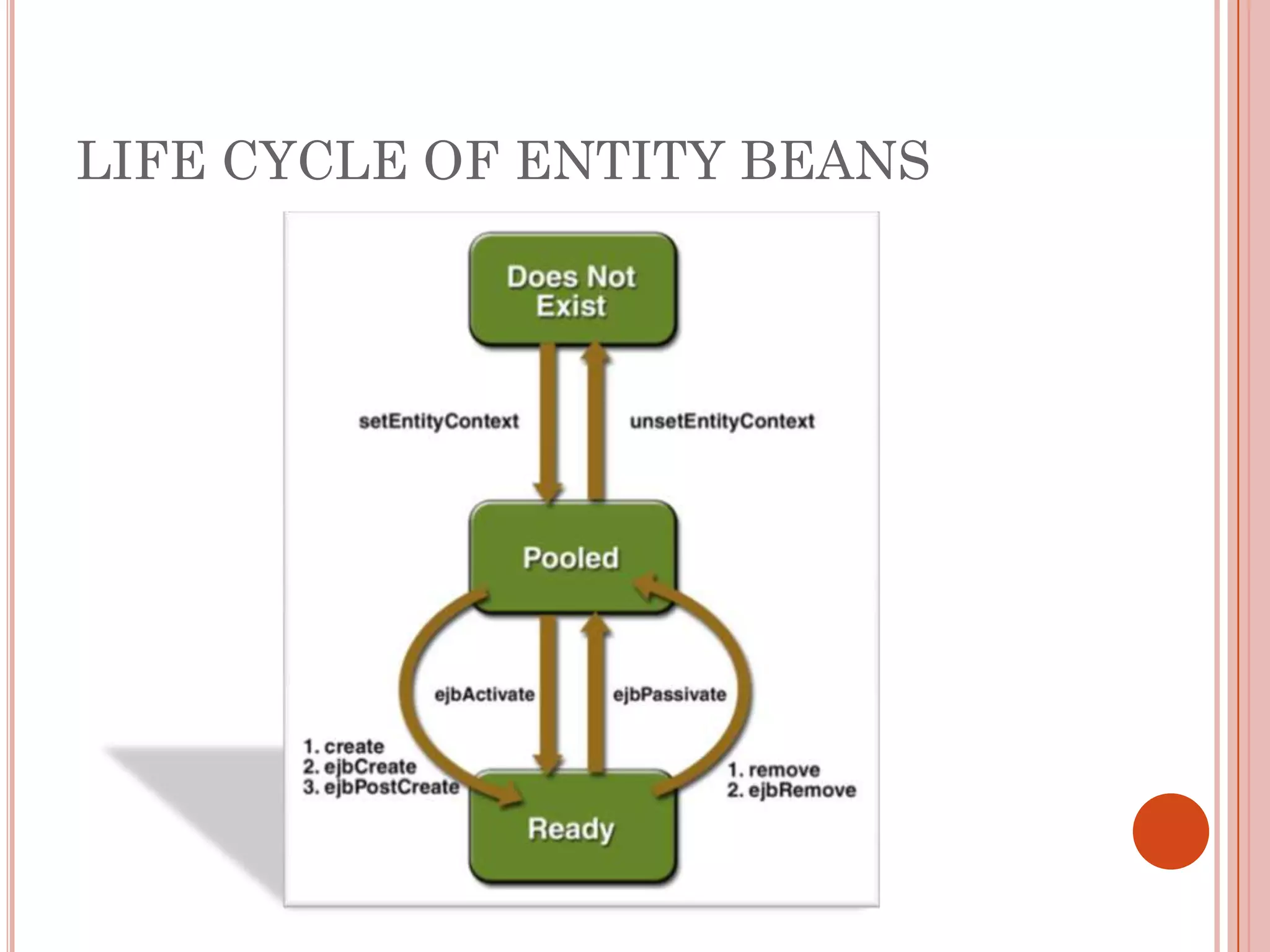
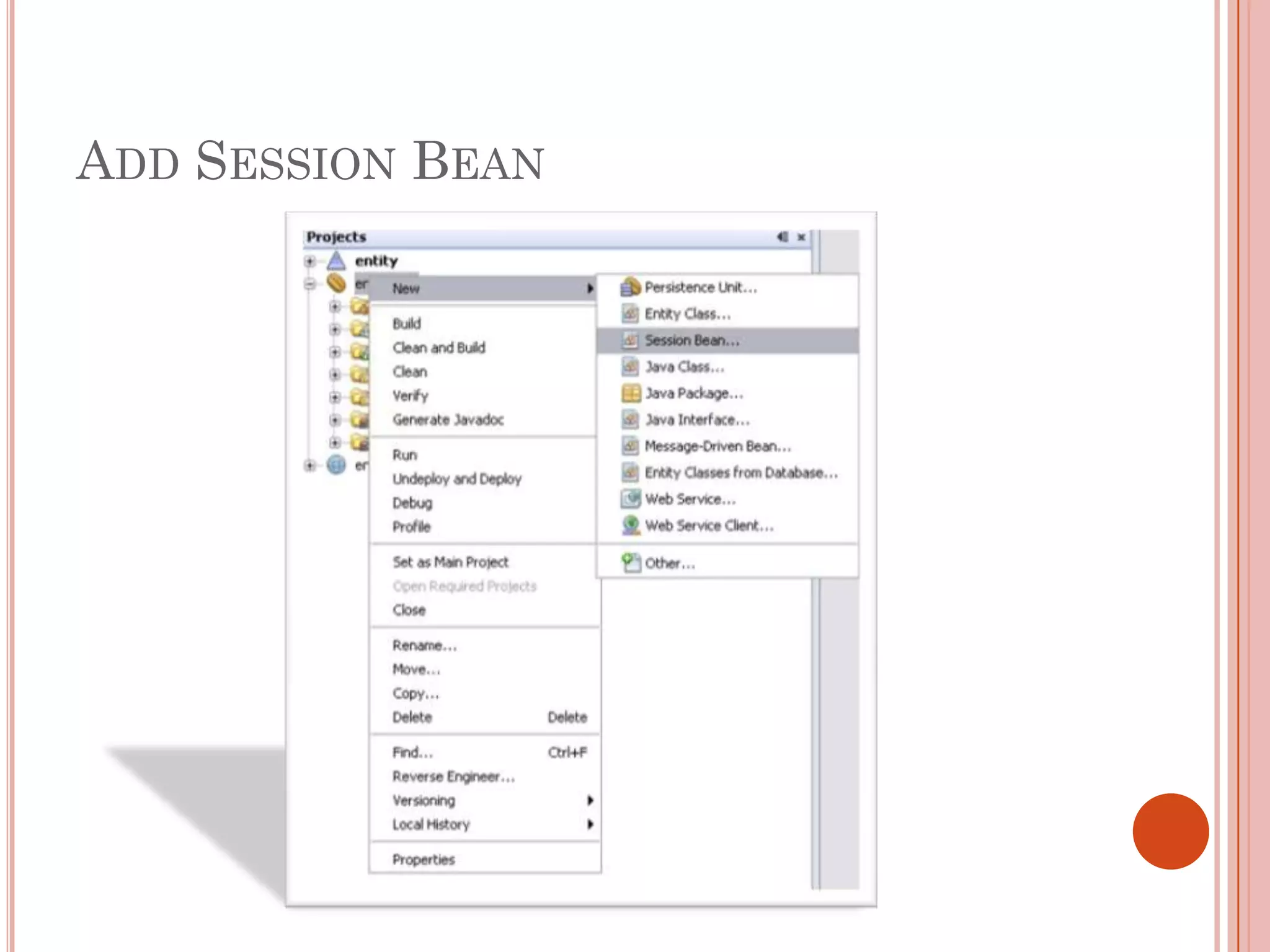
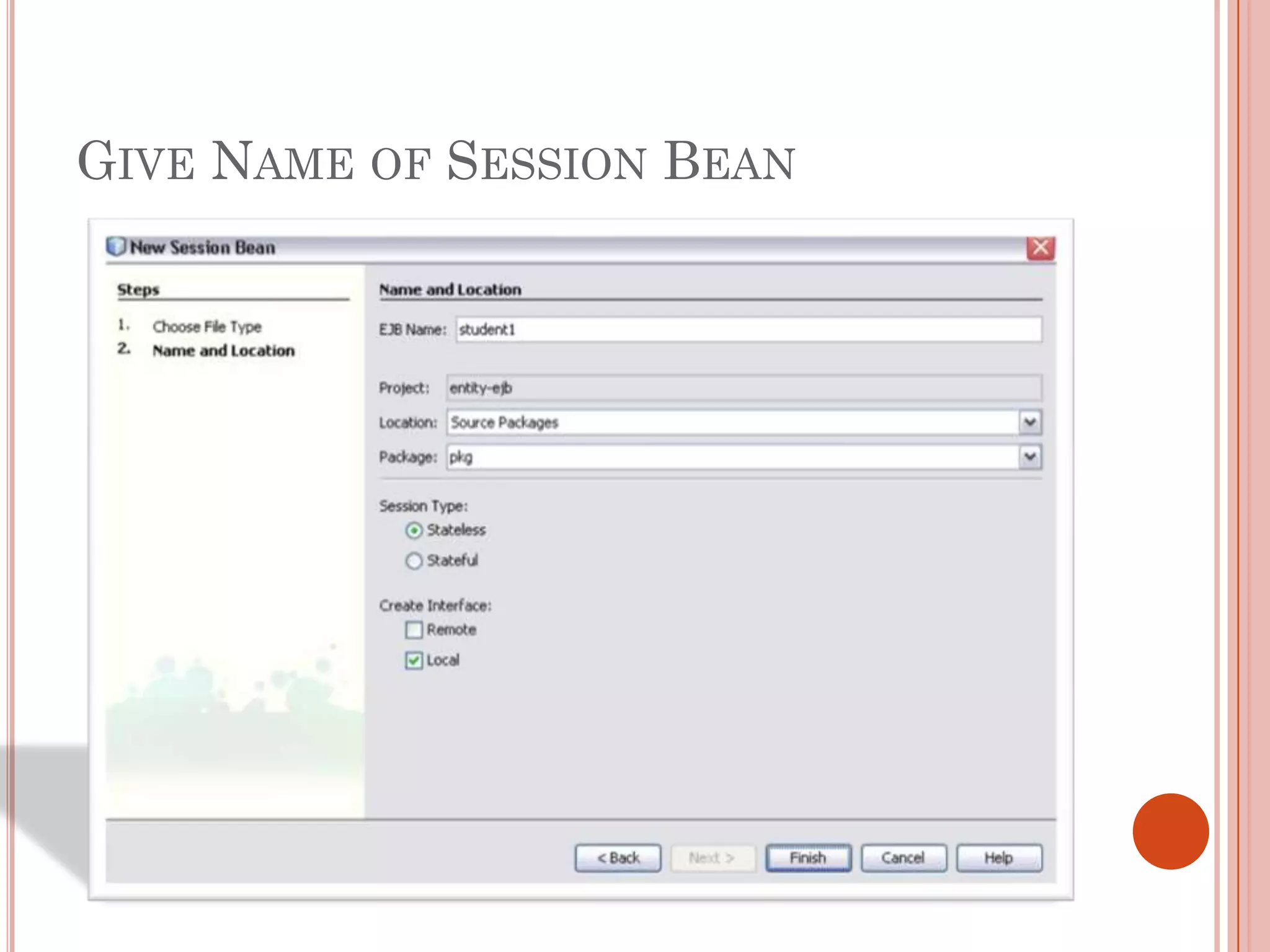
