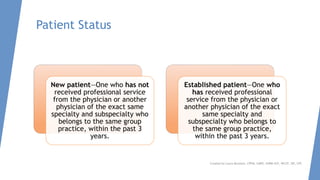
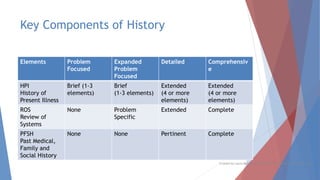
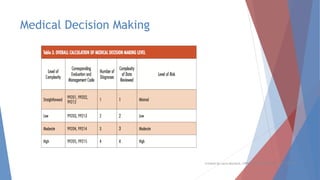
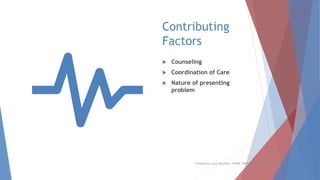
This document discusses evaluation and management coding for psychiatric services. It covers the 1995 and 1997 E/M guidelines, including differences in documentation requirements. Key aspects of history, examination, and medical decision making are outlined. Proper documentation of the chief complaint, history of present illness, review of systems, and past/family/social histories is important. Examination requirements vary based on level of service. Medical decision making considers diagnosis, data review complexity, and patient risk. Special documentation is needed for counseling or coordination of care. Overall, the document provides guidance on selecting and documenting evaluation and management codes for outpatient psychiatric care.