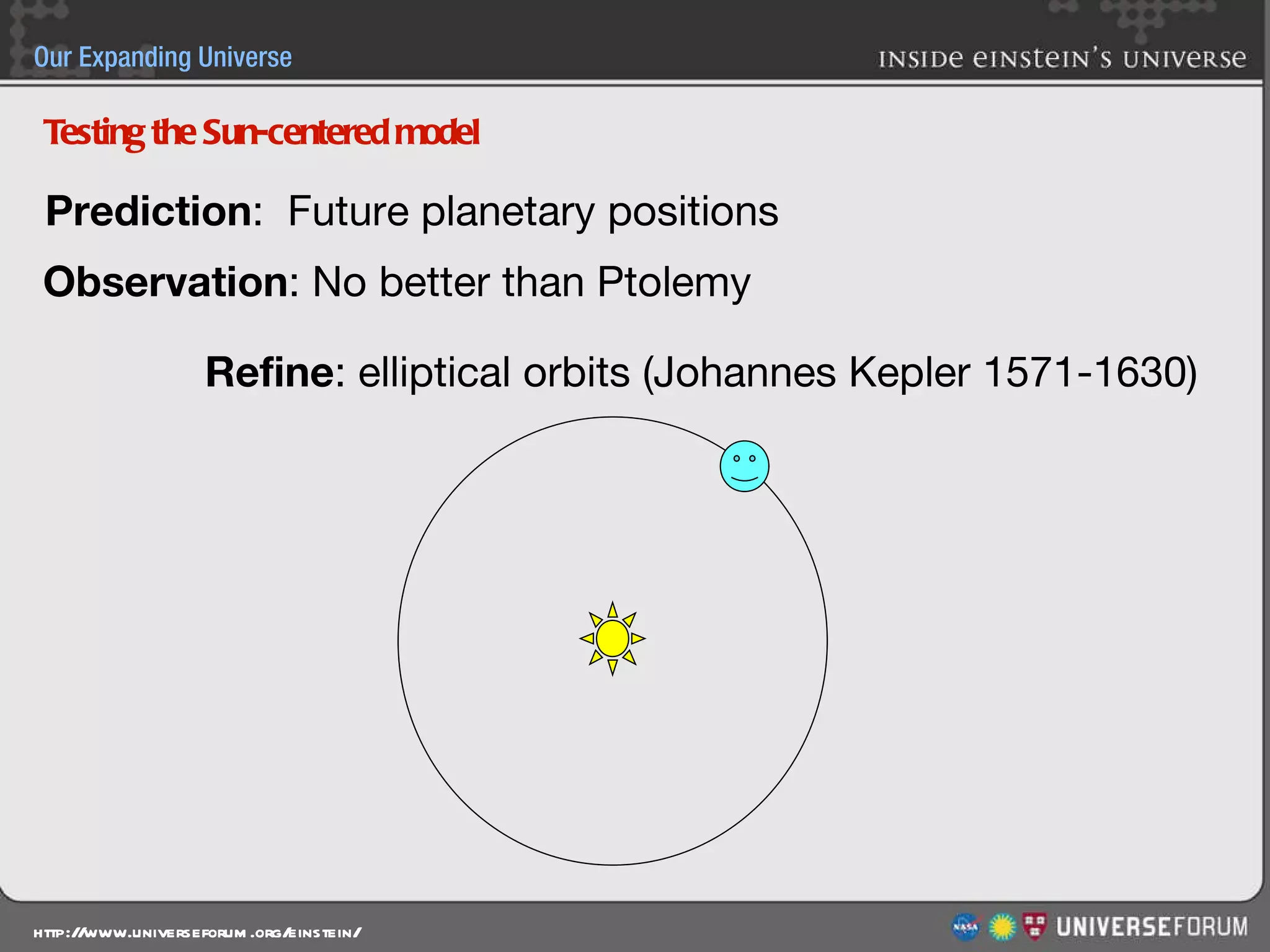
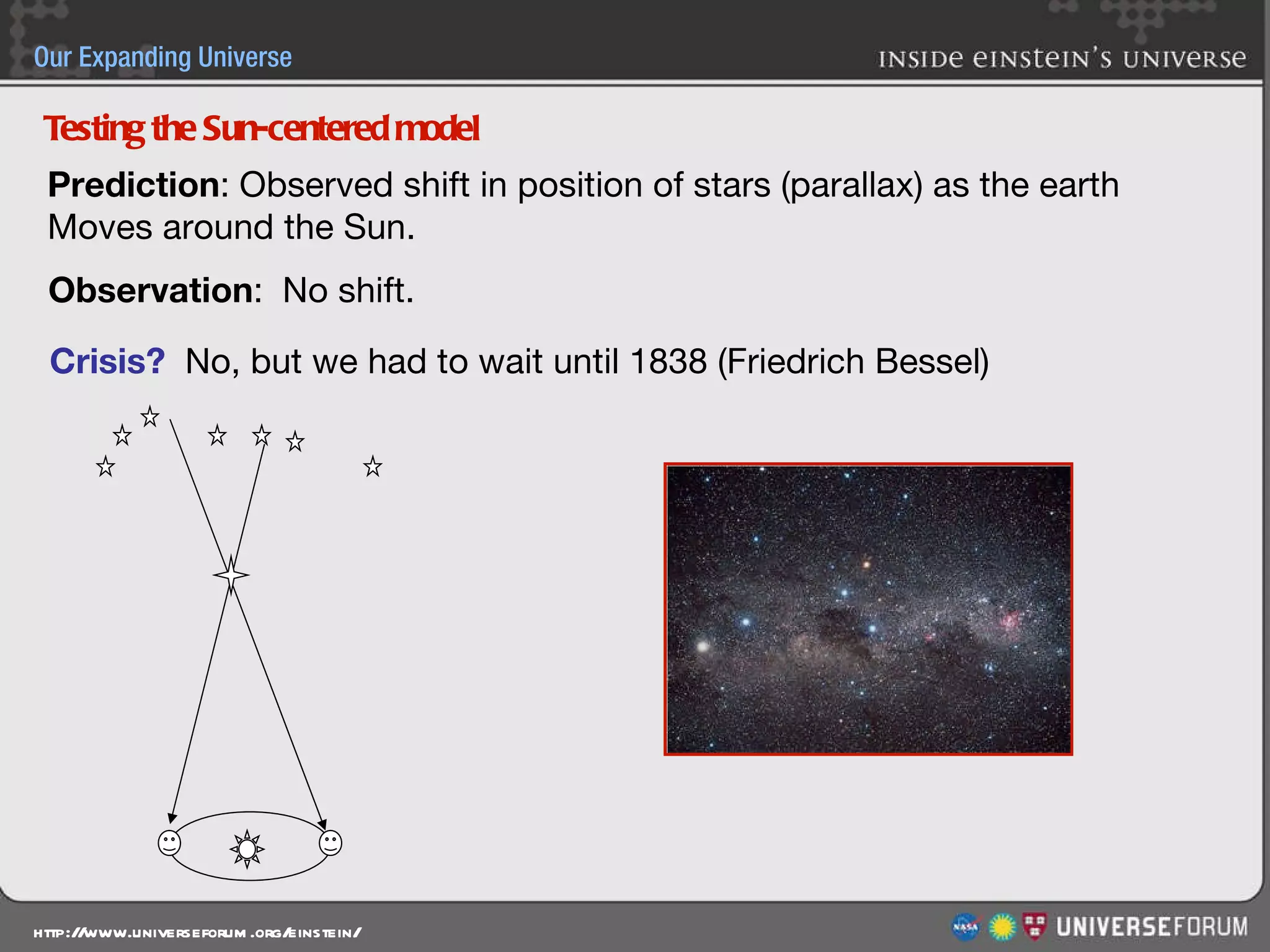
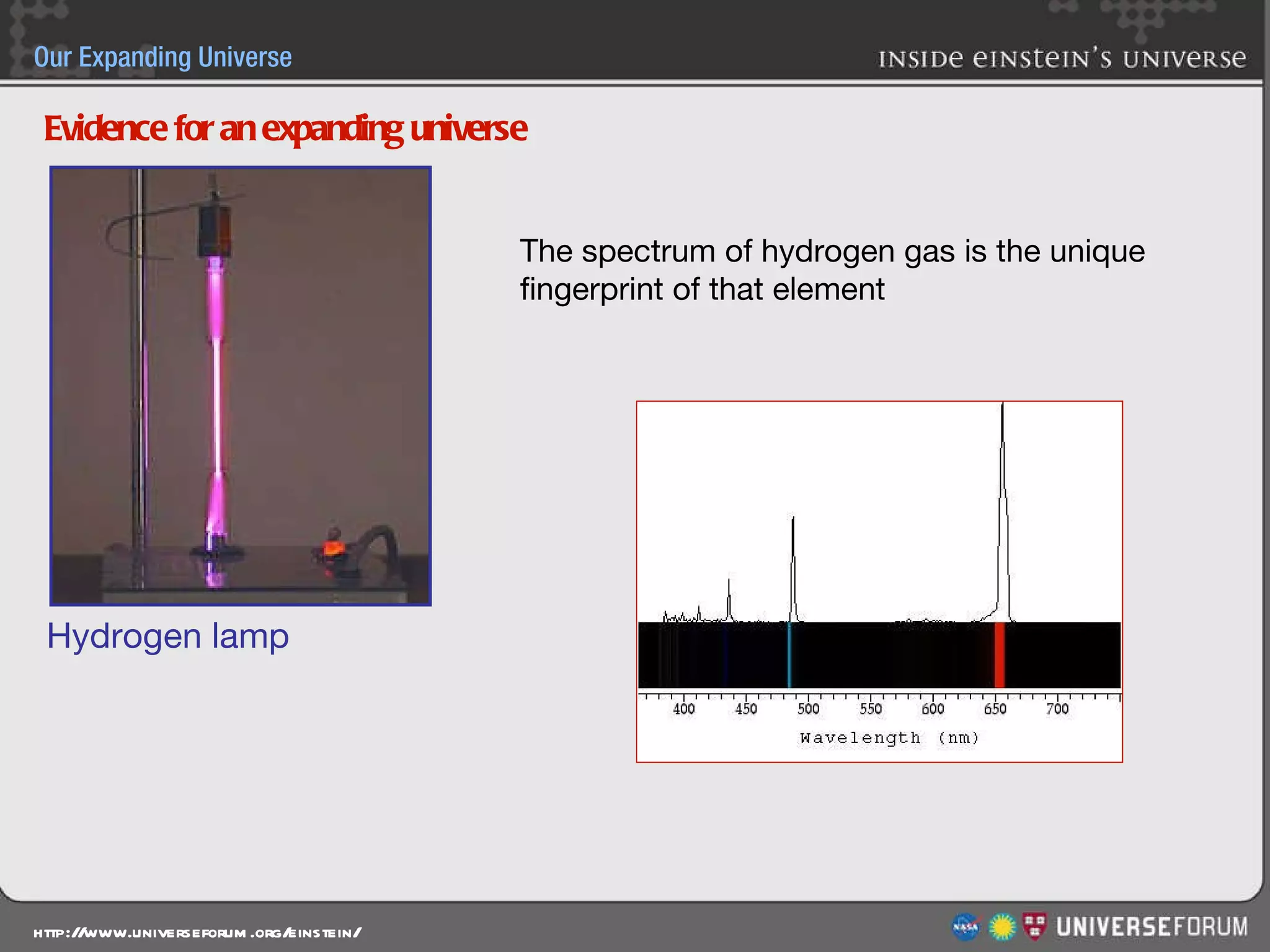