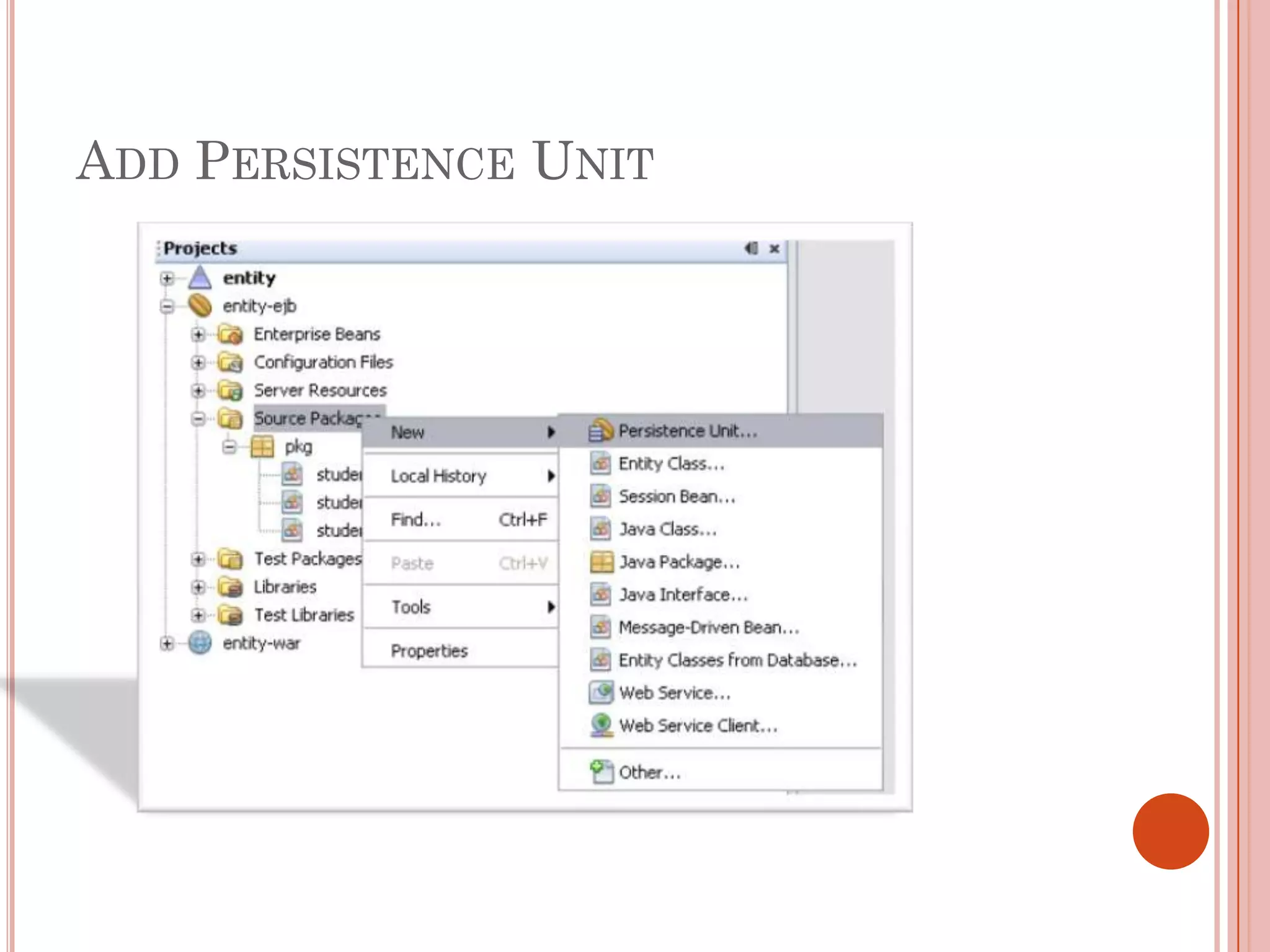
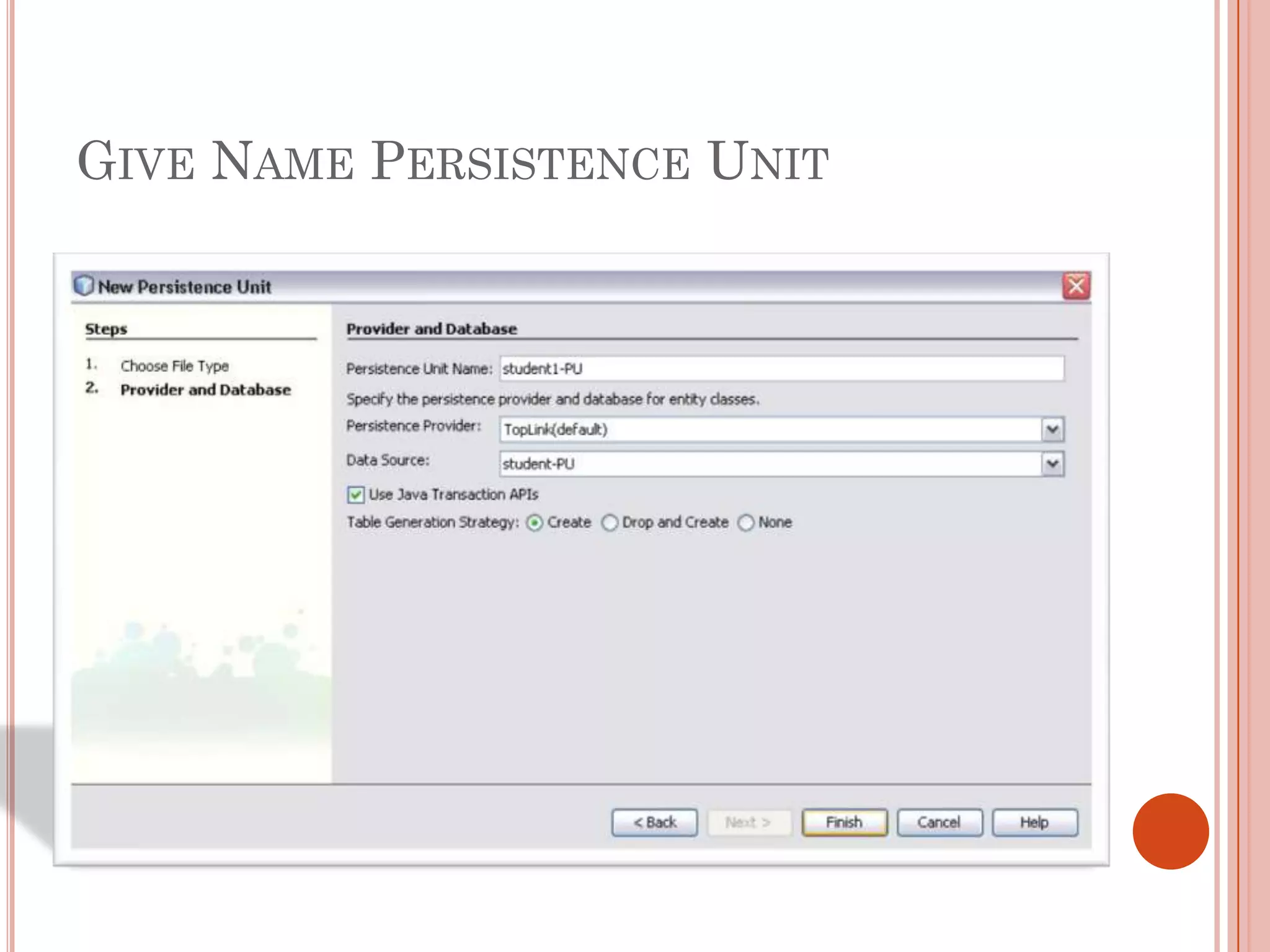
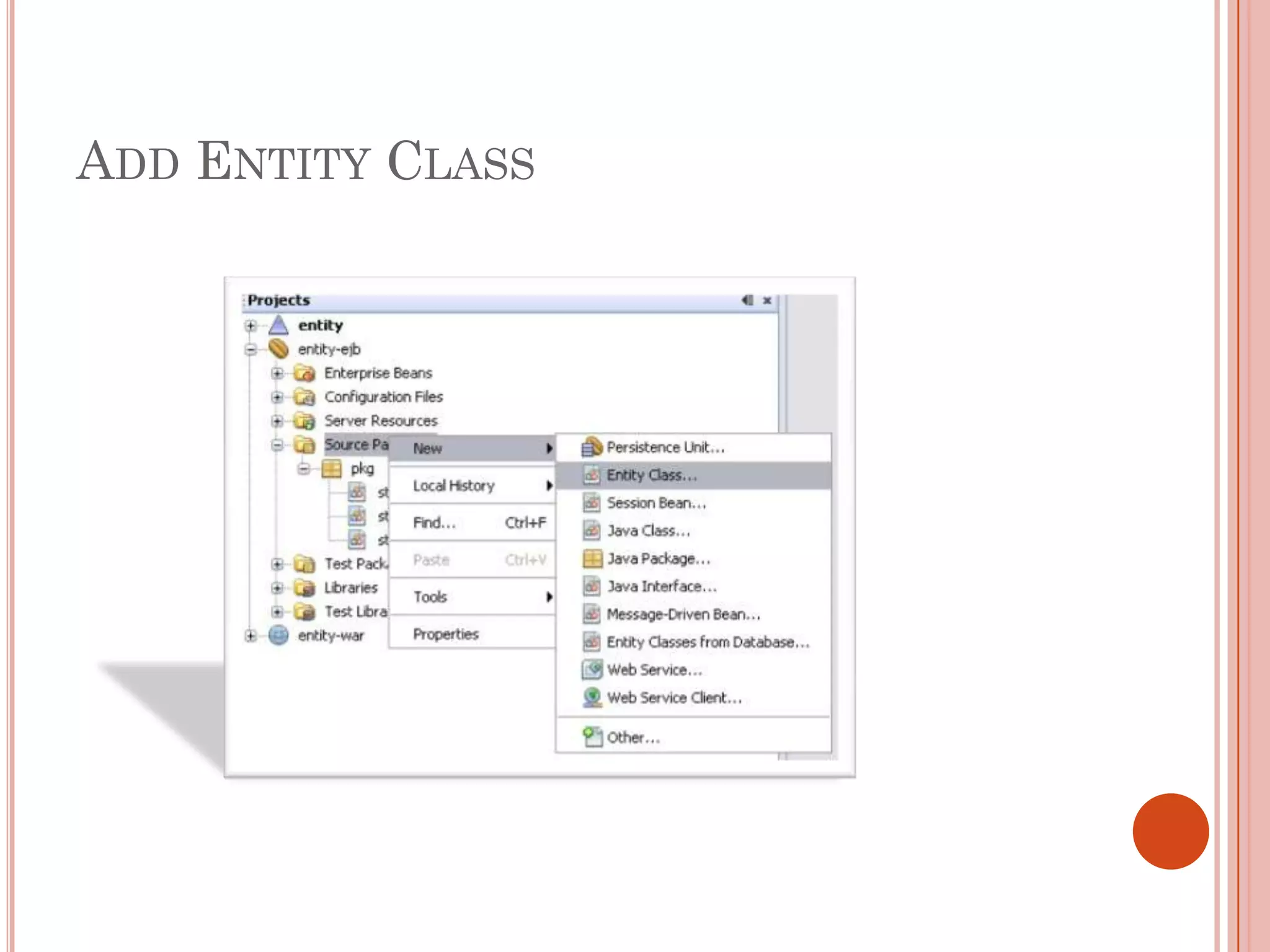
