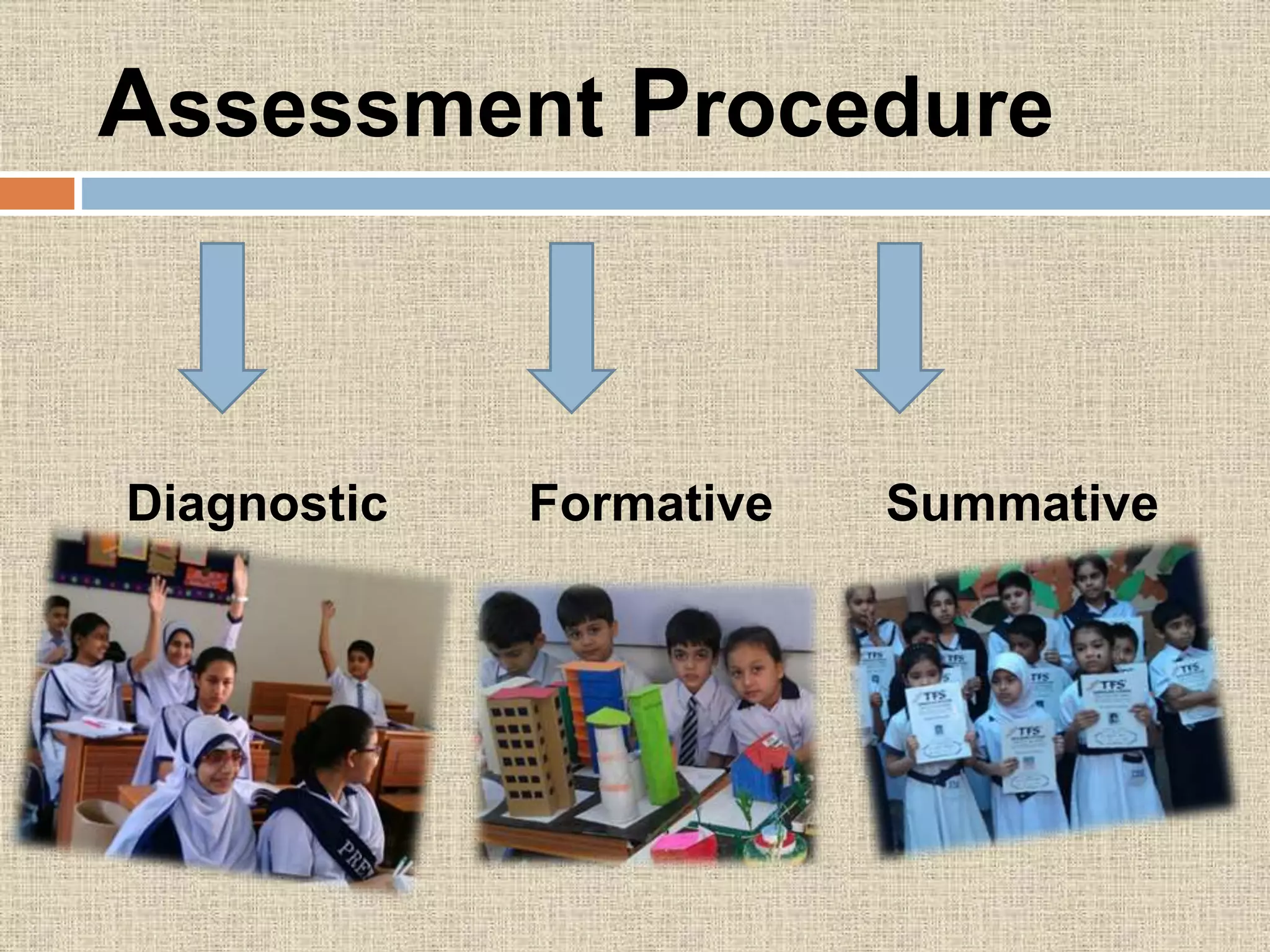
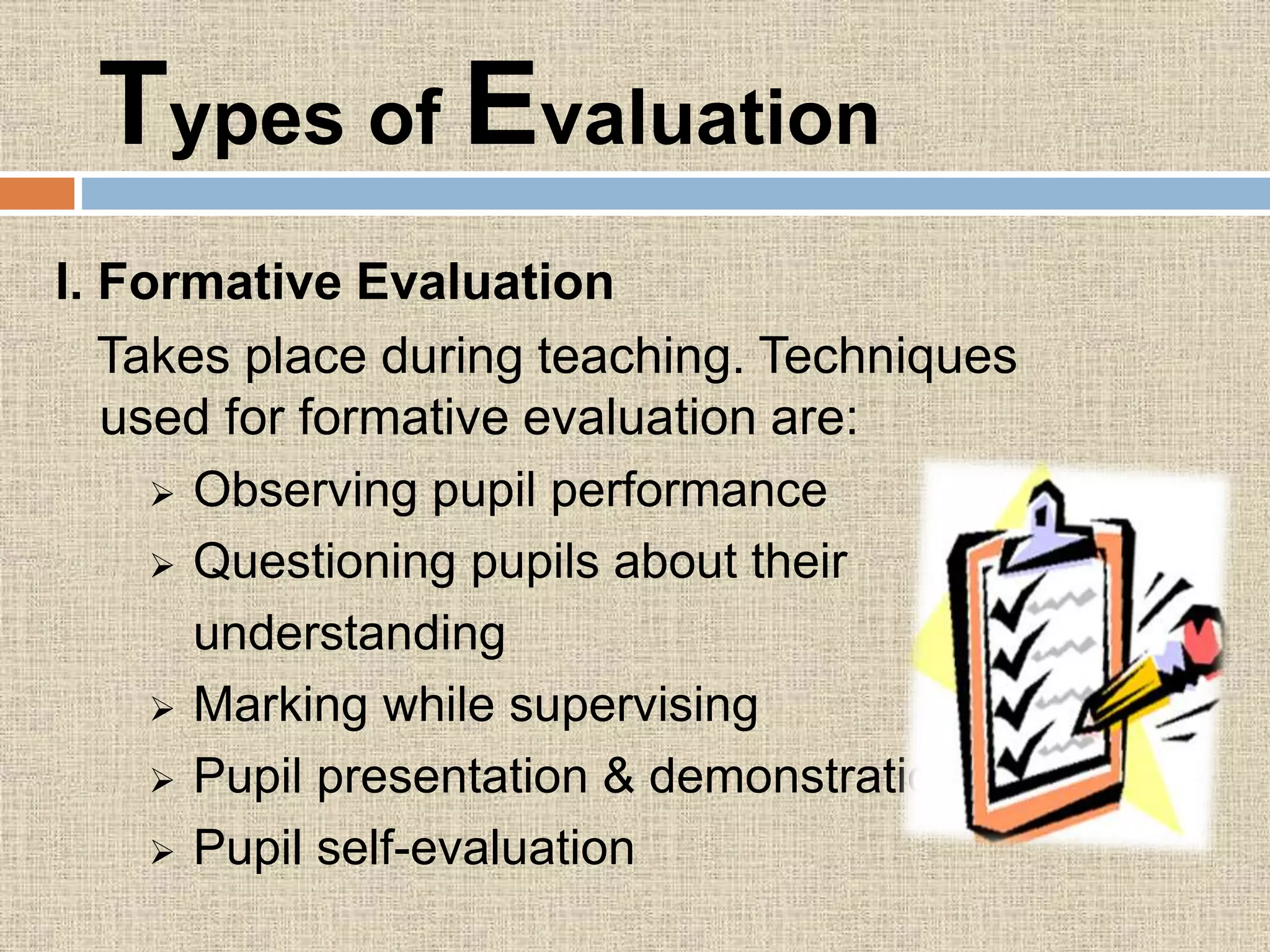
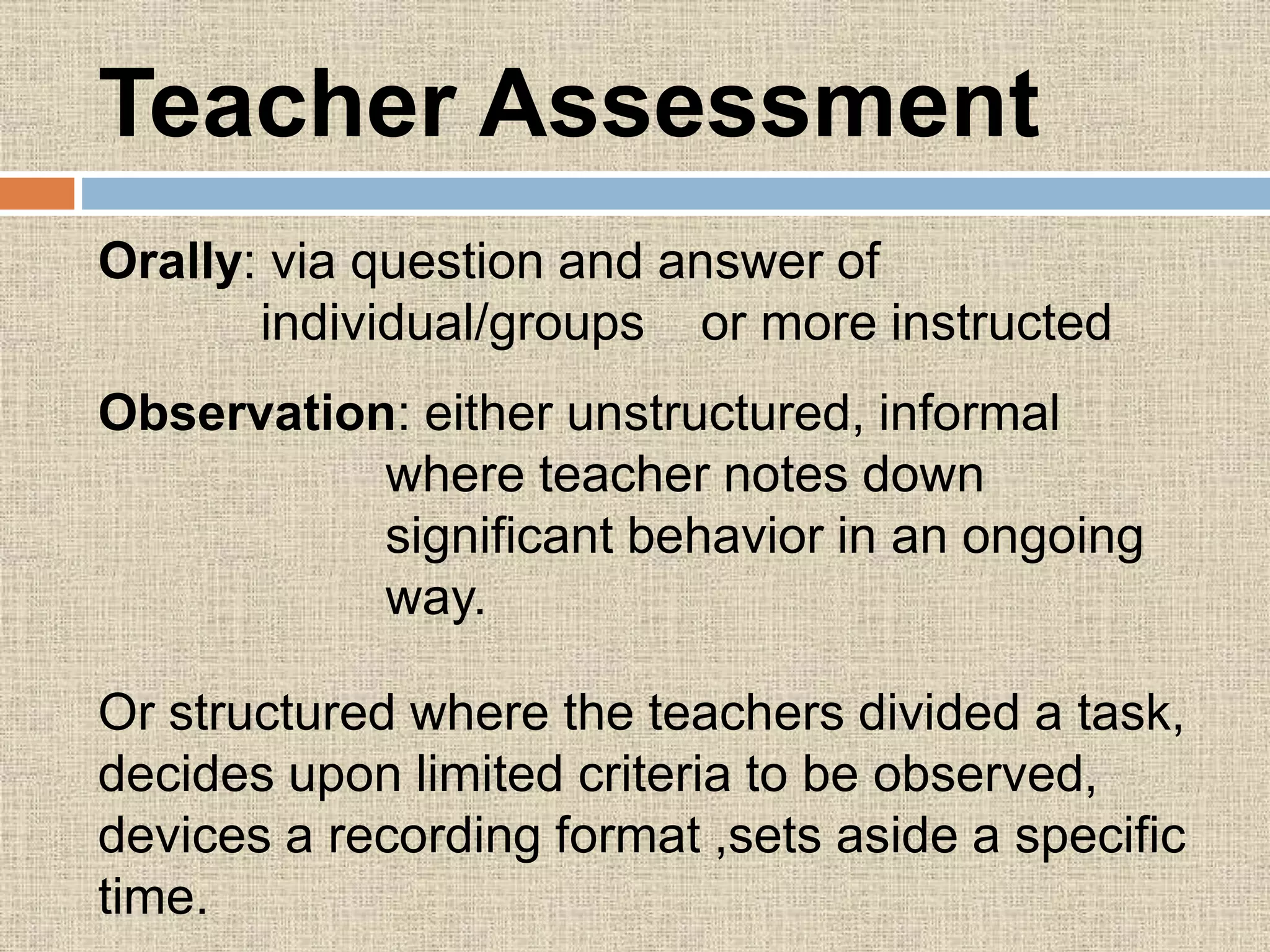
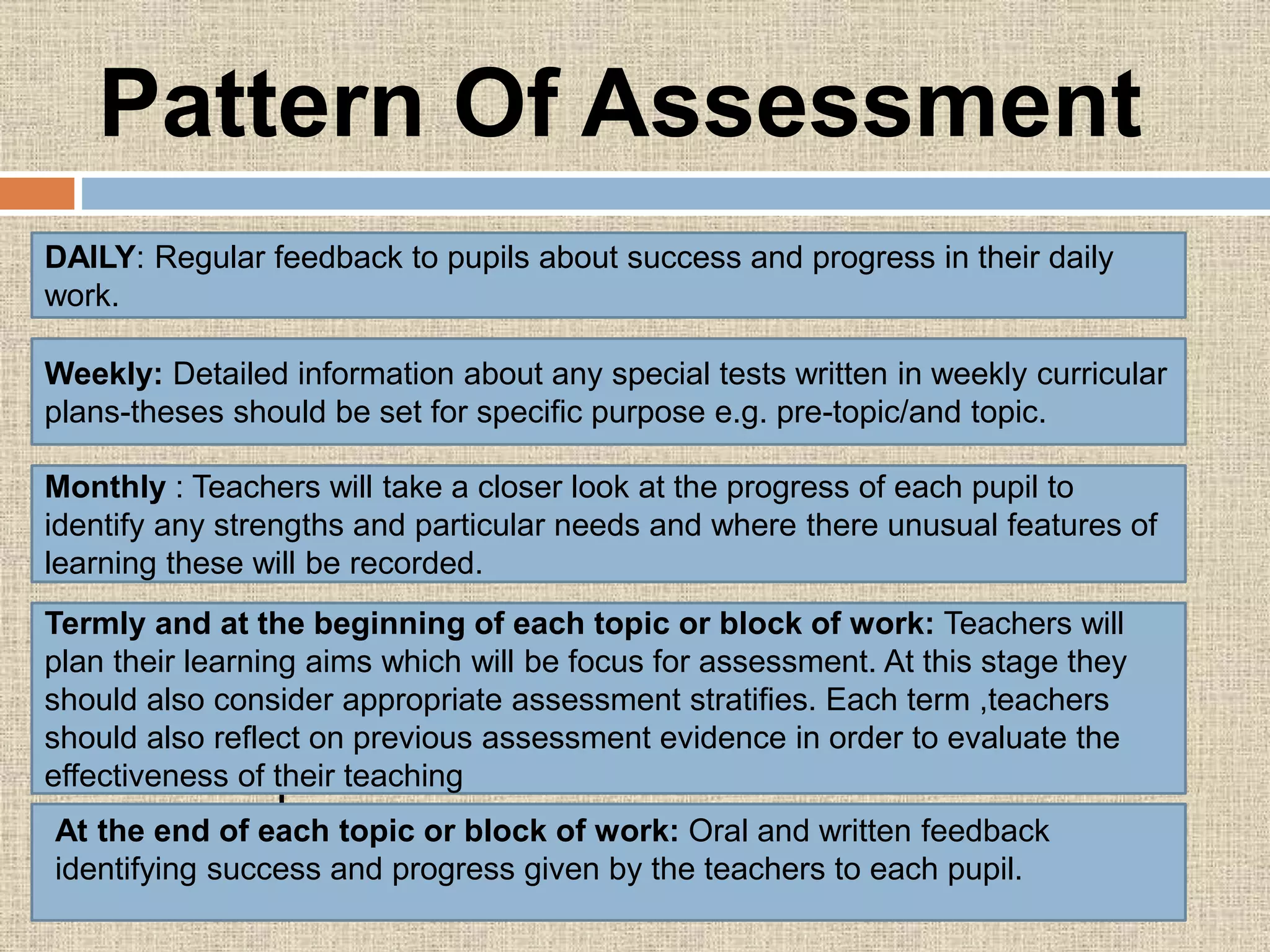