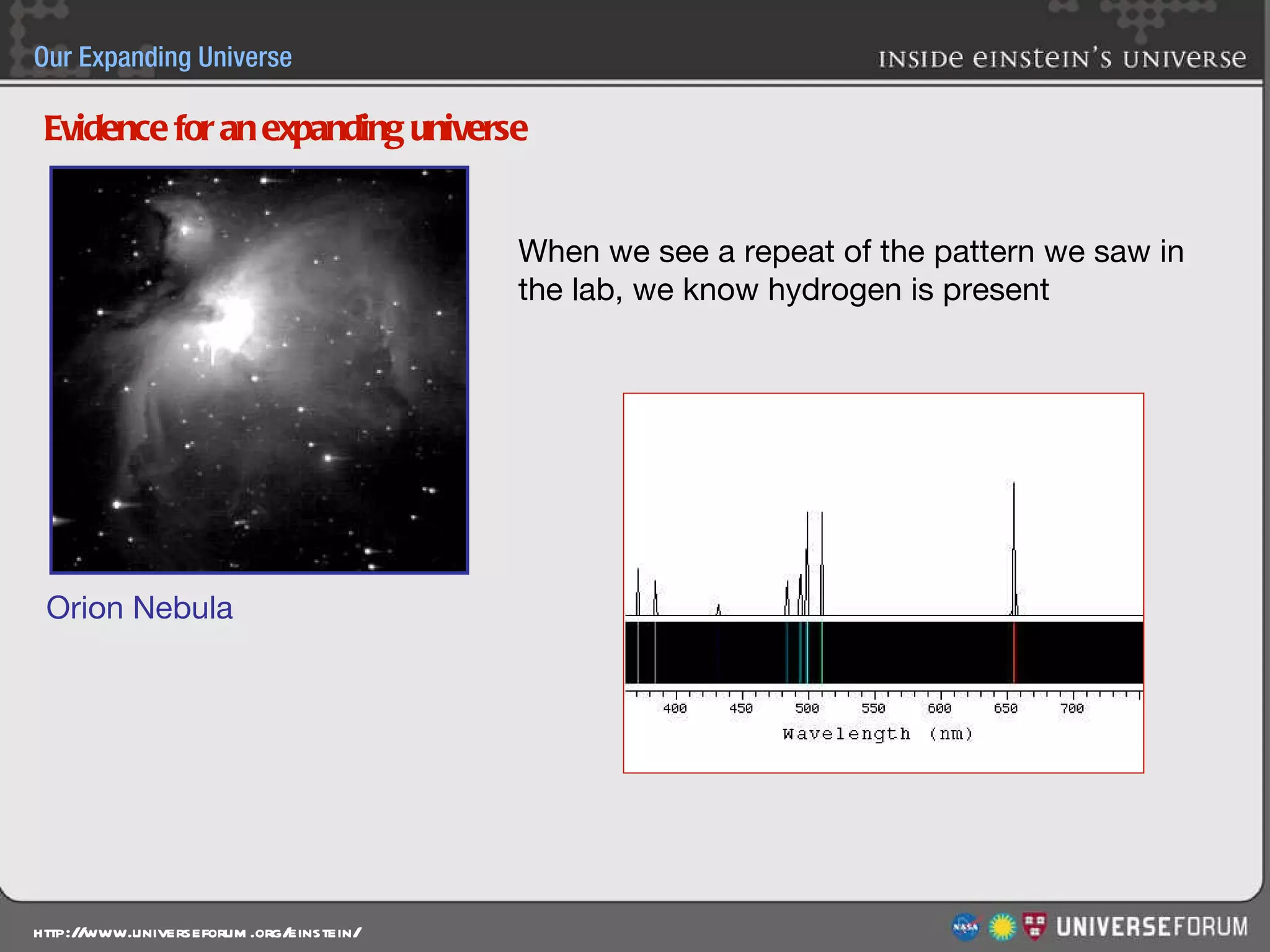
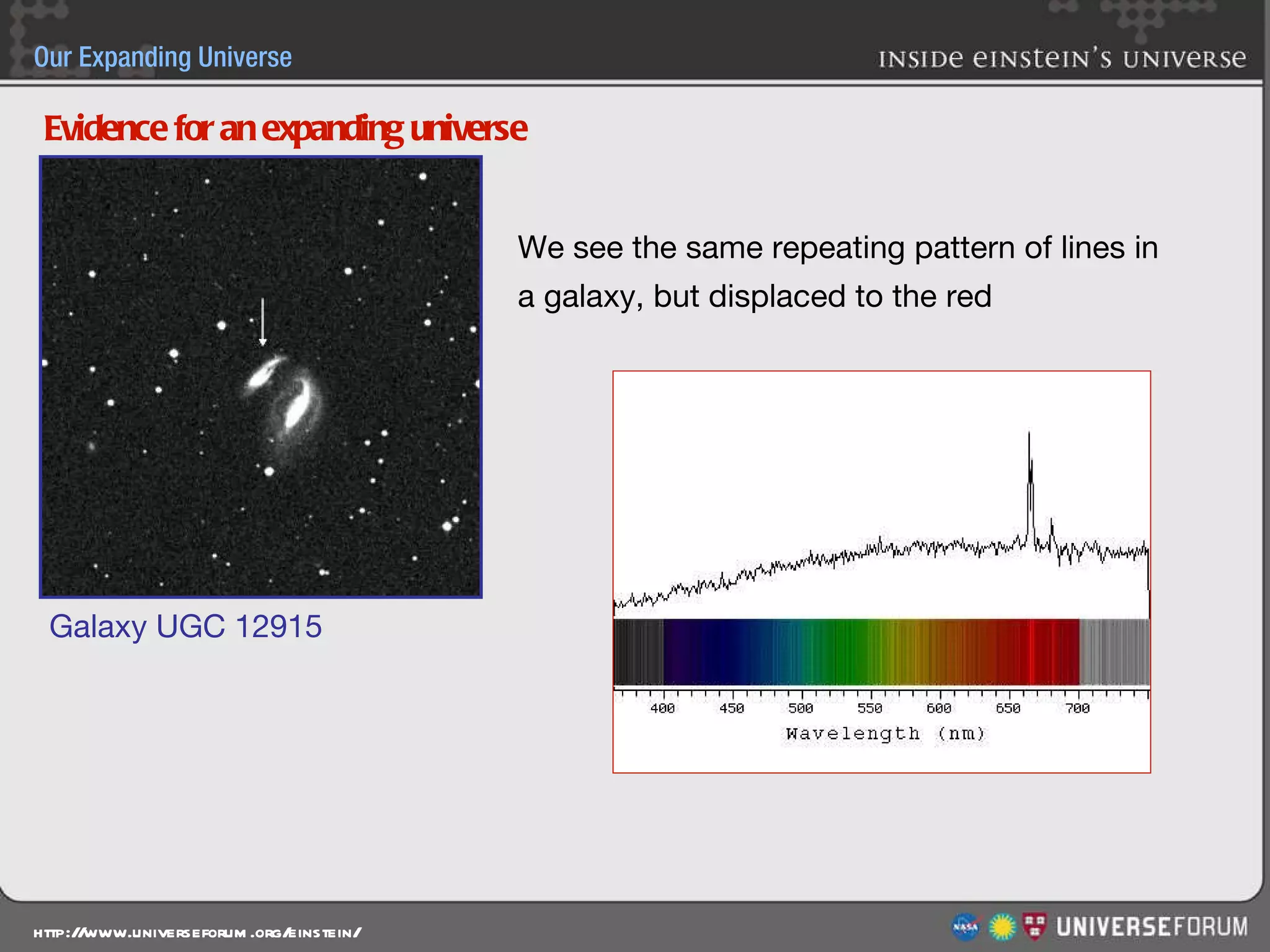
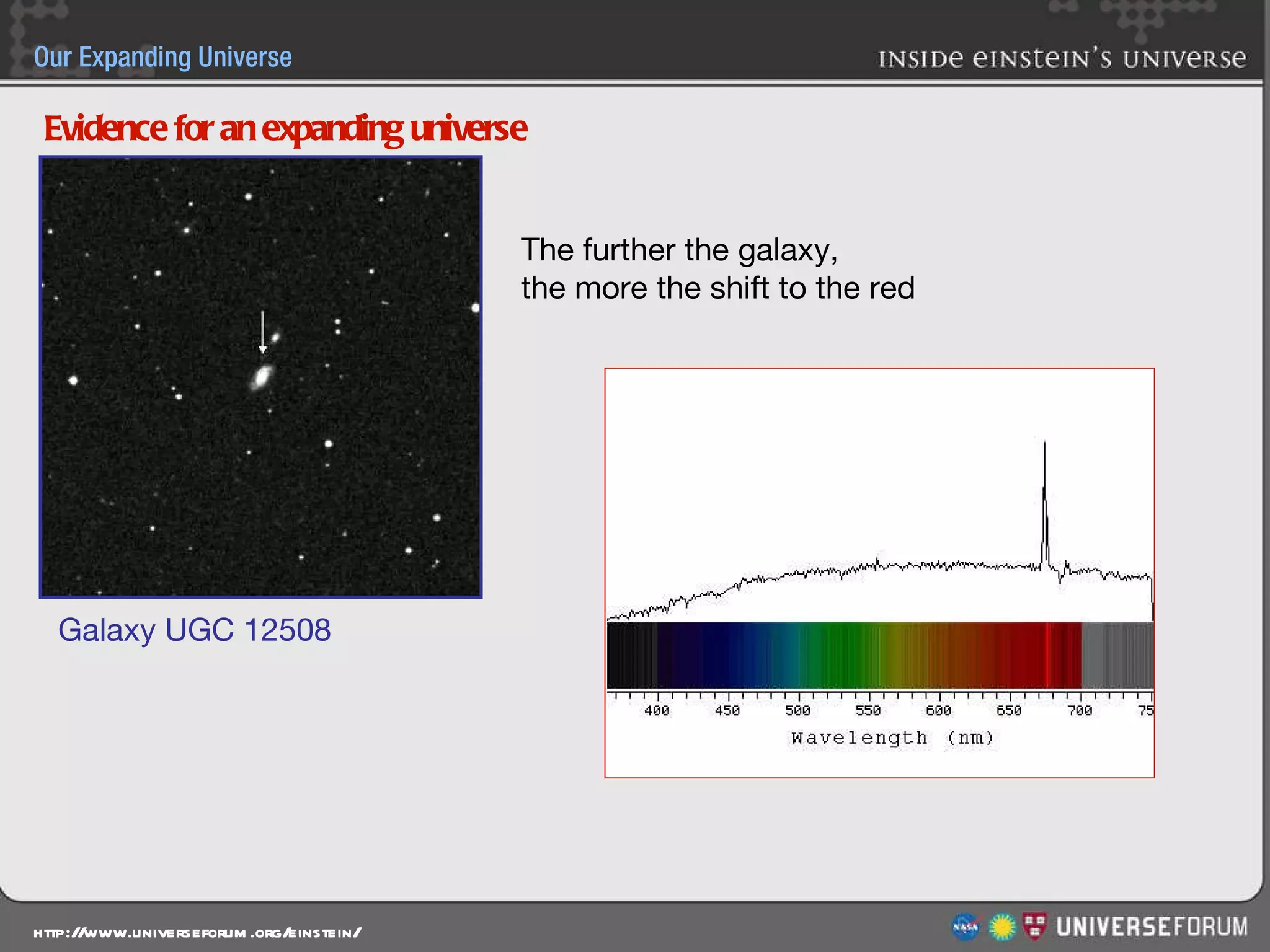