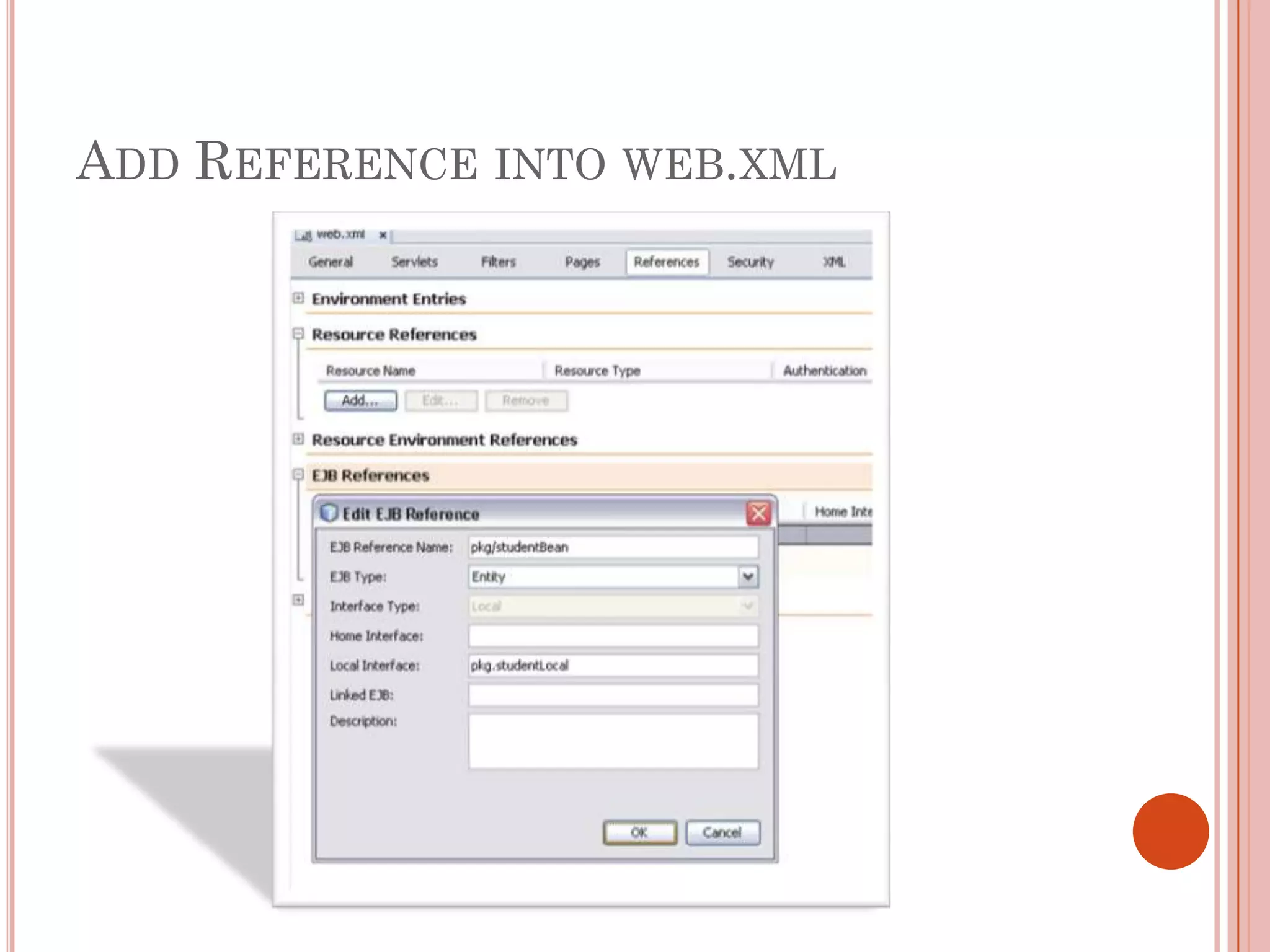
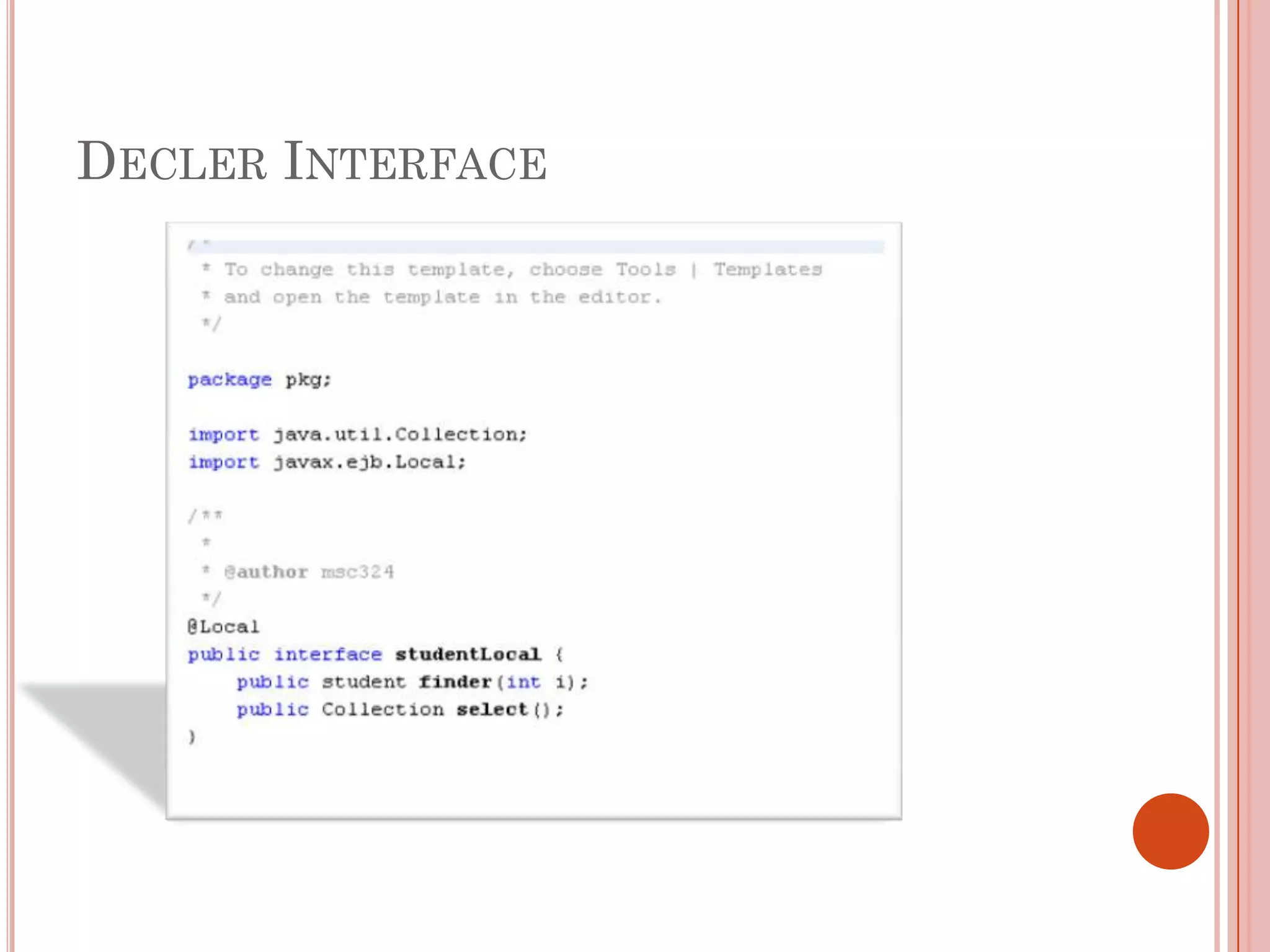
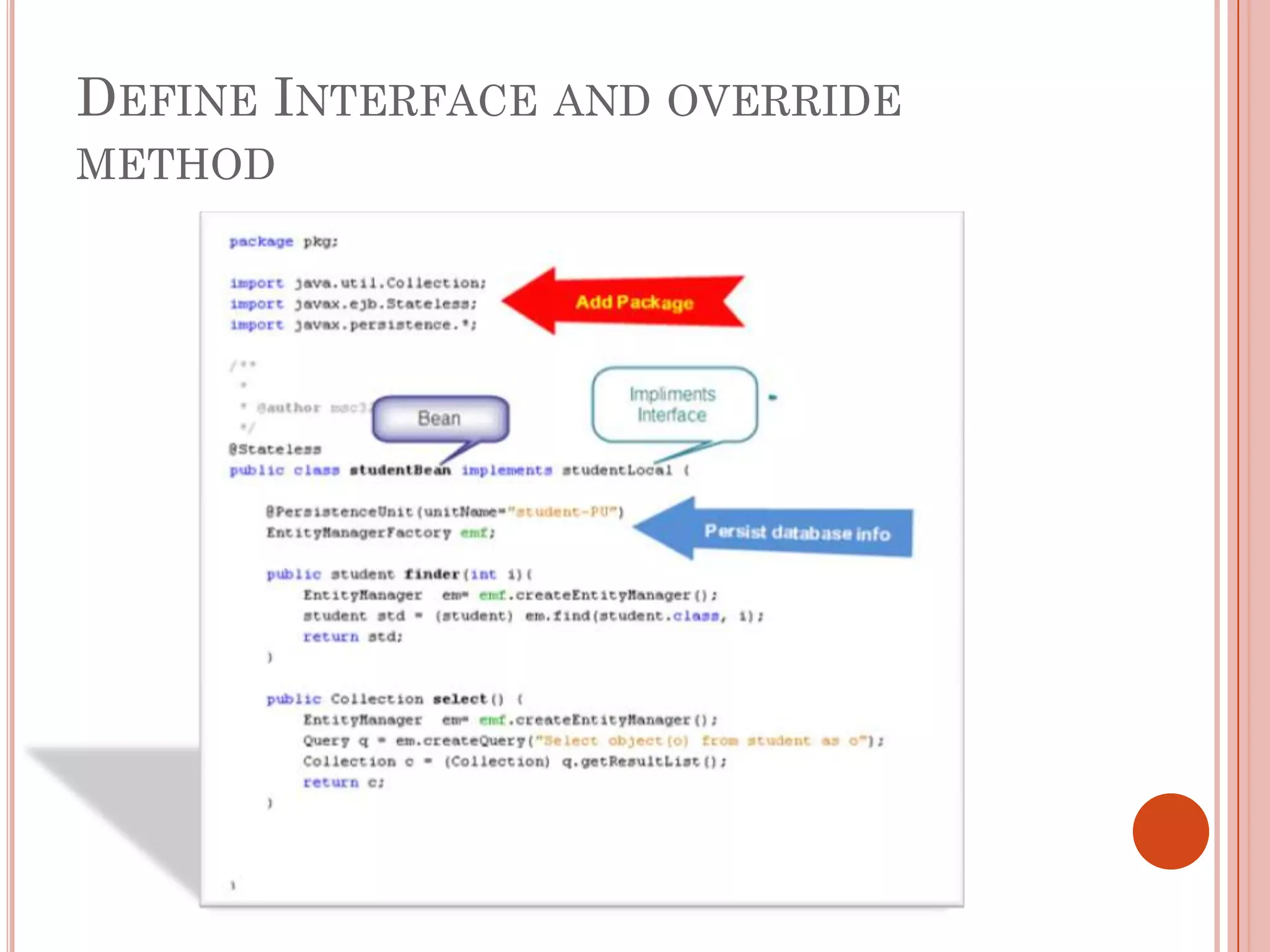