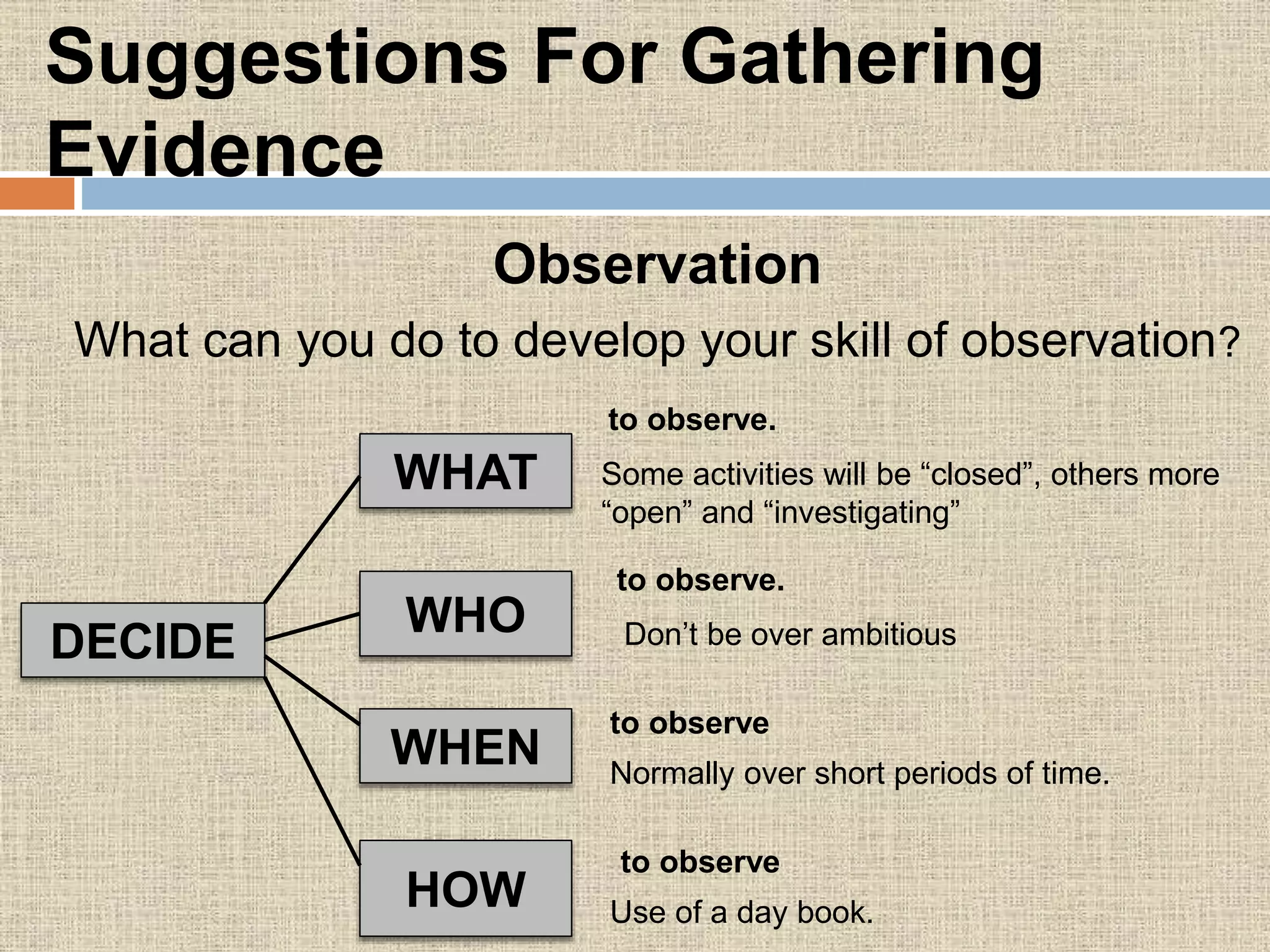
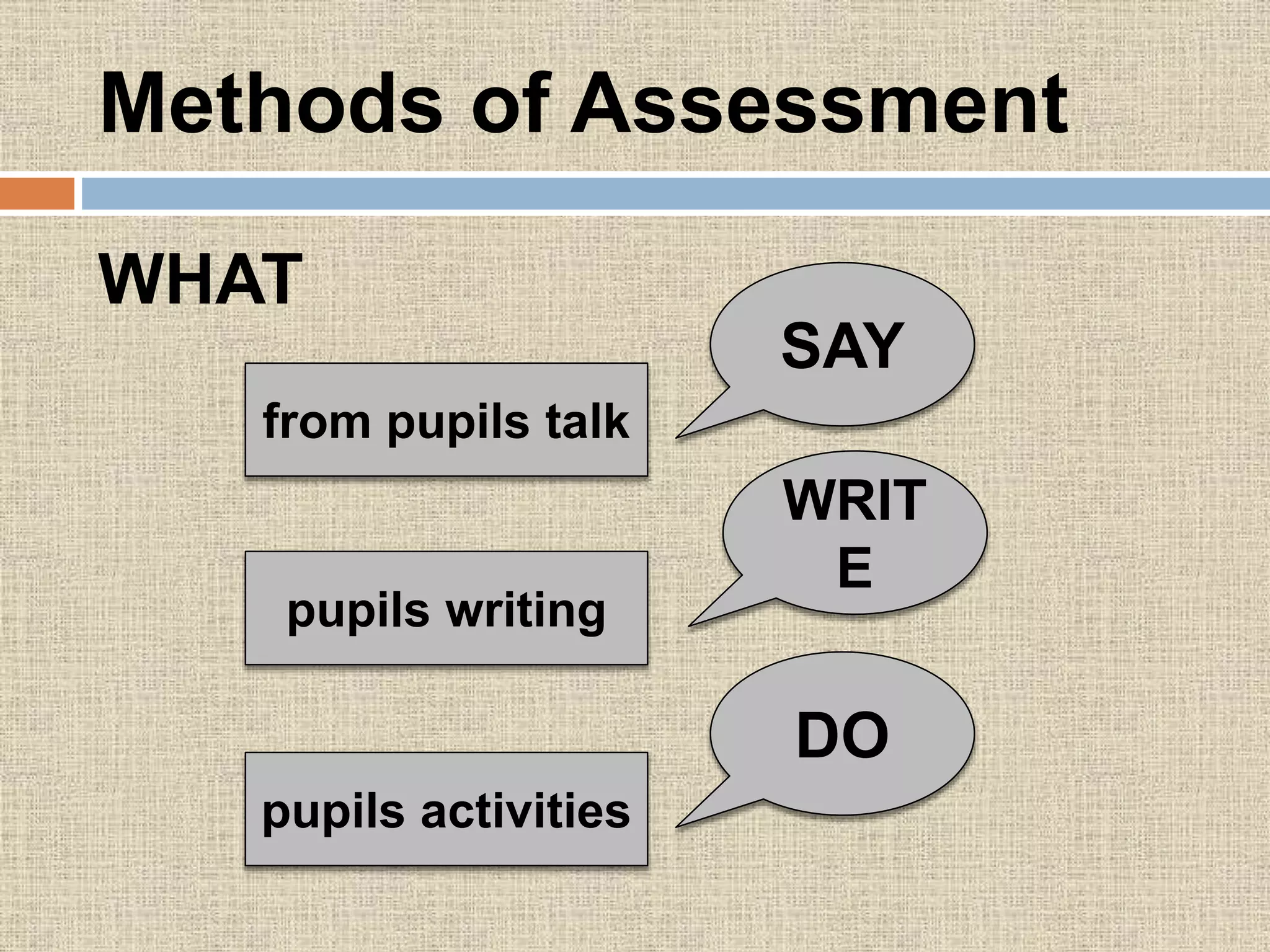
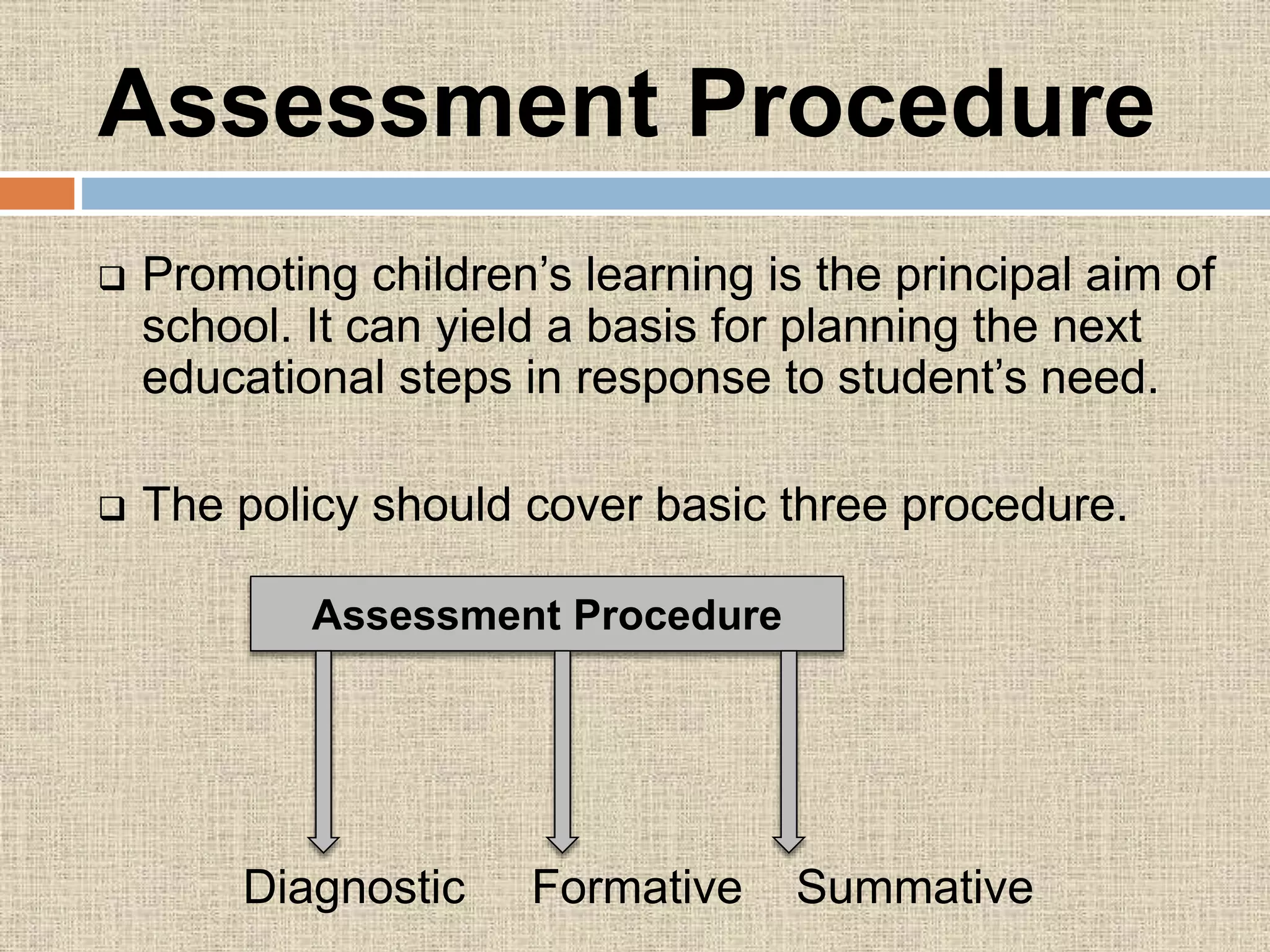
The document discusses assessment procedures including diagnostic, formative, and summative assessment. Diagnostic assessment helps teachers determine student needs and plan instruction. Formative assessment is ongoing and includes observations, discussions, and checking work to see if students are progressing. Summative assessment makes judgments about student competence and provides feedback for parents in reports. The school's assessment policy for young students includes regular informal assessment of various skills and areas without formal tests. Teachers use both formative and summative evaluation techniques including observation, questioning, tests, and student work. Evaluation plays an important role in planning by informing teachers on learning objectives, diagnosing errors, and allowing progress feedback.