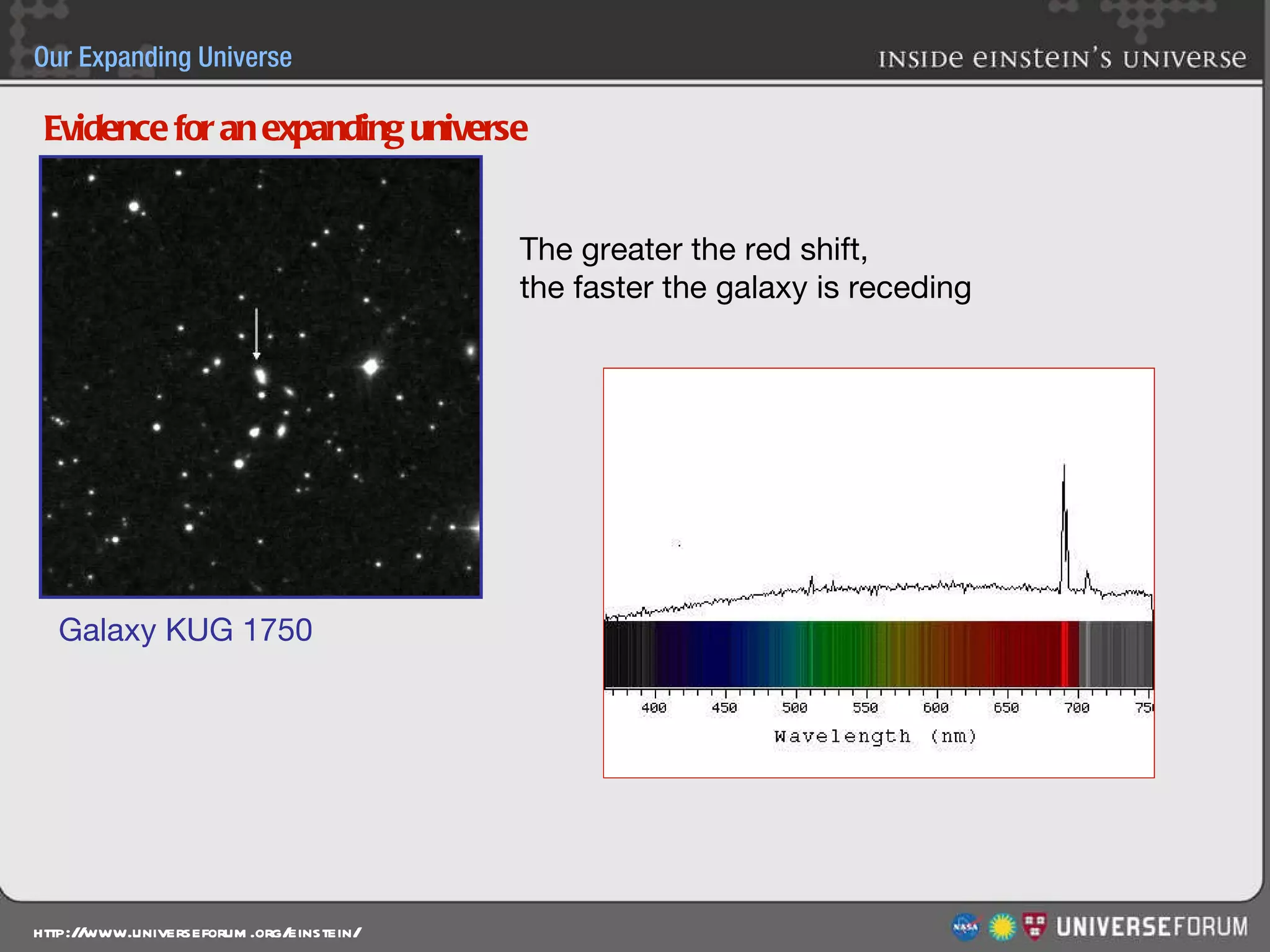
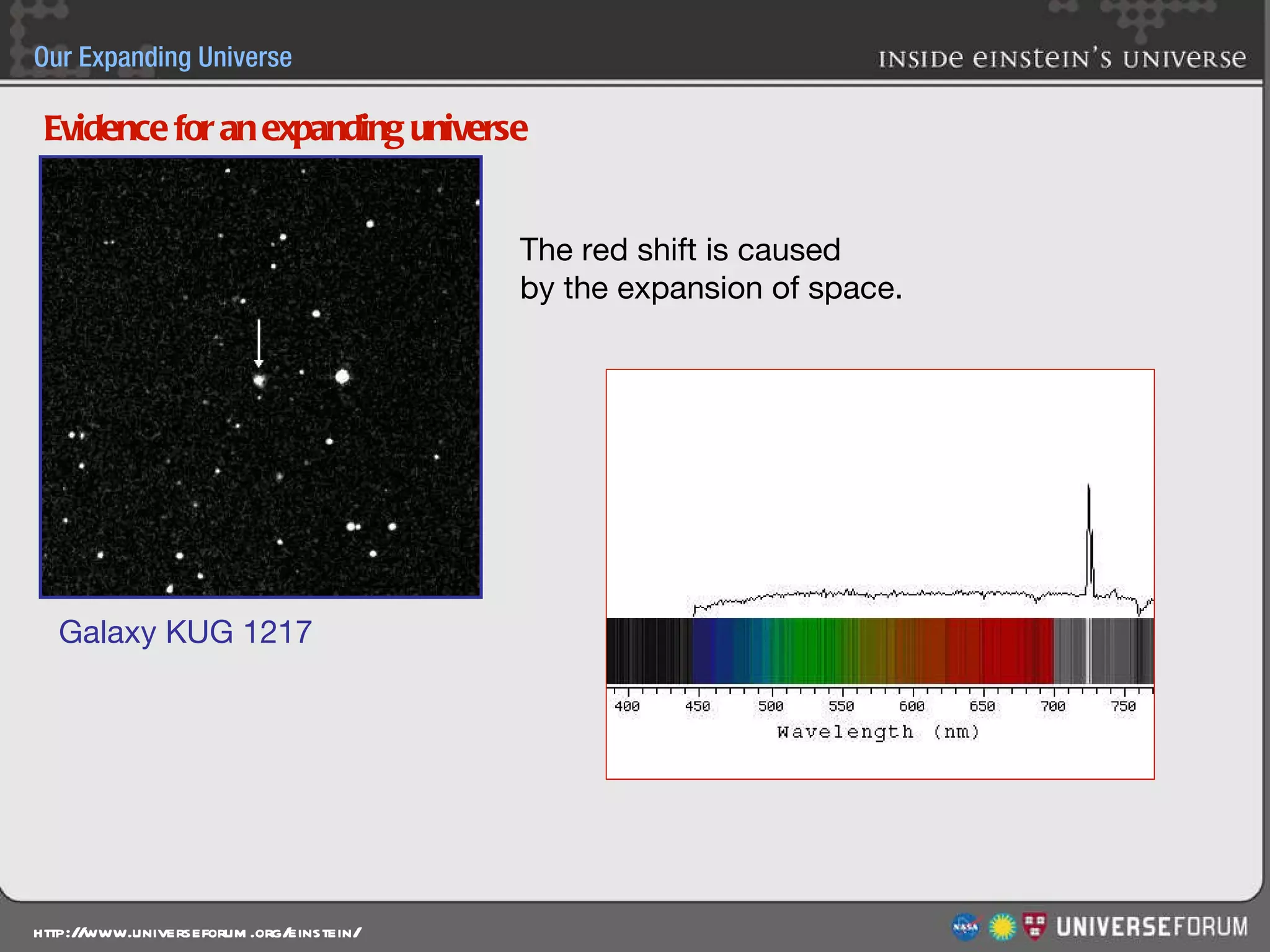
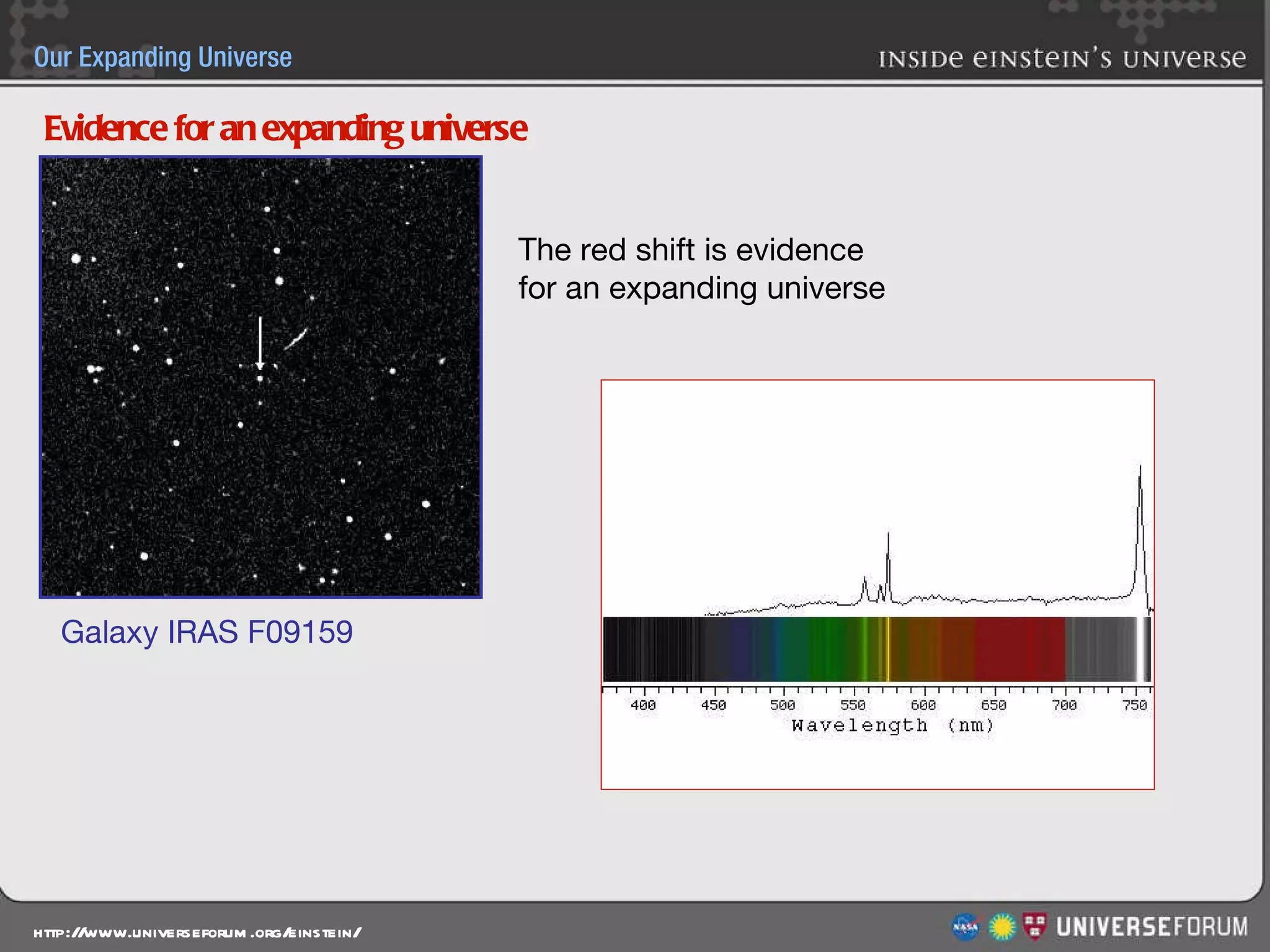
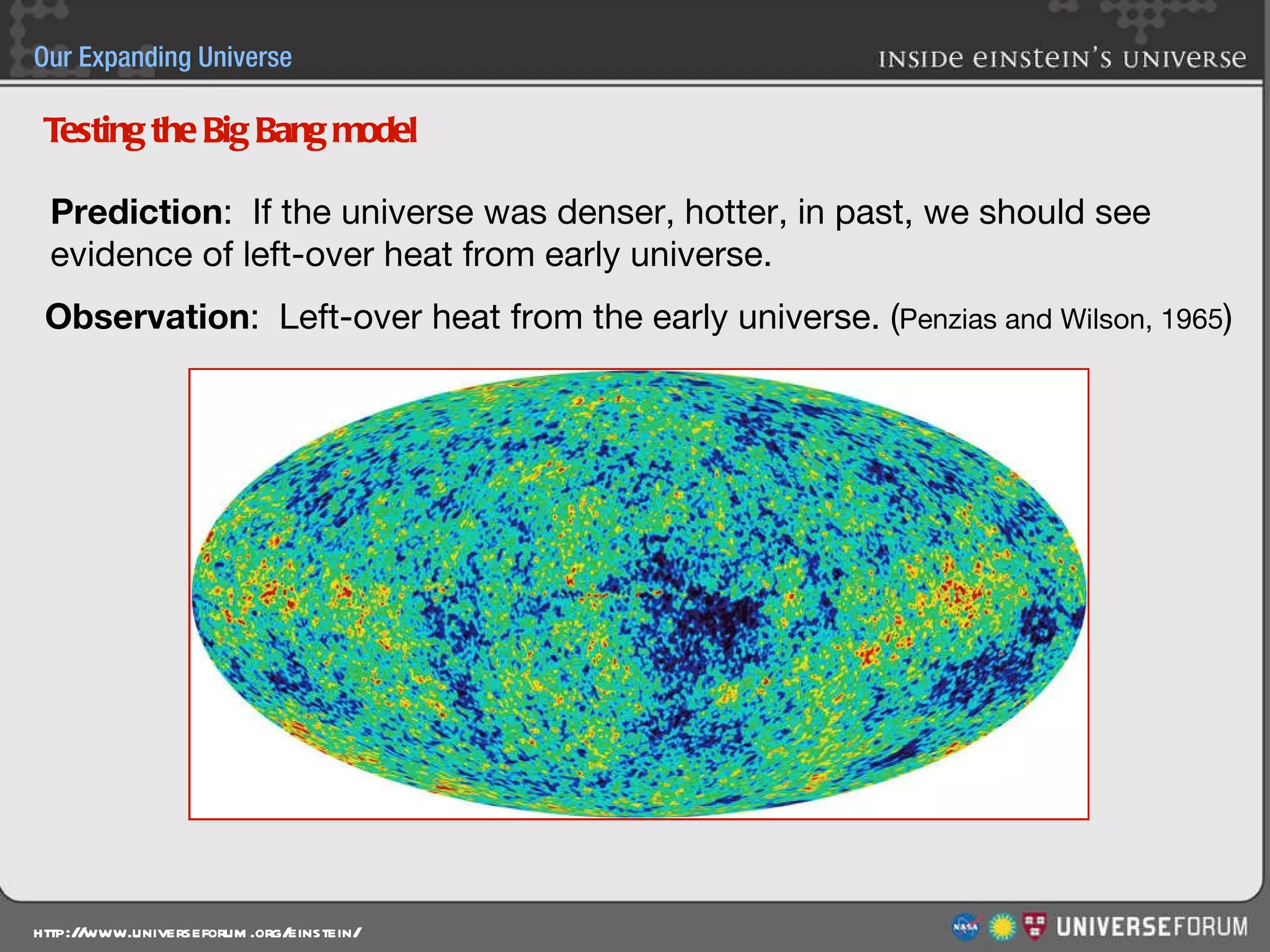