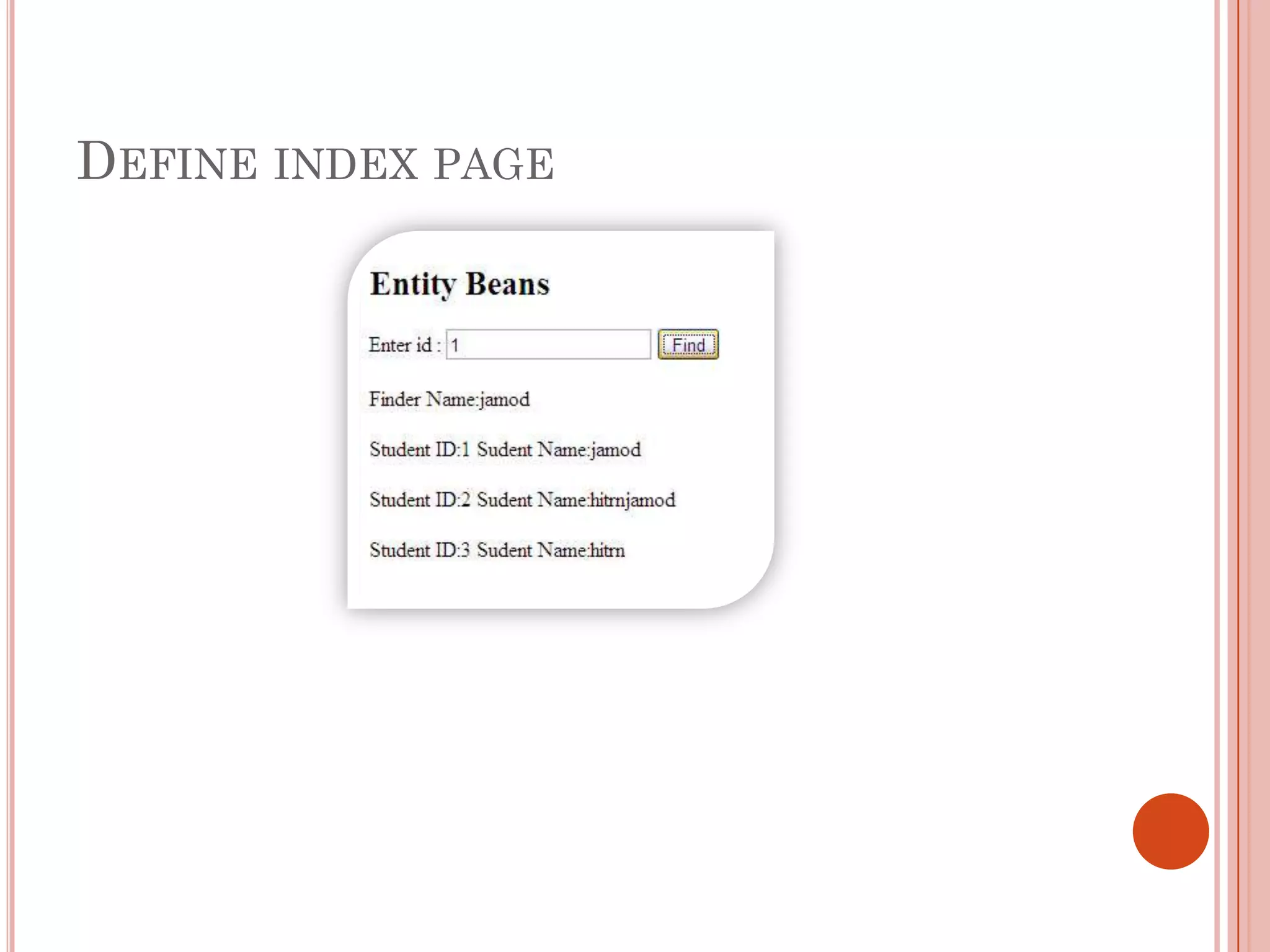
This document discusses entity beans in Java. It defines entity beans as enterprise beans that represent persistent data stored in a database. Each entity bean instance corresponds to a row in a database table. The EJB container is responsible for loading data into entity bean instances and storing it back in the database. Entity beans are persistent, meaning their state exists across client sessions. They also support shared access, with multiple clients accessing the same data through separate entity bean instances. The document outlines the characteristics and lifecycle of entity beans.