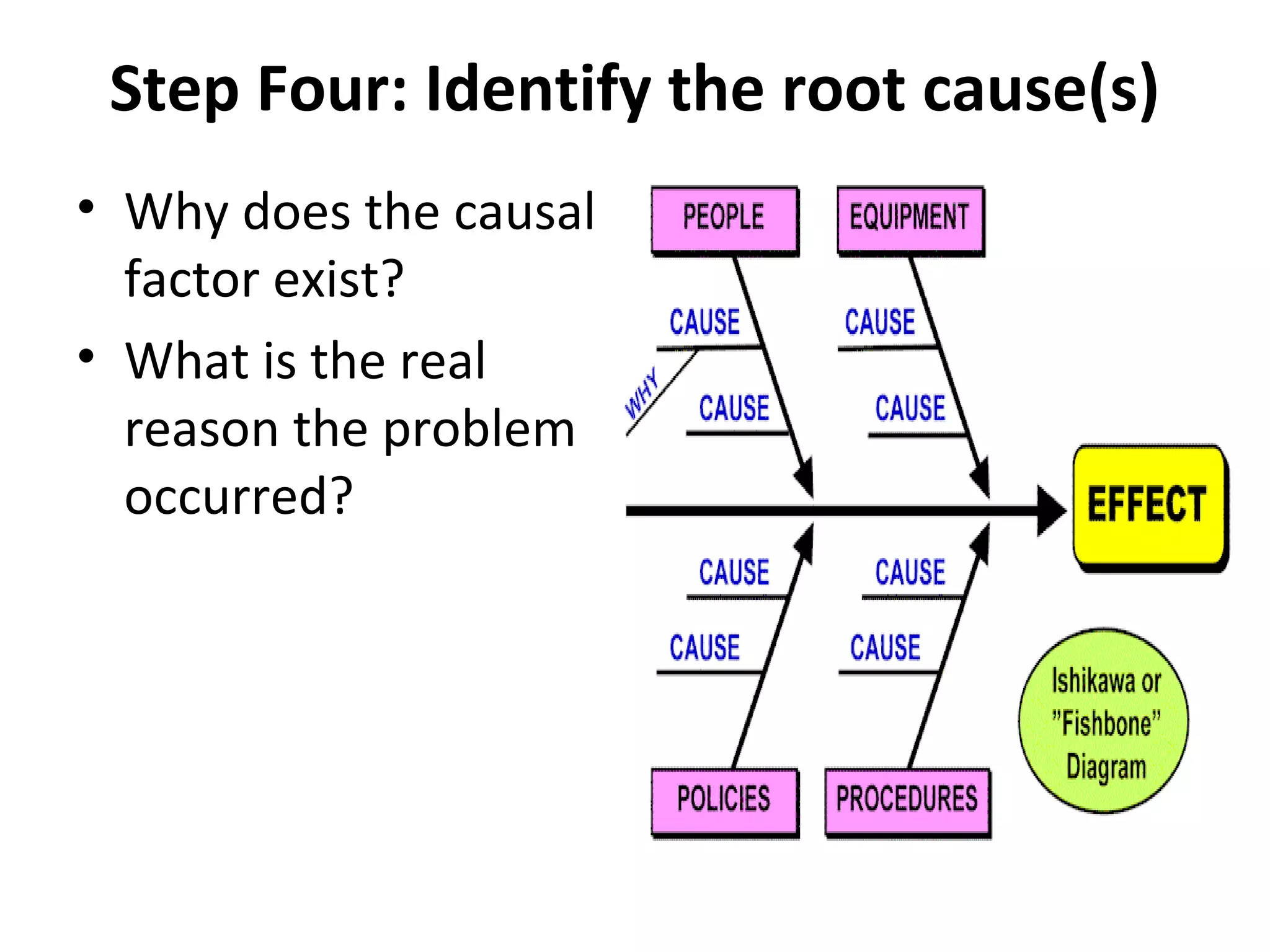
This document outlines a 5-step process for performing a root cause analysis: 1) Define the problem by describing symptoms and what is observed. 2) Collect data on how long the problem has existed, its impact, and different perspectives using a CATWOE analysis. 3) Identify possible causal factors using tools like appreciation, 5 whys, drill down, and cause-and-effect diagrams. 4) Identify the root cause of why the causal factor exists. 5) Recommend and implement solutions to prevent future occurrences, assign responsibilities, and manage risks, using continuous improvement strategies like kaizen. It provides an example task to diagnose a network printing problem at CycleWorld using this root cause analysis model.