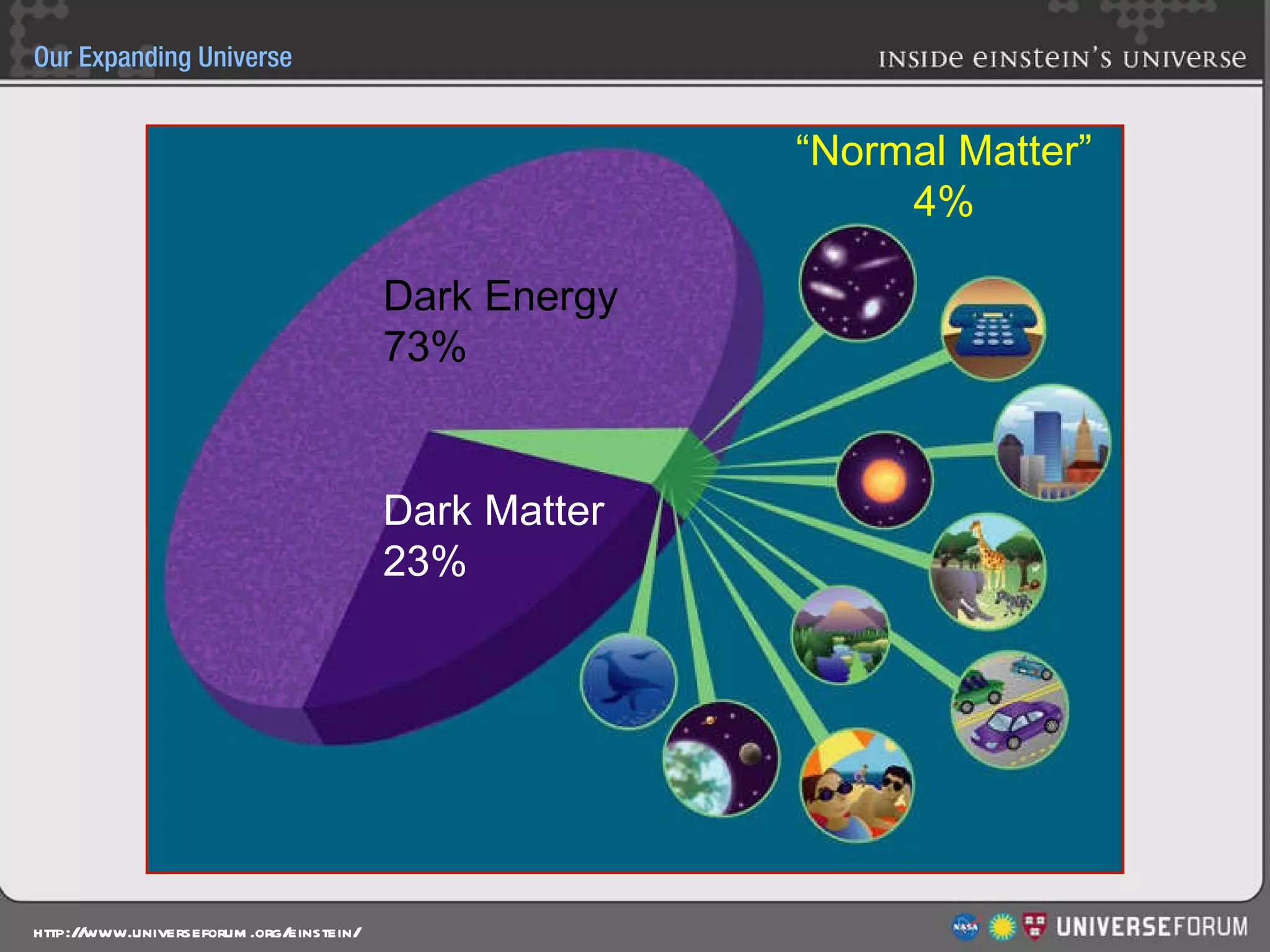
The document discusses the evolution of cosmological models throughout history from ancient times to modern day. It describes three major revolutions in cosmology: 1) the Ptolemaic Earth-centered model from the 2nd century, 2) the Copernican Sun-centered model in the 16th century, and 3) the modern Big Bang model of the 20th century. The Big Bang model is supported by evidence like the cosmic microwave background radiation and the composition of the universe being mostly hydrogen and helium. New discoveries of dark matter and dark energy have led to refinements of the Big Bang model.